Neonatal General
Neonatal General 8: NICU Practices 2
183 - Developing and Implementing a Standardized Assessment Tool for Skin-to-Skin Care in the NICU
Publication Number: 183.332

J'nae Smith, MD (she/her/hers)
Resident physician
albany medical center
Albany, New York, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background:
The NICU environment is stressful to critically ill newborns and can sustain a negative impact on their neurodevelopment. Skin-to-skin (STS) care can mitigate stress from parental separation, painful procedures, and sleep disturbance experienced in the NICU.
Objective:
Our objective is to standardize our approach to offering STS care, ultimately decreasing the time to first STS event.
The 3 specific aims of this project were to (1) survey medical staff and parents regarding experiences, attitudes, and barriers in STS, (2) develop a tool to address barriers to STS, and (3) implement the tool consistently in our patient population.
Design/Methods:
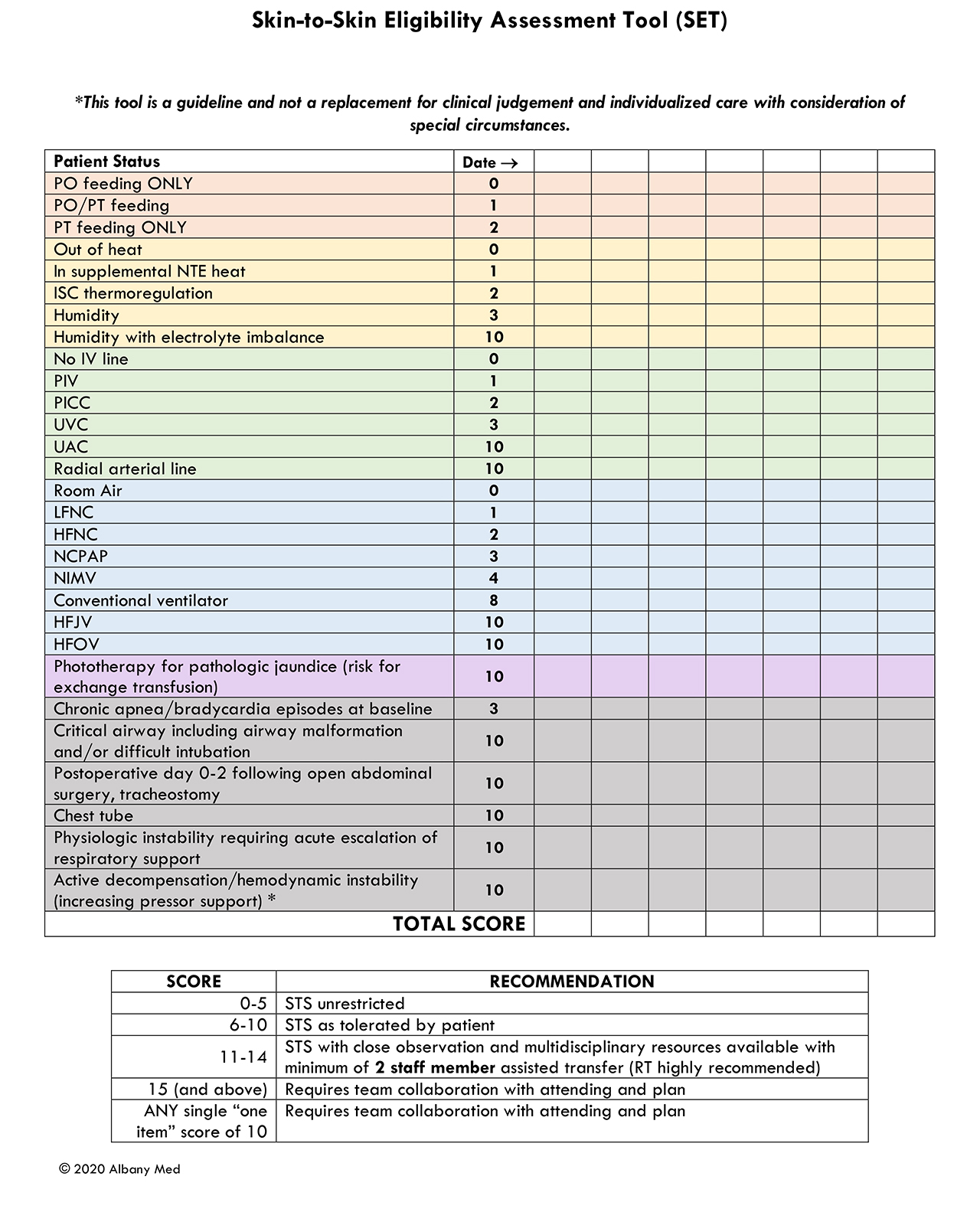
In our 60-bed Level 4 NICU, parents were surveyed to determine baseline time to first STS care, and parent perceptions of STS. Medical staff was given a case-based survey to determine practice and beliefs regarding STS (Aim 1). From these results, the Skin-to-Skin Eligibility assessment Tool (SET) was developed by a multidisciplinary team and tested for interrater reliability (Aim 2) (Image 1). The staff was educated to use the SET, and it was added to a mandatory daily nursing assessment