Neonatal Pulmonology
Neonatal Pulmonology 4: Exosomes, Stem Cells, Maternal and Fetal Environmental Effects
131 - Circulating extracellular vesicle microRNA 140-5p associated with bronchopulmonary dysplasia susceptibility in extremely preterm infants
Publication Number: 131.436

Shaili Amatya, MD, FAAP (she/her/hers)
Assistant Professor
Penn State Children's Hospital
Hershey, Pennsylvania, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is the chronic pulmonary disease of prematurity, affecting extremely preterm infants born < 28 weeks of gestation. BPD is late diagnosed at 36 weeks postmenstrual age (PMA) and leads to long-term pulmonary and neurodevelopmental impairment. Therefore, there is a need for early molecular predictors that may capture the ongoing intercellular crosstalk during lung development and chronic inflammation in BPD. EVs are intercellular messengers that carry important cytoplasmic material such as microRNA along with proteins and lipids secreted via exocytosis into almost all biofluids.
Objective: The objective of this study is to determine the circulating EV microRNA associated with BPD susceptibility in preterm infants.
Design/Methods:
Preterm infants born < 28-week gestation and 1500-gram birth weight, in the Penn State Children’s Hospital NICU, were consented for the study. Infants with chromosomal abnormalities, congenital heart disease, or multisystem organ failure were not included in the study. Discarded serum from routine lab draws was collected from 10 patients within the first 3 days of life. This method avoided excessive blood loss from preterm infants. Serum EVs were isolated via the polymer-based co-precipitation method. EV RNA was isolated using a Total Exosome RNA isolation kit. MicroRNA sequencing libraries were prepared using QIAseq microRNA library kit. The DESeq2 R package was used to perform statistical analysis using microRNA read counts obtained from high-throughput sequencing. BPD was diagnosed as a need for any respiratory support >high flow nasal cannula at 36 weeks PMA. This ongoing study is approved by the IRB at Penn State College of Medicine.
Results:
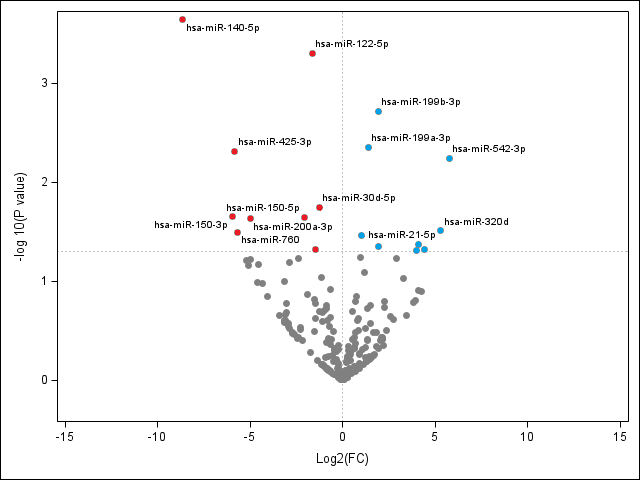
Differential expression analysis showed that early serum EV microRNAs had 105 upregulated and 115 microRNAs downregulated in patients with BPD compared to those without BPD. Serum EV microRNA 140-5p from the infants with BPD was downregulated (8-fold reduction, false discovery rate(FDR) adjusted p< 0.05) (Figure 1).
Conclusion(s): EV microRNA 140-5p is protective in preterm patients with BPD. This particular microRNA has been noted to be protective in acute lung injury. Furthermore, nuclear factor erythroid 2- related factor 2 (Nrf-2), is a known target of microRNA 140, and this transcription factor may be involved in antioxidant response of BPD. Therefore, circulating EV microRNA may mediate antioxidant pathways to discriminate BPD risk in preterm infants.