Breastfeeding/Human Milk
Breastfeeding/Human Milk 1: Human Milk in the NICU
366 - Exclusively human milk diet: Fortification with freeze-dried breast milk powder in preterm infants ≥31 weeks of gestation – Analysis of growth and safety
Publication Number: 366.101

Niels Rochow, MD, PhD (he/him/his)
Staff Neonatologist
Paracelsus Medical University, Department of Pediatrics
Nürnberg, Bayern, Germany
Presenting Author(s)
Background:
Cow's milk protein used in most fortifiers increases the risk of necrotizing enterocolitis. A fortifier made from breast milk (BM) could reduce such risk. Freeze-dried breast milk (FDBM) powder recently became available. It increases protein and energy intake but could add excess calories due to higher fat content, suggesting its use more for mature preterm infants (PT).
Objective:
This study aims to evaluate the safety of fortification with a FDBM and to compare growth with a preceding 1:1 match-pair group receiving cow’s milk-based standard fortifier.
Design/Methods:
Observational study (PT≥31weeks), study group (SG) with 12 months period: BM fortified with 4.8g/100ml FDBM (AS50-Ammeva, Werder), which adds per 100ml: 0.6g protein, 2.6g carbohydrates, 1.3g fat. Vitamins and Ca-glycerophosphate were supplemented. The control group (CG) recruited from an 18-month period had a standard fortification (FMS, Nutricia, Germany), which adds per 100mL: 1.1g protein, 2.7g carbohydrates, and 0 fat. Matching criteria for CG were birth weight±100g and gestational age ±1wk. Growth, body composition (PeaPod), clinical chemistry, and feeding tolerance were analyzed for all infants. In SG, also macronutrients of BM (MIRIS, Sweden) were analyzed daily.
Results:
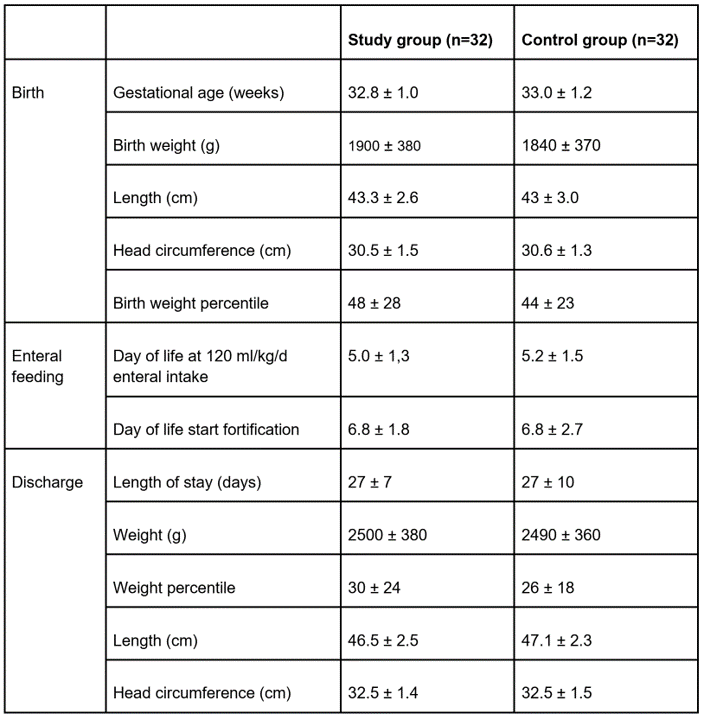
2x32 (n=64) PT were included. Patient characteristics and outcome parameters were not different between groups (Fig.1). In SG, PT received a nutritional intake of 157±8ml/kg/d, 14.0±0.9g/kg/d carbohydrates, 3.3±0.4g/kg/d protein, 7.4±1.1g/kg/d fat, and 136±12kcal/kg/d energy. In CG, infants received 161± 33 mL/kg/d. In SG, urea was 21±12mg/dl, triglycerides 105±36mg/dl, blood glucose 86±19mg/dl. At 36 weeks (PMA), fat mass was 290±110g (12±3%) and fat-free mass 2050±240g), which is comparable with healthy term infants (Hamatschek C. et al. 2020).
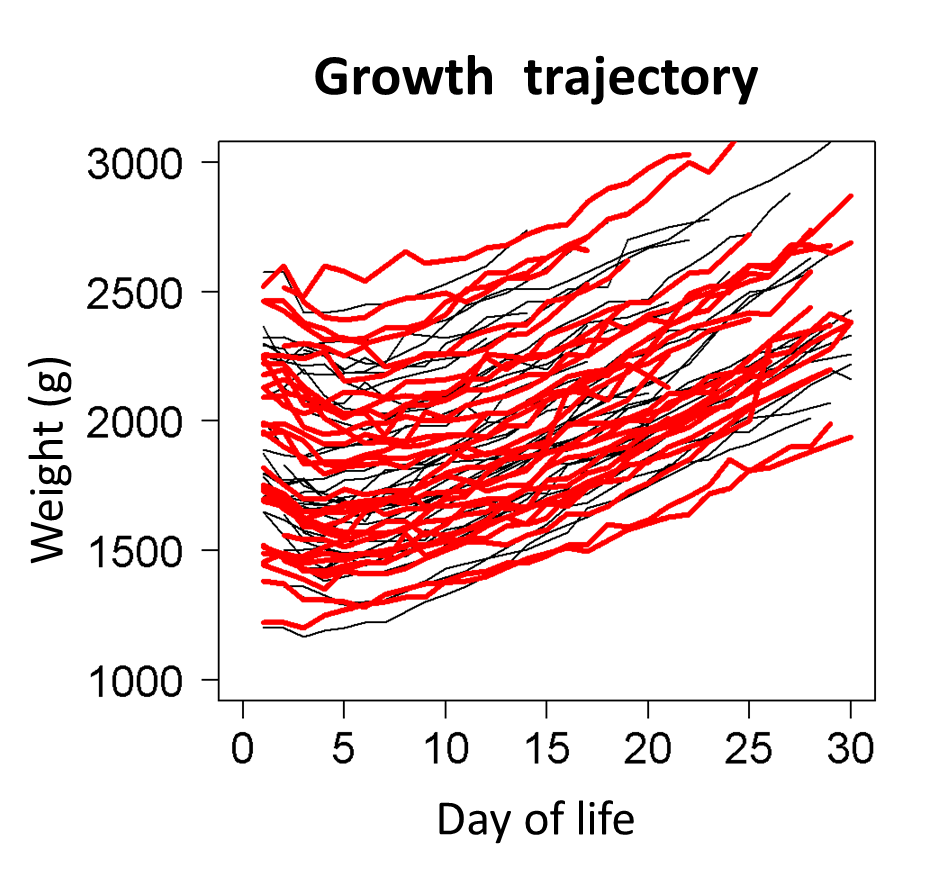
No significant differences in feeding tolerance, growth, discharge weight, length, and head circumference between groups were found (Table, Figure).
Conclusion(s):
Fortification with FDBM is promising, well tolerated by PT≥ 31 weeks, and growth is similar to cow's milk-based fortifiers. To better meet the nutritional requirements of PT (< 1.5kg), higher macronutrient intake and protein-to-energy ratio are required. Multicenter studies are needed to validate the results.