Breastfeeding/Human Milk
Breastfeeding/Human Milk 3: Human Milk Bioactives and Composition
21 - The Role of Maternal and Preterm Infant Characteristics in Concentrations of Human Milk Oligosaccharides and Lactoferrin in Maternal Milk
Publication Number: 21.201

Margaret L. Ong, MD (she/her/hers)
Neonatologist
Brigham and Women's Hospital
Boston, Massachusetts, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Human milk confers a wide range of benefits for preterm infants, including brain development and immune protection. Human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) and lactoferrin (Lf) are two important milk bioactives which may contribute to these beneficial effects. While genetics are a known determinant of the human milk profile, non-genetic maternal and infant factors may also play a role. Few studies have examined determinants of HMO and Lf content in human milk for mother-preterm infant dyads.
Objective:
To determine associations of maternal and infant characteristics with HMO and Lf concentrations in maternal milk fed to very preterm infants early in the neonatal hospitalization
Design/Methods:
Participants were 96 mothers of 105 very preterm infants (< 32wk gestational age, GA) who had milk analyzed for HMOs (n=95) and Lf (n=66). Maternal and infant characteristics included: maternal age, parity, mode of delivery, pre-pregnancy BMI (ppBMI), diabetes, HMO secretor status, days post-partum, infant GA and sex. HMO composition (µg/mL, high performance liquid chromatography) was measured on milk fed at mean 13.2±7.6d, and Lf concentration (mg/mL, electrochemiluminescence multiplex immunoassay) was measured on milk fed at 16.9±7.4d. Given skewed data, we assessed Spearman correlations of continuous characteristics with HMO and Lf concentrations and compared median concentrations between categorical groups (Wilcoxon rank sum test).
Results:
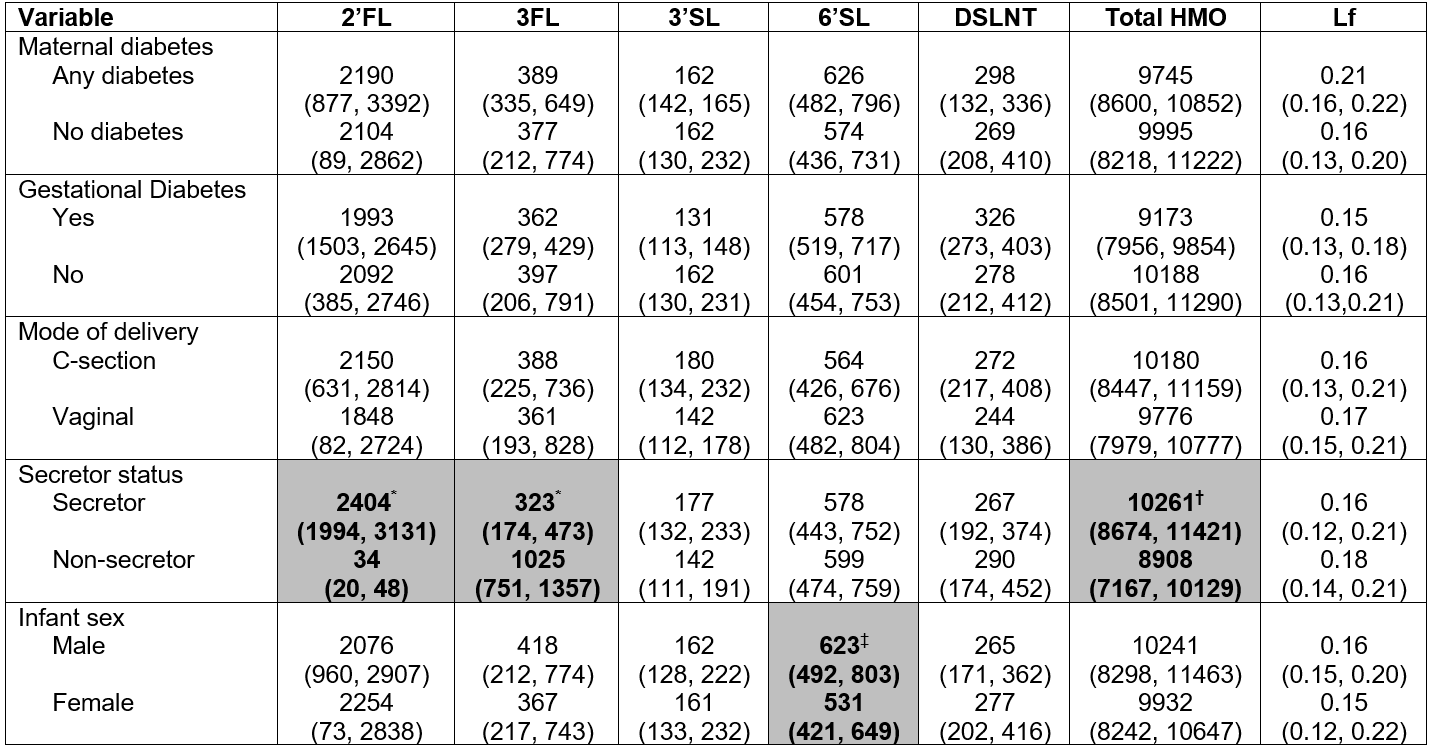
Mean GA was 28.5±2.2wk, and birthweight 1109±391g [Table 1]. Higher maternal age associated with lower DSLNT (ρ=-0.26, p=0.01) and Lf concentrations (ρ=-0.25, p=0.04). Higher ppBMI associated with higher 6’SL concentration (ρ=0.33, p=0.02). Increasing days post-partum associated with lower total HMO (ρ=-0.20, p=0.049) [Table 2]. HMO secretor mothers produced higher 2’FL (median[IQR] 2404[1994,3131] vs 34[20,48], p< 0.001), lower 3FL (323[174,473] vs 1025[751,1357], p< 0.001), and higher total HMO concentrations (10261[8674,11421] vs 8908[7167,10129], p=0.006) than non-secretors. Mothers of male (vs female) infants produced higher 6’SL concentrations (623[492,803] vs 531[421,649], p=0.047) [Table 3].
Conclusion(s):
Among mothers of very preterm infants, older age was associated with lower levels of a key protective HMO (DSLNT) and Lf levels. Increasing duration of lactation was associated with lower total HMO levels. 6'SL was higher in milk for male compared to female infants and higher for mothers with higher ppBMI. Understanding these maternal and infant determinants of milk bioactives may lend insight into strategies to improve nutritional care for this vulnerable population.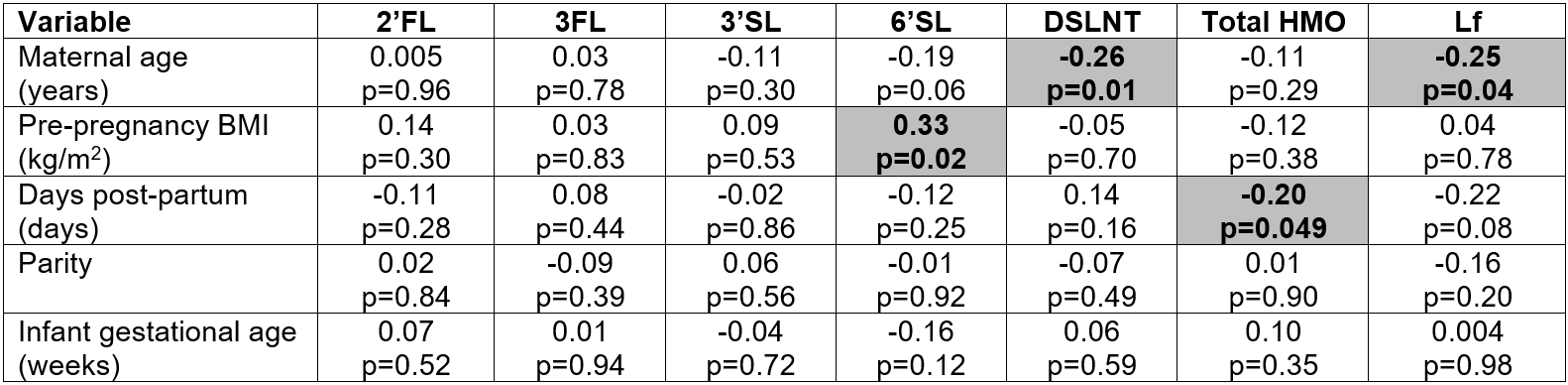
.png)
