Emergency Medicine: All Areas
Emergency Medicine 5 A
323 - Emergency Department Evaluation of Young Infants with Head Injury: Are All Young Children the Same?
Publication Number: 323.208

Todd W. Lyons, MD, MPH
Assistant Professor
Boston Children's Hospital
Wayland, Massachusetts, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: The evaluation of young infants with head trauma is challenging, as these infants can mask signs of significant head injury, are at highest risk of radiation exposure from imaging, and may be victims of non-accidental trauma.
Objective: We compared the emergency department evaluation, diagnoses and outcomes of young infants with head injuries to older children to assess differences that may affect optimal management for this vulnerable population.
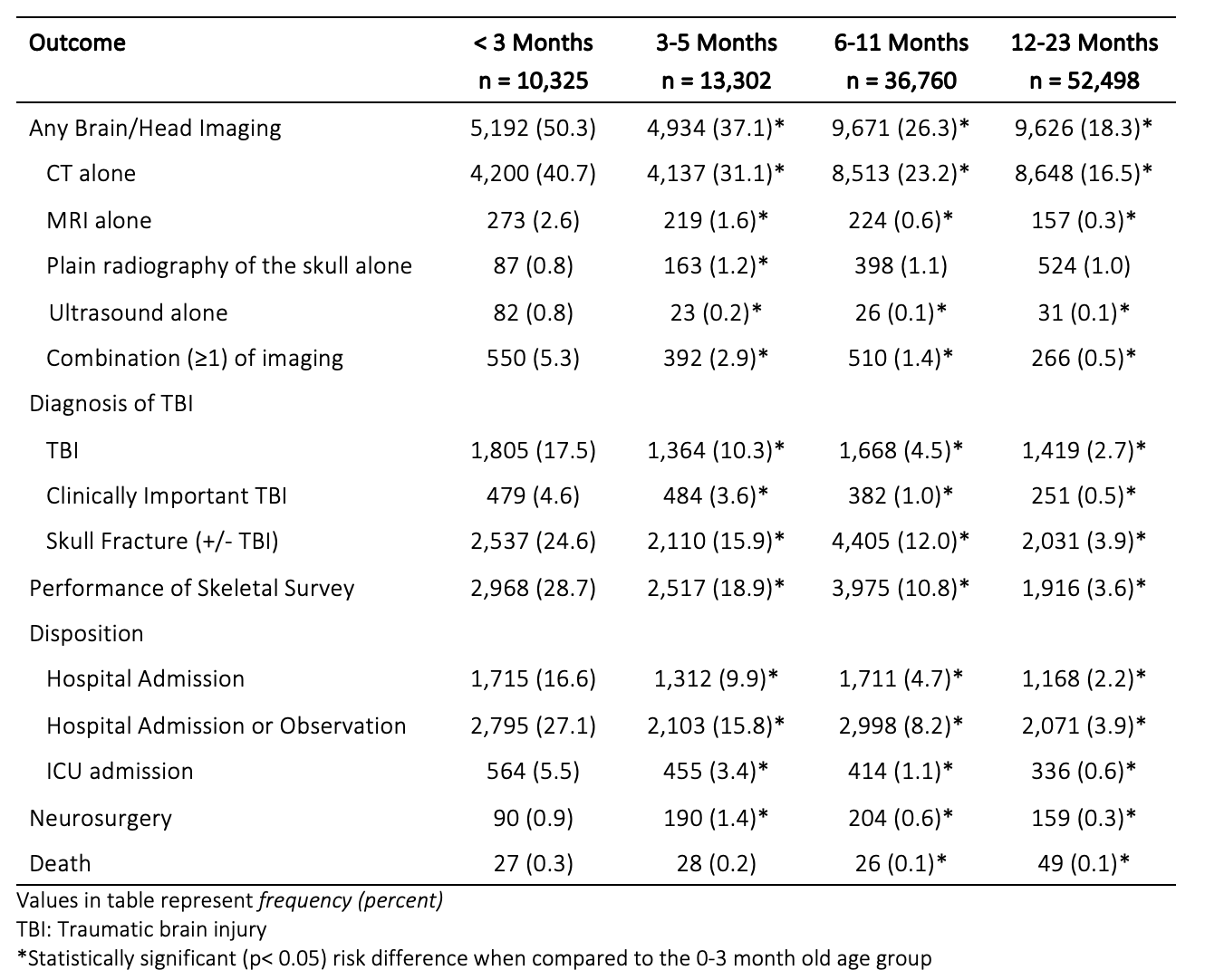
Design/Methods: We performed a retrospective, cross-sectional analysis of children < 2 years old with isolated head injuries at one of 47 emergency departments between 2015 and 2019 using the Pediatric Health Information Systems database. We included children with a diagnosis of head injury (ICD-10). We excluded children with non-isolated head injuries (ICD-10) or who had diagnostic imaging or procedure(s) not related to head injury. Because children with head injury often undergo neck imaging, we did not exclude children with isolated neck imaging. Our primary outcome was performance of diagnostic neuroimaging. Secondary outcomes were diagnosis of traumatic brain injury, clinically important traumatic brain injury (traumatic brain injury plus intubation, neurosurgery, death, or > 2 days of hospitalization), hospitalization, neurosurgery, evaluation for non-accidental trauma (defined as having a skeletal survey performed) and mortality. We compared outcomes between the youngest infants (< 3 months old) and older children (3-23 months).
Results:
We included 112,885 emergency department visits for children < 2 years old with isolated head injuries. 62,129 (55%) were by males, and 10,325 (9.1%) were by infants < 3 months of age. The youngest infants were more likely to: undergo diagnostic head imaging, to be diagnosed with a traumatic brain injury and clinically important traumatic brain injury, to be admitted to the hospital, to undergo neurosurgery, to have a skeletal survey performed, and to die (Table 1). Among those children undergoing neuroimaging, traumatic brain injuries were significantly more common in the youngest infants compared to those 12-23 months (26.4% vs. 8.8%, difference 17.6%, 95%CI 16.3-19.0%).
Conclusion(s): The youngest infants with head injuries are significantly more likely to undergo neuroimaging, be diagnosed with TBI, undergo neurosurgery and die. These findings highlighting the need for a specialized approach for this vulnerable population.