Neonatal Nephrology/AKI
Neonatal Nephrology/AKI 1
222 - Indomethacin Patent Ductus Arteriosus Prophylaxis in the Modern Era: Renal Implications
Publication Number: 222.242

Luke A. Wessler (he/him/his)
Student
Medical University of South Carolina College of Medicine
Charleston, South Carolina, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Indomethacin, a nephrotoxin, is used for patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) prophylaxis (ppx) in premature newborns, but it remains unknown if ppx is associated with acute kidney injury (AKI) when the consensus, neonatal AKI staging definition is utilized.
Objective: We aimed to determine if ppx is associated with neonatal AKI in premature infants. We hypothesized ppx receipt would be associated with AKI given its nephrotoxicity and the high susceptibility of the premature, newborn kidney to AKI.
Design/Methods:
Single center retrospective cohort study of neonates < 28 weeks gestational age (GA) and < 1,000 grams at birth (i.e., extremely low birth weight, ELBW) treated before (Cohort 1 (C1): 3/15/16-3/14/19) and after (Cohort 2 (C2): 3/15/19-3/14/22) initiation of protocolized ppx. Ppx included indomethacin 0.1mg/kg IV q24 hours for up to 3 doses in ELBW newborns < 28 WGA without contraindications.
Comparisons were made between C1 and C2. Primary outcome: early (i.e., < 7 postnatal days) AKI, defined by the modified, neonatal Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) criteria.
Results:
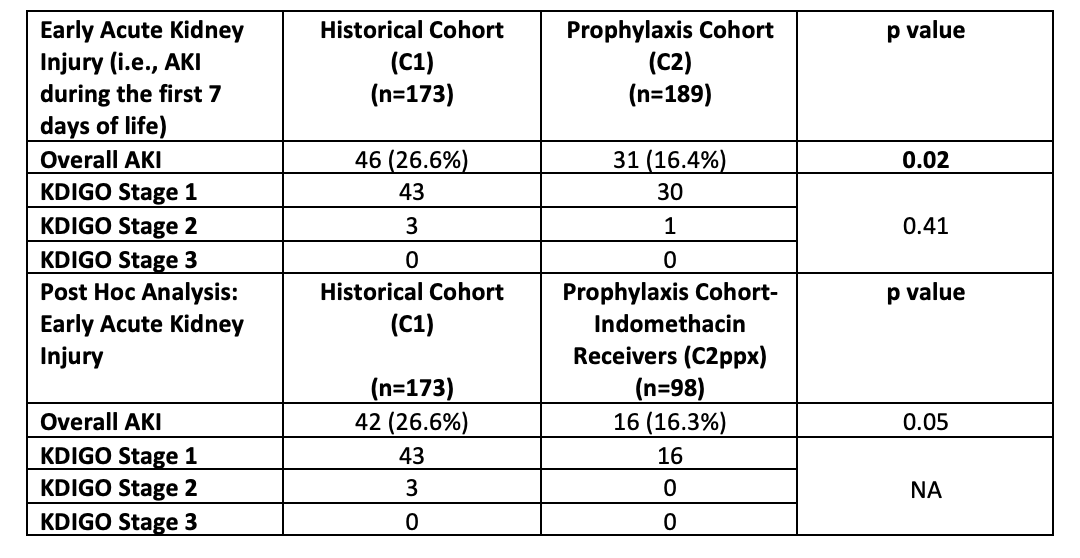
