Neonatal Quality Improvement
Neonatal Quality Improvement 5
196 - A quality improvement initiative in an Italian neonatal intensive care unit aimed to reduce late-onset sepsis in preterm infants
Publication Number: 196.439
- SB
Silvia Bonato, MD
Neonatologist
Ospedale San Bortolo Vicenza
Vicenza, Veneto, Italy
Presenting Author(s)
Background:
Late Onset Sepsis (LOS) is one of the main causes of morbidity and mortality in preterm infants.
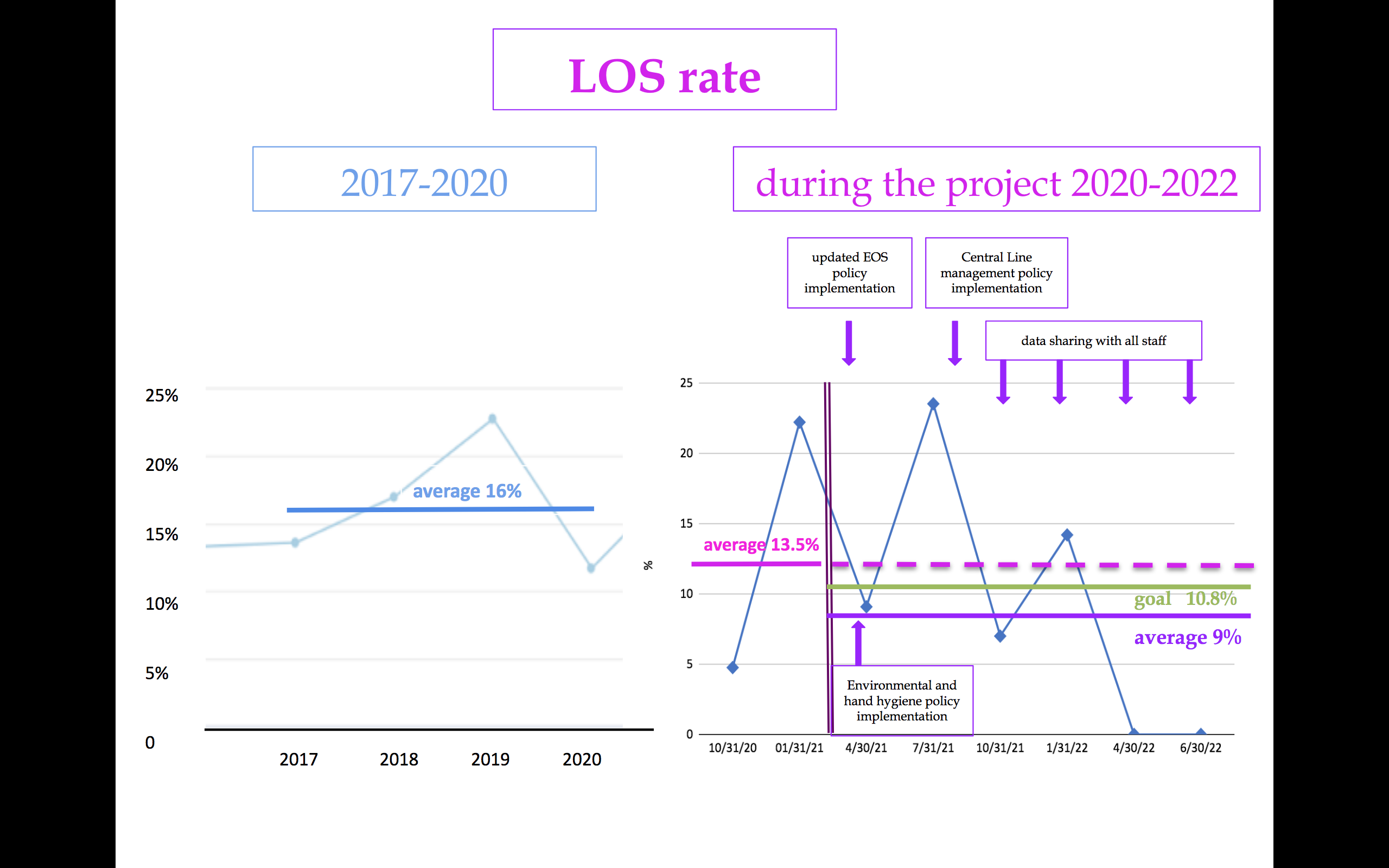
From 2017 to 2020, LOS rate was 16% in our III level Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU).
Hand hygiene practice, central line (CL) management and reduction of inappropriate exposure to antibiotics (ab) are effective ways to prevent infections.
Objective: The aim of the project was to decrease LOS rate by 20% in preterm infants, by June 2022.
Design/Methods:
Multidisciplinary working groups has created to develop the 3 primary drivers of the Quality Improvement (QI) project (fig.1):
1) Environmental and hand hygiene: we retrained our staff on hand hygiene with black box and hospital infection committee support, we used reminders and we created a new policy for environmental hygiene.
We chose and analyzed as measures the environmental and hand hygiene compliance (C).
2) Ab stewardship: we updated early-onset-sepsis (EOS) policy aimed to start ab only in preterms with risk factors for infection and/or symptoms and to stop ab within 36 hours, if the blood culture is negative and they‘re well-appearing. We collect 1-2 milliliters of blood for cultures.
The outcome measures were the ab utilization rate in the first 7 days of life (AUR7: ab days/7 x 1000) and the EOS policy C.
3) CL management: we updated CL management policy introducing check lists for CL insertion and daily care.
The measures were the checklists use C.
We collected prospective data from August 2020 to June 2022.
We introduced change ideas from March 2021.
We periodically shared the runchart of each measure with staff.
Results:
One hundred and six preterm infants born before than 30 gestational weeks or with a birth weight less than 1500 grams, 41 before and 65 after changes, 270 hand hygiene evaluations, 2400 environmental evaluations were examined.
The LOS rate decreased from 13.5% to 9% (fig. 2) thanks to the following improvements:
- hand hygiene C increased from 56% to 82%, significantly from April 2021 until the end of the project (fig.3);
- crib, patient unit, medication cart, devices hygiene C raised 100%, increased respectively from 85%, 70%, 84% and 96%;
- AUR7 decreased from 357 to 285, equal to a 20% reduction (fig.3);
- EOS policy compliance about ab starting augmented from 77% to 85%, the ab stopping C remained high: 96%.
Some measures had never been done before the project: medical phone hygiene C was 87%, CL check list use C was 63 % for insertion, 100% for daily care.
Conclusion(s):
This QI project significantly decreases LOS rate in an Italian III level NICU.
A new effort has to be made to maintain or improve this result..png)
.png)
