Neonatal General
Neonatal General 7: NICU Practices 1
174 - Reducing unplanned extubation at the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) using real-time monitoring of endotracheal tube (ETT)
Publication Number: 174.331

Khalid Al Katranji, MD (he/him/his)
Neonatal Fellow
OSF healthcare/UICOMP
Peoria, Illinois, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background:
Unplanned extubation (UE) is the fourth most common adverse event in the NICU and commonly leads to emergent intubation which has an increased risk of airway and pulmonary injury, intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH), ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP), cardiovascular collapse, increased hospital length of stay and total cost of hospitalization.
Ultrasound real-time monitoring of the endotracheal tube (RTM-ETT) is a new technology that provide continues monitoring of ETT position and patency.
Objective:
We hypothesized that using RTM-ETT monitoring would be effective in decreasing the rate of UE in neonates admitted to the NICU and that preventing UE could decrease the risk for invasive ventilation, direct cost of hospitalization, chronic lung disease (CLD) and VAP.
Design/Methods: This was an observational cohort study comparing an intervention group with RTM-ETT and a control group without RTM-ETT when the device was unavailable to the unit. All neonates who required invasive ventilation admitted to this Midwestern AAP Level 4 NICU between January 2020 to June 2022 were included in the analysis. Neonates requiring intubation in the delivery room or for a surgical procedure for less than 1 calendar day were excluded. The primary outcome was the rate of UE in events/100 ventilator days, secondary outcomes included invasive ventilator days, VAP, severe IVH (≥ Grade 3), severe retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) (≥ Grade 3), CLD at discharge, length of stay, direct cost of hospitalization and mortality.
Results:
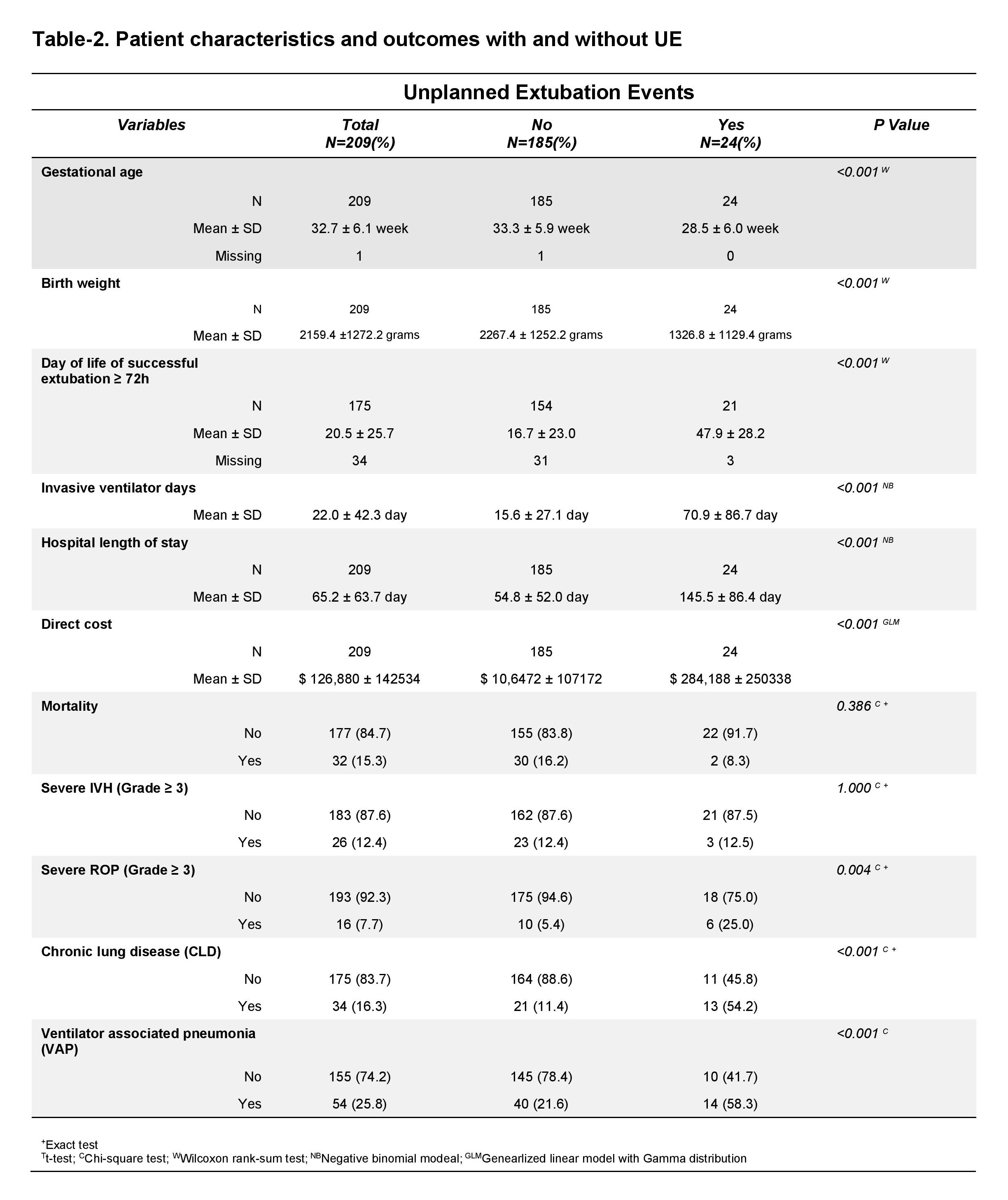
A total of 209 neonates were included: 89 in the intervention group and 120 in the control group. The rate of UE was 0.48/100 ventilator days in the intervention group and 1.78/100 ventilator days in the control group. No other measures to decrease the rate of UE were undertaken during this timeframe. No differences between events were found (Table 1). Univariate analyses were used to compare outcomes between neonates with an UE vs those without an UE controlling for gestational age and birth weight (Table 2). The average length of invasive ventilation for patients with an UE was 4.12 times those without an UE. The risk of VAP was 3.38 times higher, CLD was 5.32 times higher, length of stay was 2.14 higher, and direct cost of hospitalization was 2.32 times higher. There was no difference in rate of severe IVH, severe ROP, or mortality (Table 3).
