Neonatal Pulmonology
Neonatal Pulmonology 2: BPD Clinical
265 - Vitamin D deficiency in preterm infants and it's association with Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia (BPD)
Publication Number: 265.34

Mohammad Adnan, MD FAAP (he/him/his)
Attending Neonatologist
Indiana University health Ball memorial hospital
Muncie, Indiana, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Despite advancements in ventilation strategies and various preventive therapies, the incidence of BPD in Preterm infants remains high. Newer research is also looking into other factors that may potentially contribute to BPD. Vitamin D deficiency (VDD) is known to be common in preterm infants with a prevalence ranging from 20-60%. Vitamin D plays a role beyond bone homeostasis and is also believed to be involved in lung development and maturity. Animal studies have supported the role of VDD in the causation of BPD but the results from human studies remain inconclusive.
Objective:
1) To study the prevalence of VDD at birth and trends of 25(OH)D levels in infants < 32 weeks of gestation.
2) To determine the association of VDD with BPD.
Design/Methods: This is a prospective cohort study conducted at John Stroger, Jr. Hospital of Cook County, Chicago. Infants born at less than 32 weeks were included. The study was approved by the institutional review board. 25(OH)D level was measured at birth, weekly until 4 weeks, and then biweekly until 10 weeks or discharge. VDD was defined as 25(OH)D < 20 ng/ml. BPD was defined as oxygen requirement for more than 4 weeks and then assessed for severity at 36 weeks of corrected gestation. Vitamin D was supplemented via parenteral and enteral routes as per unit protocol. SPSS version 22 was used for data analysis.
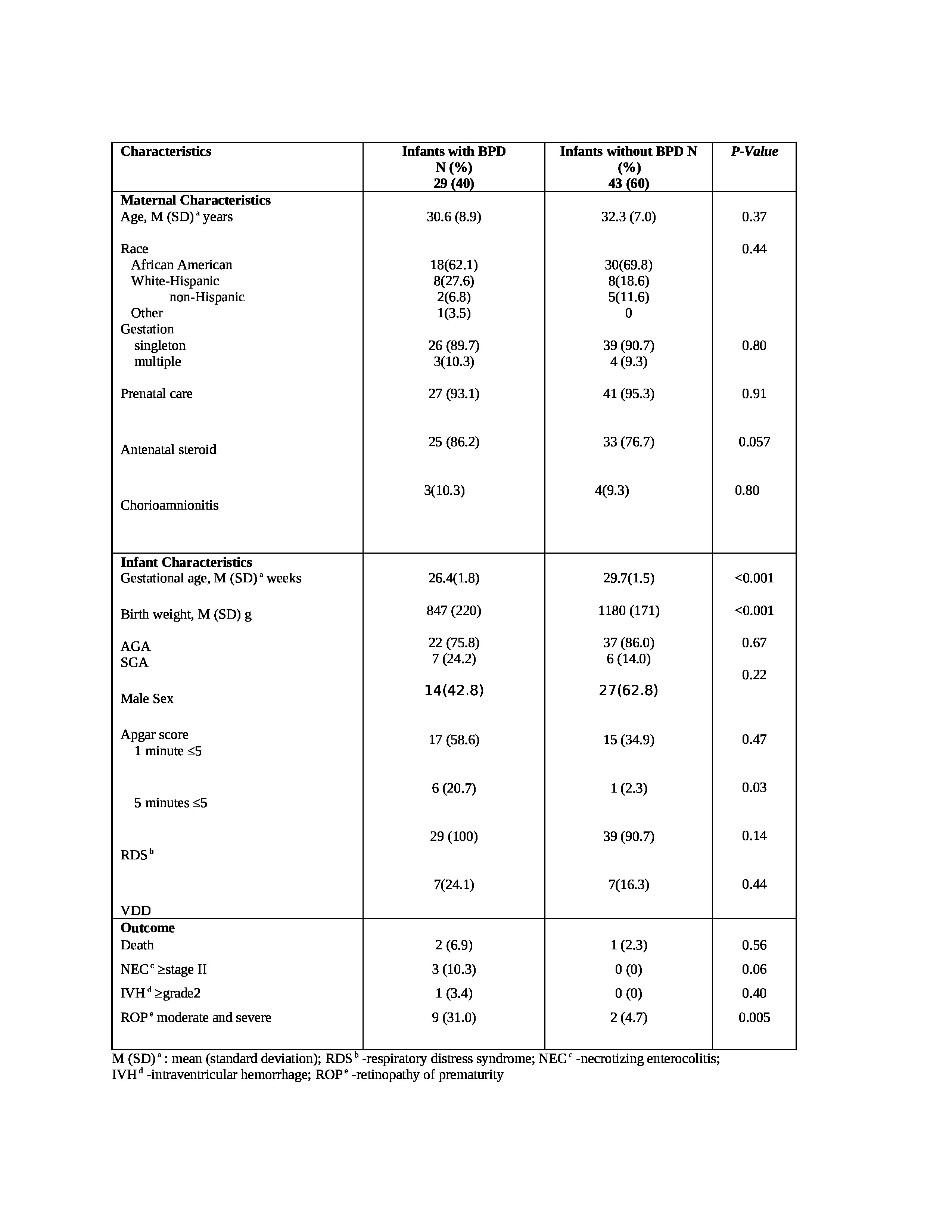
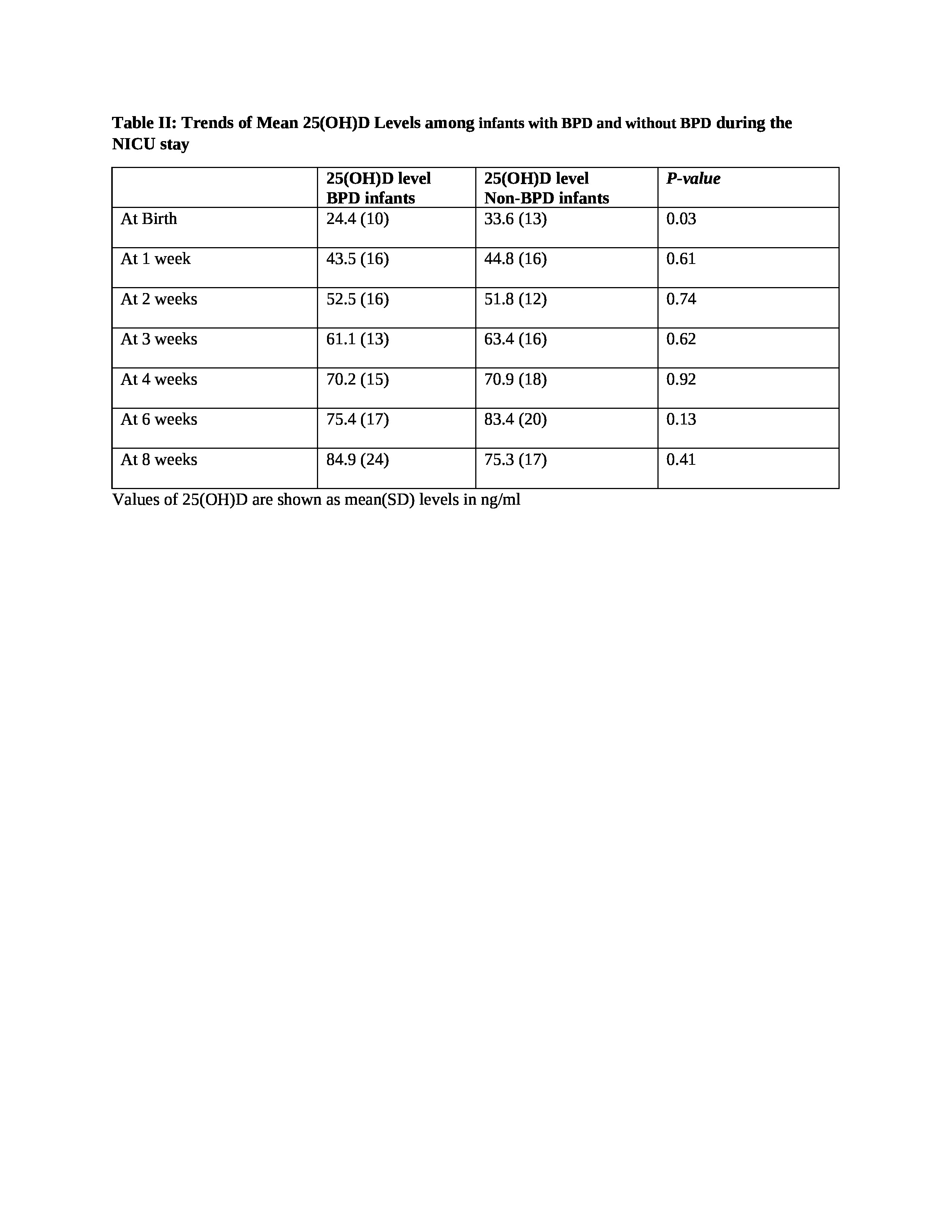
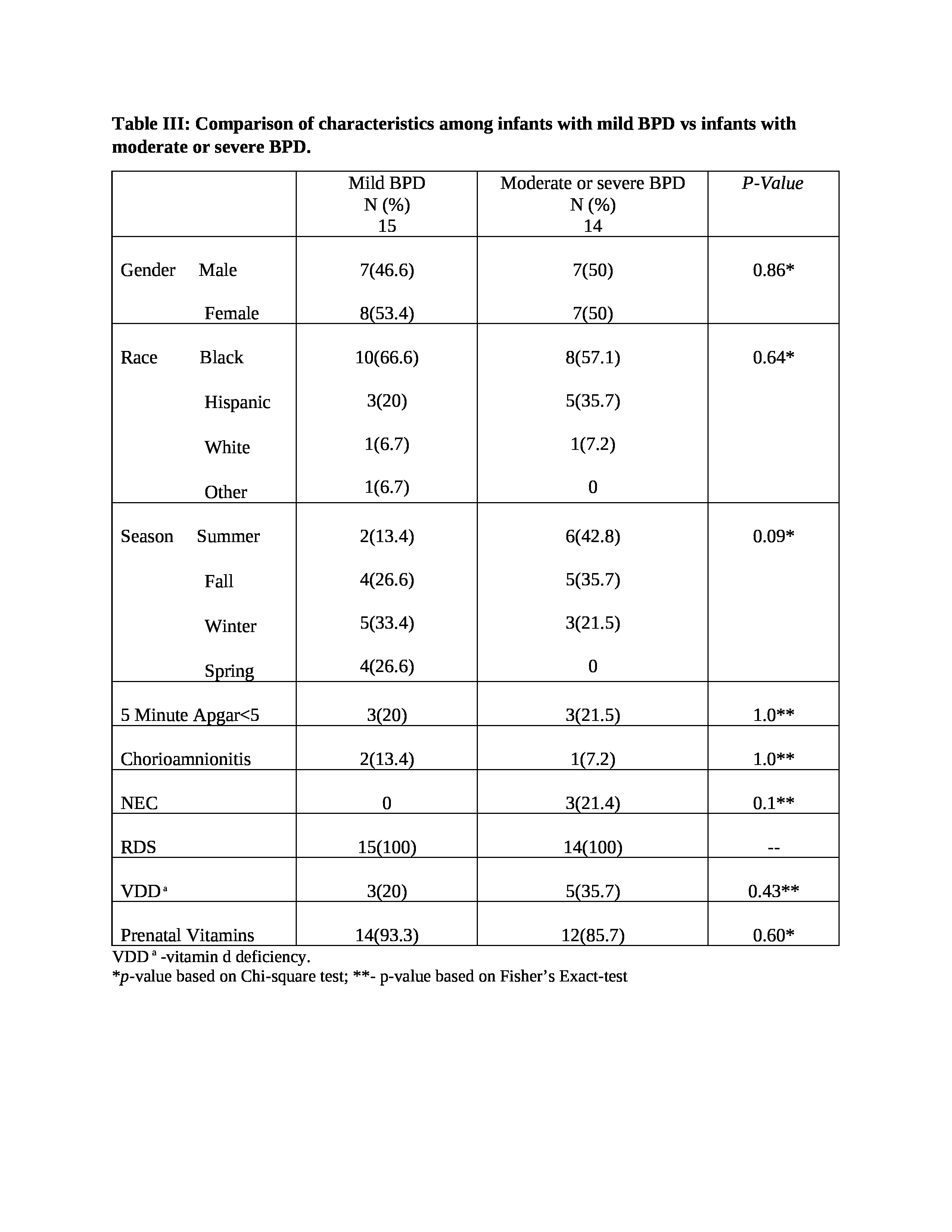
Results: Study included 72 infants with a mean birth weight of 1046+252 grams, gestation 28.3+2.3) weeks,58% males, and 67% black infants. VDD was present in 14(19.7%) infants at birth. BPD was diagnosed in 29 (41%) infants out of which 15 (21%) had mild, 4 (5.5%) had moderate, and 10 (14%) had severe BPD. Table I compares the characteristics among infants with and without BPD. Infants were more likely to be diagnosed with BPD if they were more preterm, had lower birth weight, and had lower 25(OH) D at birth. However, after applying a multiple logistic regression model to this data, gestation age was the only factor significantly associated with the development of BPD. Table II shows trends of mean 25(OH) levels in infants with and without BPD. All of the study infants attained vitamin D sufficiency [25(OH) D >30 ng/ml] by the end of 2 weeks and none of them had VDD afterward. We did not find any significant difference in the prevalence of VDD among infants diagnosed with mild vs combined moderate-severe BPD (Table III).
Conclusion(s):
In our study, VDD at birth was not associated with the development of BPD. However, at the time of BPD diagnosis, none of the infants had VDD.