Quality Improvement/Patient Safety: Primary & Subspecialty Outpatient Quality Improvement
QI 2: Screening in Primary Care
682 - Lipid Screening Intervention Bundle Improves Screening Rates in 9-11 Year Olds
Publication Number: 682.152

Ruth E. Gardner, MD (she/her/hers)
Assistant Professor
Penn State Children's Hospital, Pennsylvania, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background:
Universal lipid screening is recommended for children age 9-11 years, based on 2011 guidelines by the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. The rationale for screening is that atherosclerosis begins in childhood, and interventions may prevent development of adult cardiovascular disease. Despite these recommendations, screening rates remain low.
Objective:
In this quality improvement project, we aimed to use implementation of a point-of-care (POC) lipid testing program, electronic medical record (EMR) decision support and provider education to increase lipid screening rates at 9-11 year well visits.
Design/Methods:
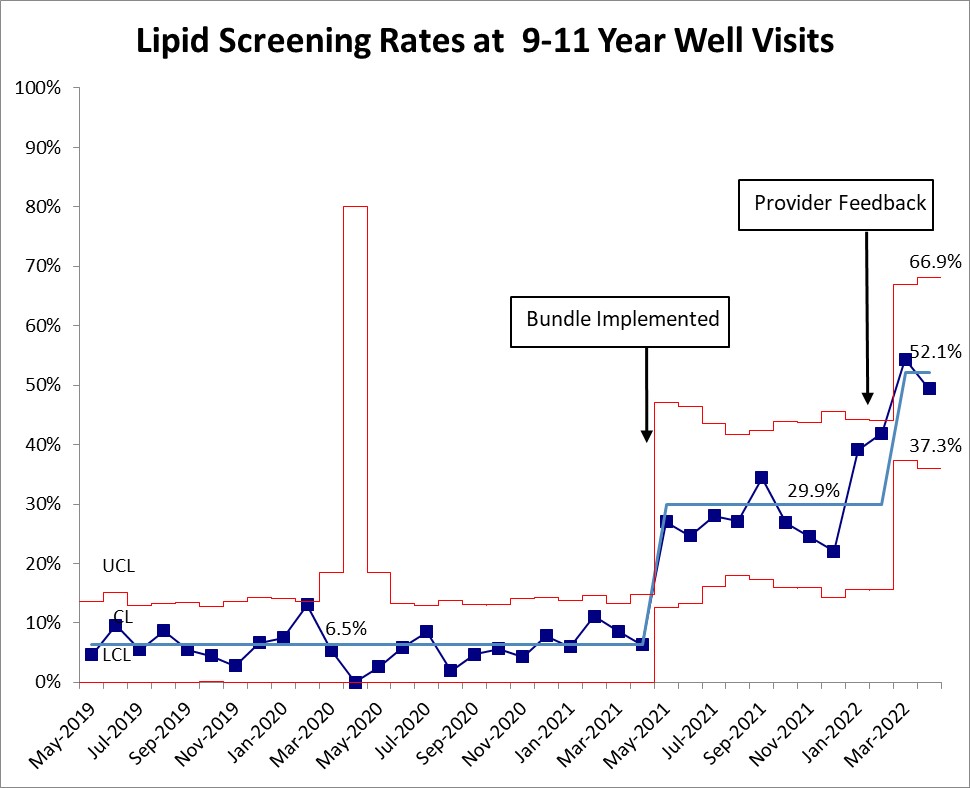
EMR data abstraction was used to collect information about receipt of lipid testing within 30 days of all 9-11 year well visits at a large academic pediatric primary care practice. The proportion of visits with lipid testing completed were tabulated monthly. Baseline rates were measured from May 2019-April 2021; we chose a 2-year period because of disruptions to well-child care in spring 2020 from the COVID-19 pandemic. During the baseline, patients were given an order for venipuncture testing at a separate laboratory location if lipid testing was ordered. POC testing in the form of in-office capillary testing was implemented in May 2021, along with provider education. Well visit documentation templates were also changed to include prompts for lipid screening at relevant ages and well visit EMR order sets were modified to include orders for lipid testing. Targeted provider feedback regarding individualized rates was provided in February 2022. Screening rates were plotted monthly on statistical process control charts (p-charts) from May 2019 through April 2022.
Results:
There was a mean of 102 eligible well visits per month (range 63-133, not including the months of March-May 2020 when well visits were actively canceled in this age range). The baseline lipid screening rate was 6.5%. After the bundled intervention in May 2021 there was a centerline shift (single point above the upper control limit) to 29.9%. Following targeted provider feedback in February 2022 there was a second centerline shift (single point above the upper control limit) to 52.1%.
Conclusion(s):
A bundled intervention including implementation of POC testing, provider education and EMR decision support was associated with significant improvement in lipid screening rates for 9-11 year olds. Further improvement in screening rates could focus on targeted provider feedback and education.