Conclusion(s):
Using ultrasound real time ETT monitoring (RTM-ETT) was successful in reducing the number of unplanned extubations in the NICU. UE was associated with longer invasive ventilation days, higher direct cost, and higher odds of CLD and VAP.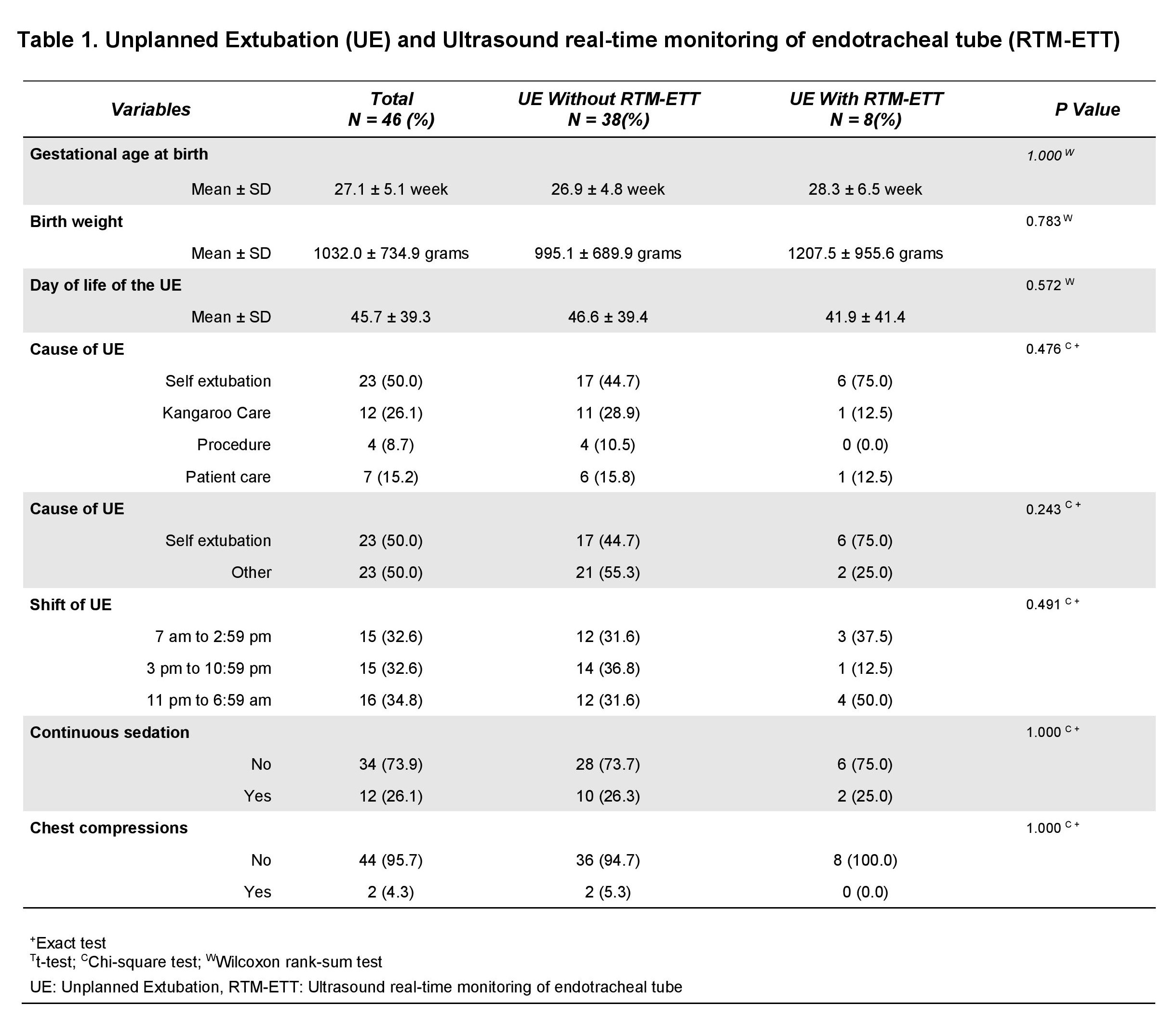
.jpg)
