Neonatal General
Neonatal General 1: Basic Science and Cardiovascular
256 - Cardiac Troponin-I Level at 24 Hours After Birth in Stable Newborn Infants
Publication Number: 256.13

David Charles Rosario, MD (he/him/his)
Pediatric Resident
Albany Medical Center
Derwood, Maryland, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Cardiac troponin-I is a known biomarker of myocardial injury, but its diagnostic utility is unclear in newborns. Studies show that elevated troponin-I levels in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy may be predictive of the degree of tissue injury, but normal ranges have been extrapolated from data in older children or adults.
Objective: Our study aims to establish normative data for cardiac troponin-I in stable newborns and to assess any variation in levels based on the mode of delivery, newborn resuscitation, and maternal diabetes status.
Design/Methods:
This is an IRB-approved, prospective, observational study of babies born >35 weeks’ gestation admitted to our well-baby nursery. Infants with congenital heart disease were excluded. After obtaining parental consent, we evaluated troponin-I using a validated point-of-care testing method bundled with state newborn screening at 24 hours of life. If troponin-I results were at least three-fold the cut-off for the normal level of 0.04 ng/ml in older children or adults (i.e. 0.12 ng/ml), electrocardiogram (EKG) and echocardiography were performed by cardiology. Descriptive analysis of the troponin-I levels was done to gather normative data for this population. Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used to compare troponin-I levels between various subgroups, as shown in Table 2. A p-value < 0.05 was considered significant.
Results:
151 patients consented and 132 had adequate samples resulted. Two patients had troponin-I levels (0.12 and 0.32 ng/ml, both outliers) that warranted EKG and echocardiography—they had normal myocardial function and followed up outpatient with no adverse reports. It was discovered that both these infants were born to mothers with SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy. A total of thirteen patients were born to SARS-CoV-2 positive mothers. These were analyzed as a subgroup, and troponin-I levels were elevated compared to the remaining 119 subjects (p< 0.001). There were no differences in troponin-I between the other subgroups.
Conclusion(s):
This study helps establish normative data for cardiac troponin-I levels in healthy term newborns. There were no statistically significant differences in troponin-I levels between mode of delivery, delivery resuscitation, or maternal diabetes status. Troponin-I levels in neonates born to SARS-CoV-2 positive mothers were elevated compared to those born to mothers negative for infection. Larger scale studies are warranted to further understand the clinical implications of cardiac troponin-I in neonates born to mothers with SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy.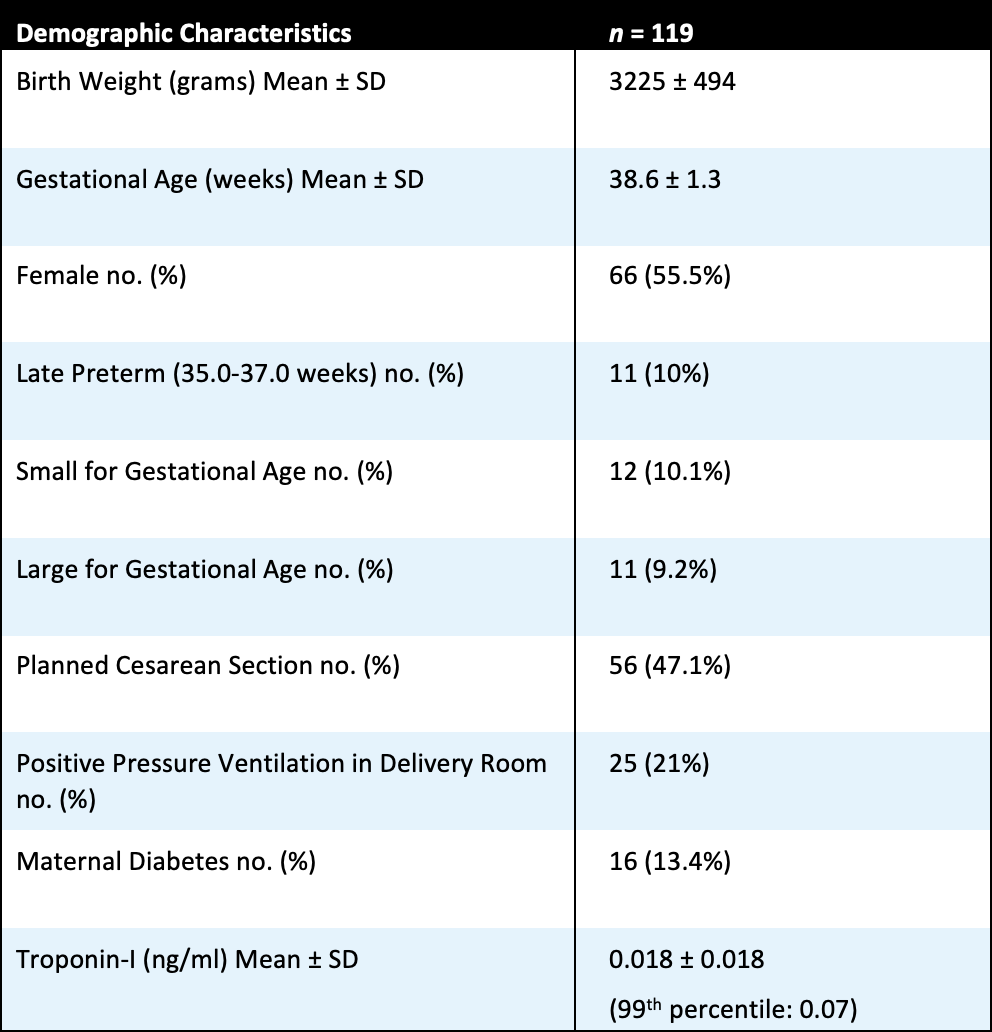
.png)