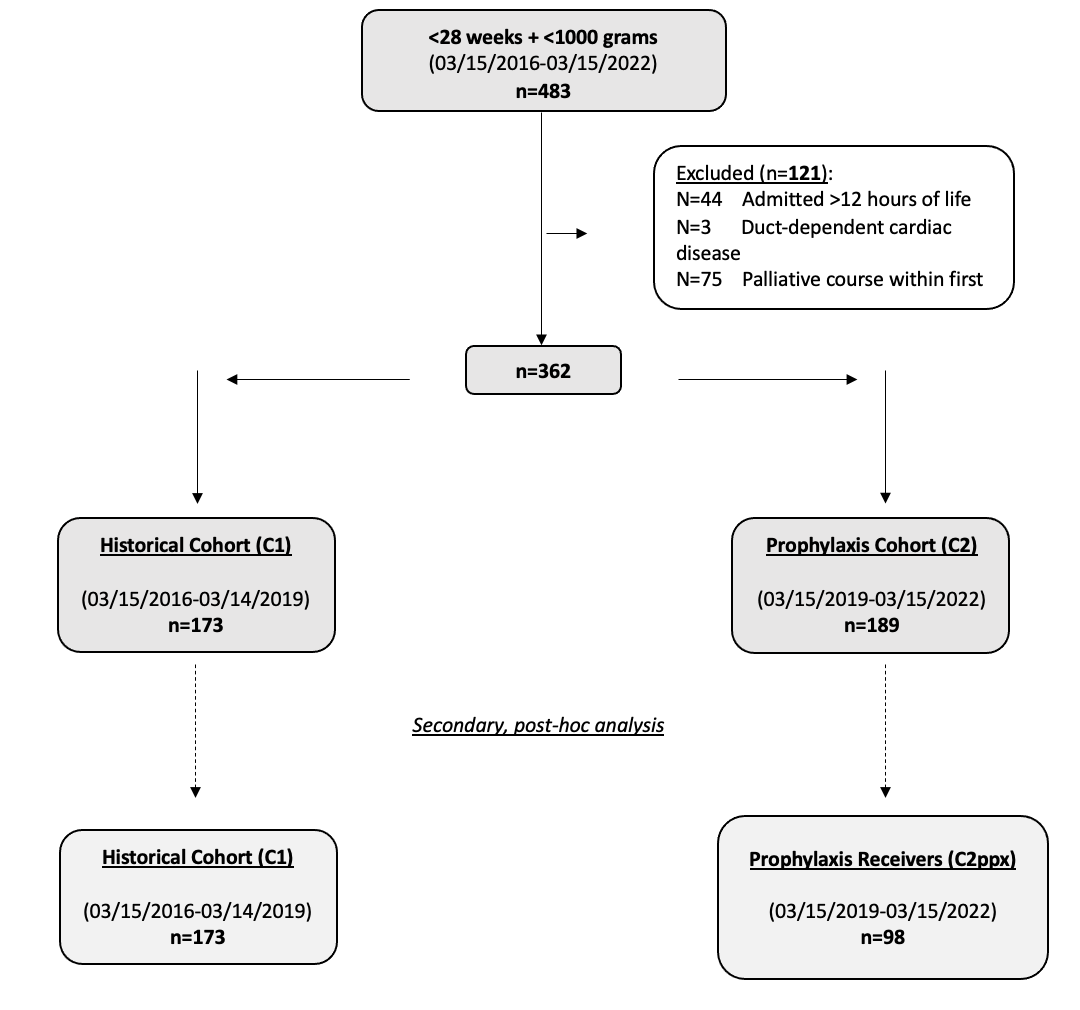
Of 483 screened infants, 362 were included in the study (C1: n= 173; C2: n=189, Figure 1). Baseline characteristics including GA, birth weight, gender, race, and ethnicity were similar between cohorts. Of 189 eligible neonates in C2, 98 (52%) received ppx with most completing a full course (1 dose: 16.3%; 2 doses: 10.2%; 3 doses: 73.5%). A decreased incidence of early AKI was noted in C2 (C1: 26.6% vs. C2: 16.4%; p=0.02, Table).
To better assess the association between ppx receipt and AKI, a secondary, post-hoc analysis comparing all neonates in C1 to only those who received ppx in C2 (i.e., C2ppx) was also conducted (C1: n=173; C2ppx: n=98, Figure). When comparing baseline characteristics between C1 and C2ppx, GA differed between groups with ppx receivers having significantly higher GA than historical counterparts (C1: median 25 weeks [IQR 24-26] vs. C2ppx: 26 weeks [25-27]; p< 0.01). Birthweight, gender, race, and ethnicity were similar between groups. When comparing AKI rates, we did not detect an association between ppx receipt and AKI (C1: 26.6% vs. C2ppx: 16.3%; p=0.05, Table).
Conclusion(s): Despite the potential nephrotoxicity of indomethacin in a highly susceptible premature, newborn kidney, indomethacin PDA ppx was not associated with increased early neonatal AKI in our single-center cohort of ELBW neonates. Further studies with larger samples sizes are needed to fully elucidate the association between indomethacin PPX and early neonatal AKI.