Emergency Medicine: All Areas
Emergency Medicine 4
68 - Liver Transaminase Concentrations in Children with Acute SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Publication Number: 68.112

Madeleine W. Sumner, A.B. (she/her/hers)
Medical Student
The University of Western Ontario - Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry
London, Ontario, Canada
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Previous reports estimate that over one third of SARS-CoV-2 infected children have elevated transaminases during acute illness. It remains unclear whether SARS-CoV-2 is more likely to cause elevated transaminases than other respiratory viruses.
Objective: To evaluate the relationship between SARS-CoV-2 infection and liver injury by comparing serum transaminase concentrations among children tested for SARS-CoV-2 and other respiratory viruses in pediatric emergency departments.
Design/Methods:
Eligible children included those < 18 years with suspected SARS-CoV-2 who were tested using molecular approaches in 41 EDs in 10 countries between March 7, 2020, and June 15, 2021 (PERN database), and 14 Canadian EDs between August 6, 2020, and February 22, 2022 (PERC database). We analyzed the first aspartate (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) concentrations available and constructed multivariate linear regression models with the natural log of serum transaminase concentrations as continuous dependent variables to compare values among children infected by different respiratory viruses.
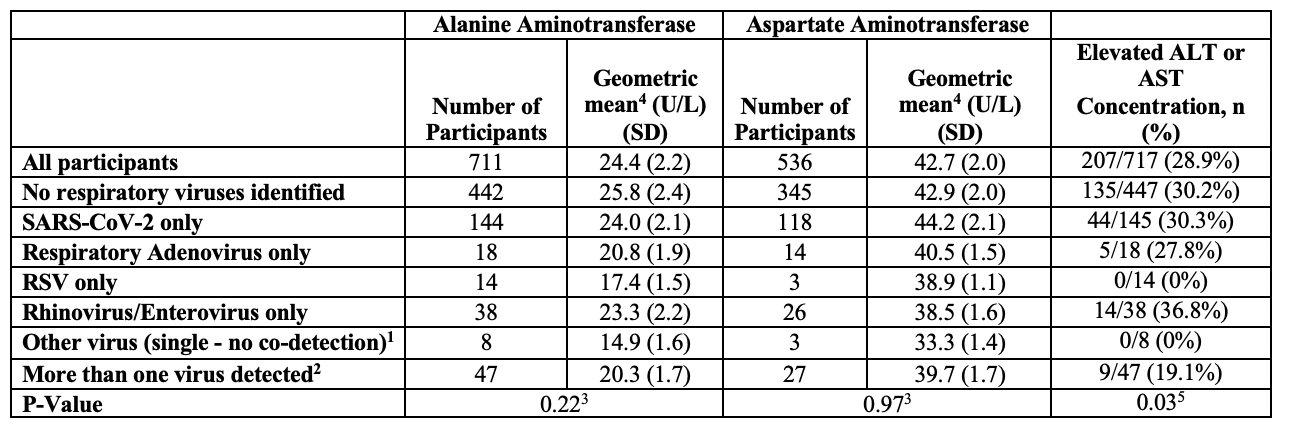
