Neonatal-Perinatal Health Care Delivery: Practices and Procedures
Neonatal-Perinatal Health Care Delivery 2: Practices: Monitoring, Devices, Respiratory Care
737 - Incubator-Based Active Noise Control Device: Comparison to Foam Ear Covers and Zone of Noise Reduction Quantification
Publication Number: 737.245

George M. Hutchinson, PhD
CEO
Invictus Medical
San Antonio, Texas, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background:
Excess noise exposure in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) is consistently higher than current recommendations and may adversely affect neonatal sleep, weight gain and overall health. Various approaches have been attempted to address this noise problem, but these attempts have not proven consistently effective. Single-family rooms have become more prevalent and been shown to reduce noise levels, but not to the levels recommended by guidelines and may be associated with adverse outcomes related to diminished infant interactions.
Objective:
We sought to measure the level of noise reduction provided by commercially available neonatal ear covers and to compare this to that provided by a novel active noise control (ANC) device that does not require patient contact designed for use in neonatal incubators.
Design/Methods:
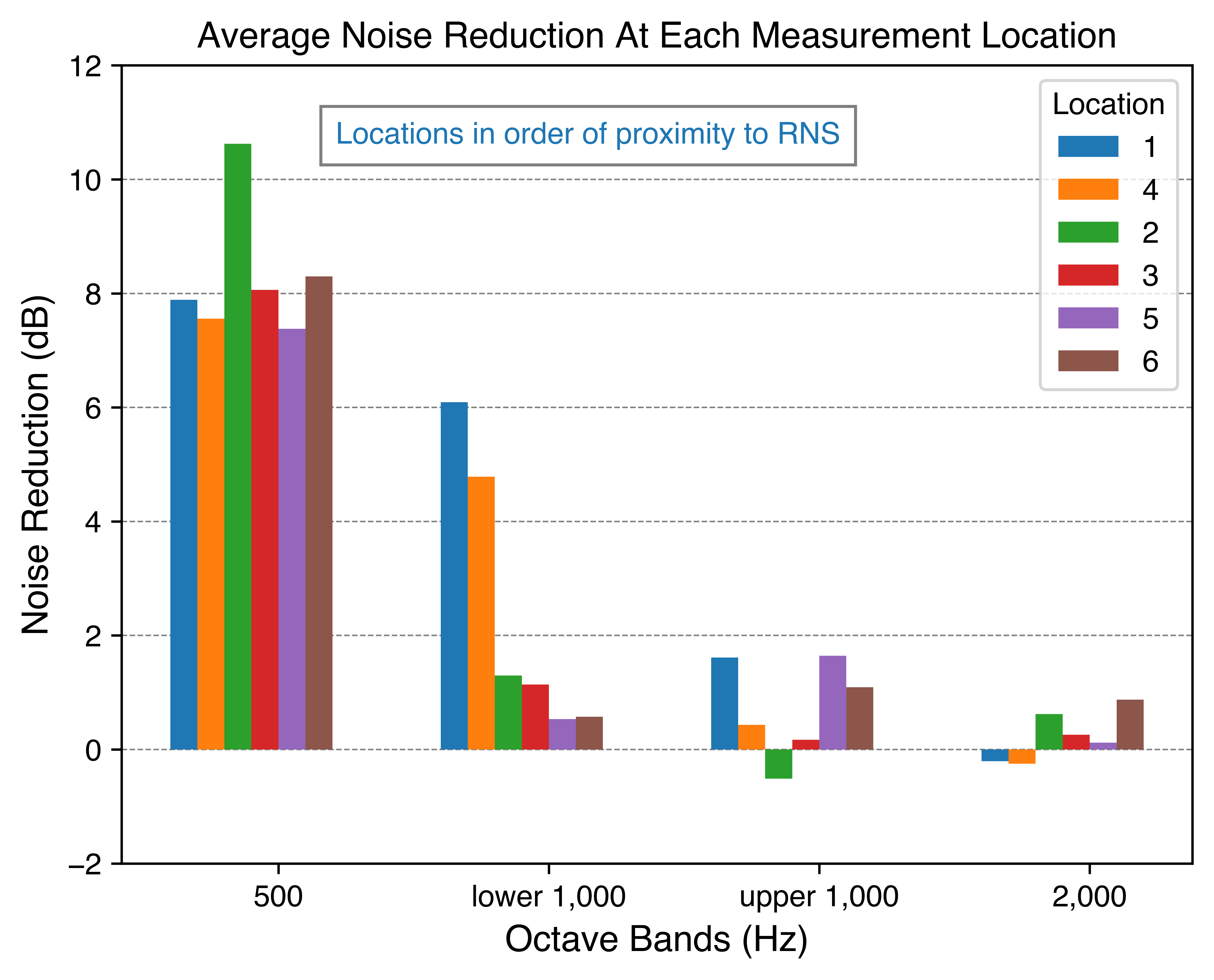
The noise reduction effects of the ANC device were compared to that provided by adhesive foam ear covers. For each sound sequence tested, sound pressure measurements were made at a test manikin ear under four test conditions: (1) control - no noise reduction, (2) active noise control device, (3) ear covers without hair, and (4) ear covers positioned on hair. The effect of patient position on noise reduction was evaluated by measuring noise reduction at both ears of a manikin in six positions within an incubator with each sound sequence (Fig 1).
Results:
The ANC device provided greater noise reduction than the ear covers in seven of the eight sound sequences tested in which a noise reduction greater than the JND was achieved (Table 1). When the ear cover's adhesive begins to peel off the infant, we found that the ear cover could amplify the sound at the ear rather than attenuating it. For noise reduction using the ANC device, the average noise reduction ranged from 2.3 to 3.4 fold for all sound sequences' primary frequencies in the 500 Hz octave band at all positions tested within the incubator. It provided better reduction for frequencies below 1,000 Hz than above 1,000 Hz (Fig 2).
Conclusion(s):
The ANC device provided superior noise reduction to the ear covers in this simulated environment test for all alarm sounds where the noise reduction difference was greater than the JND. Adhesively affixed ear covers have risks associated with skin integrity and, when peeling off, can amplify sounds rather than attenuate. Noise reduction may improve sleep hygiene and weight gain at the levels provided by adhesive ear covers. These simulation results demonstrate, in principle, the ability to successfully utilize active noise cancellation in the NICU setting to reduce environmental noise exposure..png)
.png)
