Neonatal Respiratory Assessment/Support/Ventilation
Neonatal Respiratory Assessment/Support/Ventilation 3: Physiology 2 and Clinical Outcomes
345 - Changes of DCO2 corrected by weight increases the correlation with variations of PaCO2 in newborns receiving HFV.
Publication Number: 345.346

Matias Luco, MD (he/him/his)
Assistant Professor
Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile
Las Condes, Region Metropolitana, Chile
Presenting Author(s)
Background:
Keeping the arterial pressure of CO2 (PaCO2) stable is challenging and highly relevant in high-frequency ventilation (HFV). A continuous monitoring value that correlates with the variations in PaCO2 would be desirable. New models of mechanical ventilators can measure the tidal volume during HFV and thus deliver the diffusion coefficient of CO2 (DCO2). This is obtained by the square of this tidal volume multiplied by the frequency of ventilation. In newborns, weak correlation has been found between absolute values of DCO2 and PaCO2.
We propose that DCO2 variations corrected by the patient's weight over time will correlate better with PaCO2 than absolute DCO2 values. No previous study has assessed this potential relationship.
Objective:
To evaluate the correlation between the changes of DCO2 corrected by weight (DCO2corr) with the variations of PaCO2 in newborns receiving HFV. The variation in DCO2corr during high-frequency ventilation is a good indicator of changes in the patient's PaCO2. However, this correlation is not equivalent between the different brands of mechanical ventilators.
Design/Methods: All neonates over 34 weeks of gestation who required HFV during 2019-2020 were included. Concomitant PaCO2 and DCO2 were recorded prospectively every time an arterial gas was taken. The changes in PaCO2 and DCO2corr were analyzed by Pearson's correlation coefficient, globally and separately by ventilator’s brand.
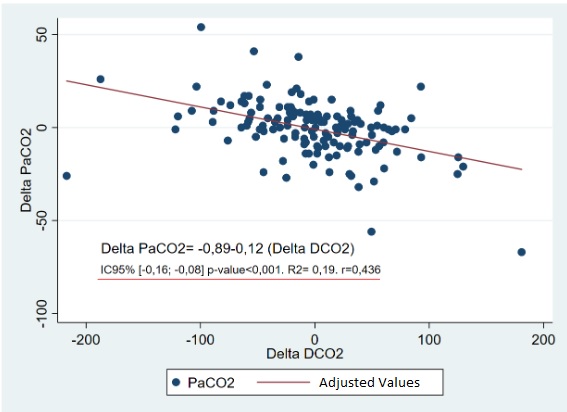
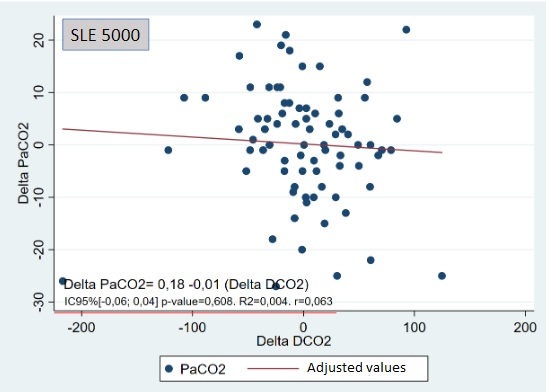
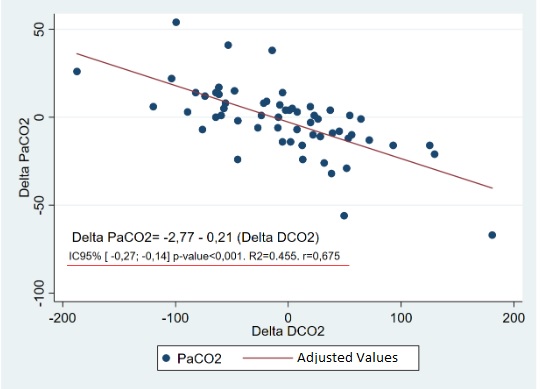
Results: We analyzed 138 values from 21 infants using SLE5000 (SLE, UK) or Fabian (Acutronic, Switzerland) ventilators. PaCO2 and DCO2corr variations correlated moderately but significantly (r=-0.43; p< 0.001). When analyzed by ventilator's brand, 78 paired values from SLE 5000 showed no significant correlation (r=-0.59; p=0.6), contrasting with 59 paired values from Fabian that proved a strong and significant correlation (r=-0.67; p< 0.001).
Conclusion(s):