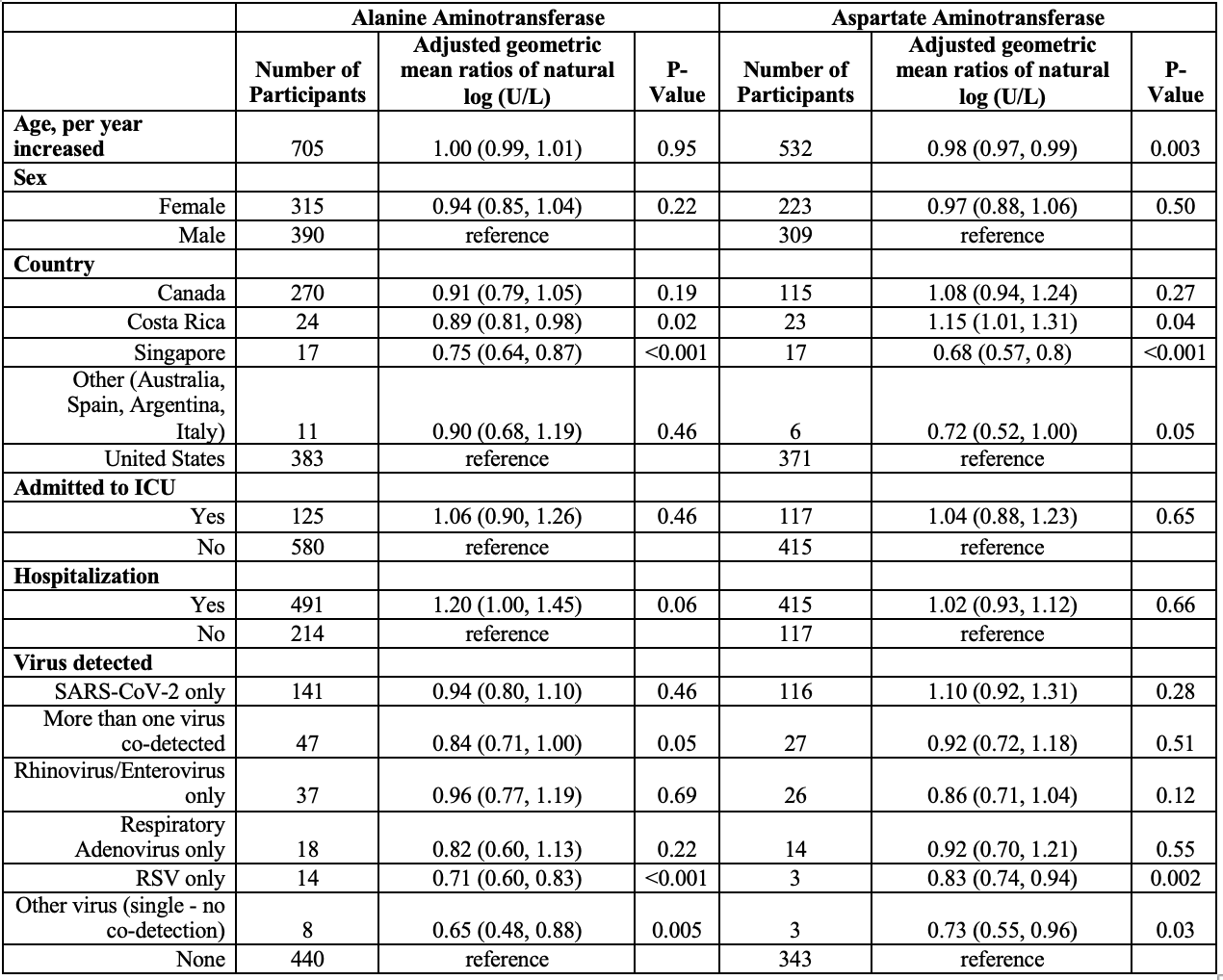
Results: Of 16,933 enrolled children, 6,099 (36.0%) had transaminase concentrations measured; 4,326 (25.6%) were SARS-CoV-2 positive, and 2,604 (15.4%) were tested for additional respiratory viruses. AST and ALT testing was performed in 27.3% (711/2,604) and 20.6% (536/2,604) of those tested for respiratory viruses, and 145/4326 (3.4%) of SARS-CoV-2 positive children. Transaminase concentrations were elevated in 30.3% (44/145) of SARS-CoV-2-positive children. Serum ALT levels were elevated in 5/18 (27.8%), and 14/38 (36.8%) of children with isolated detection of adenovirus and enterovirus/rhinovirus, respectively. Among children testing negative for any virus, 135/447 (30.2%) had an elevated AST or ALT (P >0.99, compared to isolated SARS-CoV-2 positive). In the multivariable model, SARS-CoV-2 detection was not associated with elevated ALT (OR: 0.94; 95%CI: 0.80, 1.1) or AST (OR: 1.10; 95%CI: 0.92, 1.31) concentrations, with negative respiratory panel as the referent group. Ninety-day follow-up was completed in 80.8% (3,494/4,326) of SARS-CoV-2 positive children; no cases of new-onset liver disease were reported.
Conclusion(s):
Among those tested, transaminase concentrations did not vary in a clinically relevant or statistically significant manner between SARS-CoV-2-positive children and those whose tests were negative for all viral respiratory pathogens. In multivariate analysis, acute SARS-CoV-2 infection was not independently associated with increased initial transaminase concentrations compared to other respiratory viruses.