General Pediatrics: Primary Care/Prevention
General Pediatrics 1
108 - Improving Plagiocephaly Anticipatory Guidance in the Pediatric Primary Care Clinic
Publication Number: 108.114
- JF
Jairus Adrian R. Flores, MD (he/him/his)
PGY2
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
Jackson Heights, New York, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background:
Positional plagiocephaly is defined by the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) as the flattening of a baby's growing skull due to mechanical factors. After the Back to Sleep campaign, a 2013 study showed a rise of positional plagiocephaly to 46.6%. Providing parents with early Anticipatory Guidance (AG) about plagiocephaly can help prevent the development and progression of positional plagiocephaly and avoid unnecessary referrals.
Objective:
The aim of this study is to increase Plagiocephaly AG to 50% in all infants presenting for their initial newborn visit through the 6-month Health Maintenance Visit (HMV) in Monday Pediatric Continuity Clinic within 4 months.
Design/Methods:
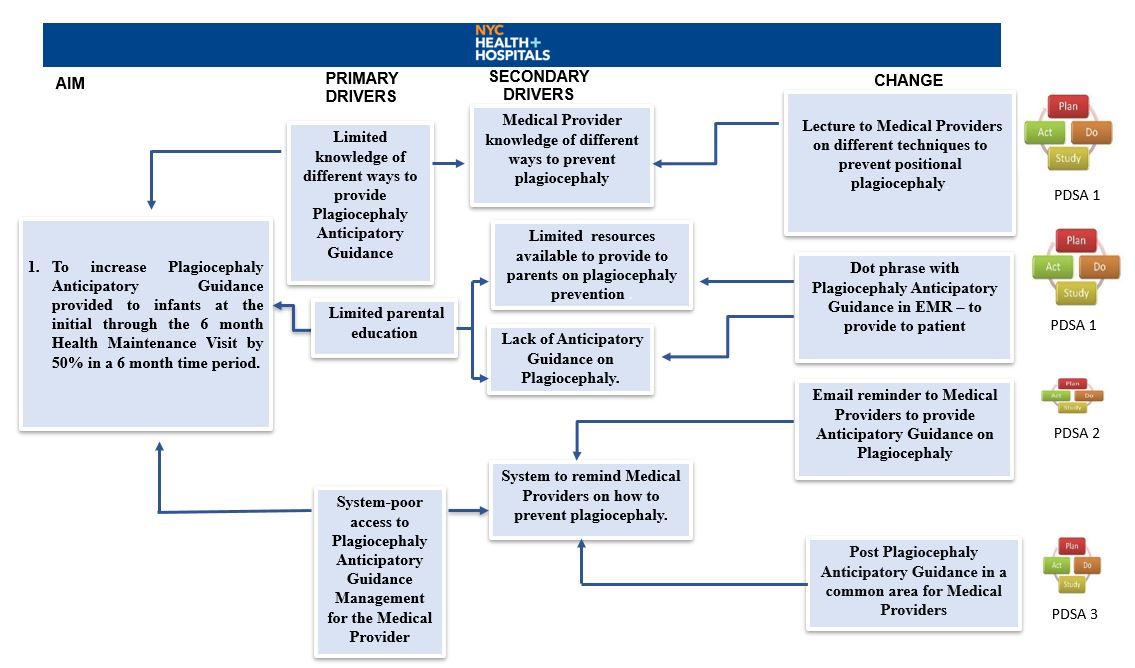
We used the IHI Model of improvement consisting of an Aim statement, measures and PDSA cycles. Baseline data on Plagiocephaly AG provided to infants at their initial through 6-month HMV was collected from May to August 2022. Charts were reviewed during the study period of September to December 2022. 3 PDSA cycles (fig 1) were conducted with Outcome measure: percent of infants at the initial newborn visit to the 6-month HMV given Plagiocephaly AG. Process Measure: use of a dot phrase for AG and the Balancing Measure: referral to specialists.
In PDSA 1, a lecture was given to providers and a patient educational hand out (fig 2) was created in our EMR and were made available in 4 languages. PDSA cycle 2 involved email reminders to providers and PDSA cycle 3 included posting the educational hand out in a common area for the providers as a visual reminder.
Results:
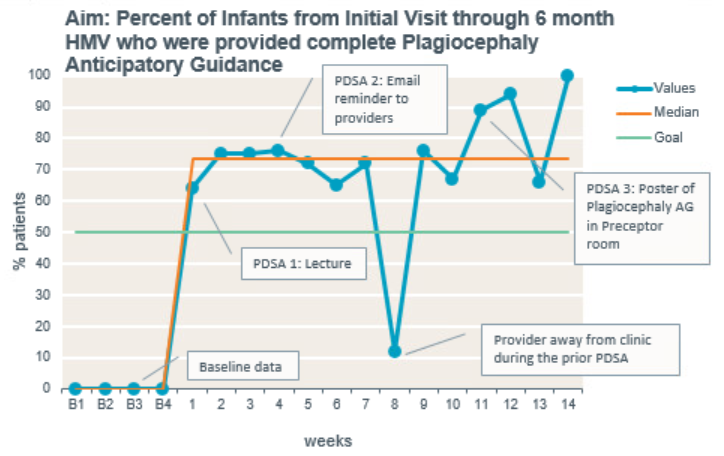
Baseline data showed there were 2/50 (4%) patients between newborn and 6 months with plagiocephaly. 8/50 (16%) were given no plagiocephaly AG and the remaining with partial AG (tummy time only). 2 (4%) were referred to specialists at the 6-month visit and none were prescribed helmets. 303 patients were seen during the study period. After the completion of 3 PDSA cycles (fig 3), a total of 69% (209) patients received complete AG on plagiocephaly. Most data points were above our goal, no shifts or trends seen. 6 (2%) patients were diagnosed with plagiocephaly, showing a decreased incidence of positional plagiocephaly compared to baseline. None of them were referred to specialists or prescribed helmets.
Conclusion(s):
Through our Quality Improvement project aimed at increasing Plagiocephaly AG we were able to improve patient education to infants presenting for their initial newborn visit through the 6-month HMV. We also noted a decrease in the diagnosis of plagiocephaly and number of referrals to specialists. Providing detailed plagiocephaly AG should be emphasized early.