in the electronic health record. SET scores, gestational age (birth and adjusted), and weights were collected on all bedded NICU patients (unless admitted on the day of assessment) over 7 selected days across 14 months to audit consistent use of the SET tool in a large range of patients (Aim 3).
Results:
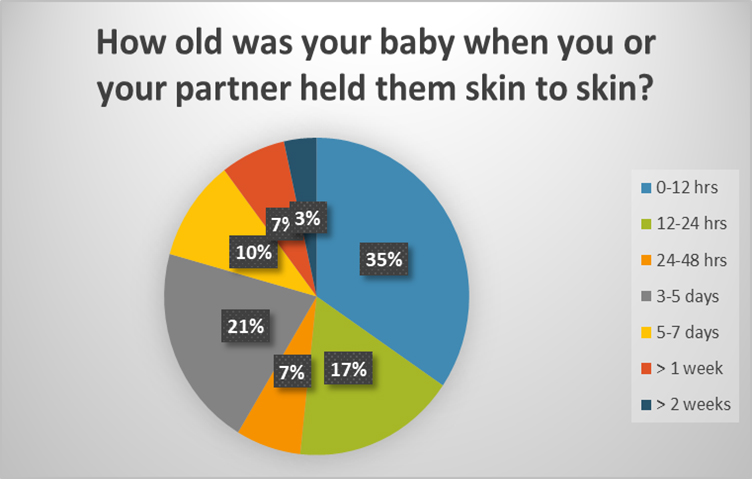
Parent surveys revealed a wide variation in time to first STS (Image 2). Staff surveys identified facility/environment, negative staff attitudes, lack of assistance with practice/transfer, lack of appreciation for STS benefits, and balancing technical risks as barriers to STS care (Aim 1).
Interrater reliability testing showed no difference in scores between 5 raters assessing 20 patients (Aim 2).
In the SET score audit, there were 300 eligible patients on the NICU census over the 7 selected days. Median weight was 2.1 kg (IQR 1.44-2.57). Median adjusted gestational age was 35 2/7 weeks (IQR 32 5/7 - 37 3/7). 99% of eligible patients evaluated received a daily SET score. SET scores ranged from 0-36 with a mean score of 5.95 (± 6.7), mode of 2, and median score of 3 (IQR 2-8) (Aim 3).
Conclusion(s):
The SET tool was developed based on parent and staff input and can be practically and consistently applied to standardize and evaluate eligibility for STS care in a Level 4 NICU. COVID-19 delayed initiation of further improvement cycles to increase access to STS. Next steps include resurveying our staff and parents, and auditing our time to first skin-to-skin care.