Neonatal Quality Improvement
Neonatal Quality Improvement 2
660 - Evolving Neonatal Resuscitation Programs and Its Association with Neonatal Mortality Rate Improvement in Periviable Infants: a Population Data in Taiwan.
Publication Number: 660.139
- WC
WEIYING CHU, MD
Fellow
National Cheng Kung University Hospital
Tainan, Tainan, Taiwan (Republic of China)
Presenting Author(s)
Background:
Neonatal resuscitation program (NRP) has been developed for newborn care for decades and received regular updates every 5 years. NRP provides better survival outcomes for newborns. However, studies on the impact of updating NRP protocols on neonatal mortality (NM, deaths during the first 28 days of age) of periviable infants (PIs) are limited. PIs born at 22–25 weeks gestational age (wGA) have high NM rate and some studies have reported improved survival after the threshold of viability update from 24 wGA to 22 wGA in NRP 7th version (ver.) in 2015. Large scale population data is still lacking. We aim to investigate the improvement of NM rate in PIs after the three recent NRP revisions in a nation-wide study.
Objective:
To analyze the trend of NM rates of PIs under different NRP versions/epochs.
Design/Methods:
This retrospective study used Premature Baby Foundation of Taiwan population database from 2001 to 2019 with IRB approval. We enrolled PIs born at 22–25 wGA. Demographic data within 28 days of life (DOL) were collected, including GA, birth body weight (BW), sex, fifth-minute Apgar score, pH of blood gas at admission, antenatal steroid treatment, respiratory distress syndrome requiring surfactant therapy, and mortality status at 28th DOL. Records with missing essential data were excluded.
Epochs were defined by the time periods using each published NRP version (ver.): I (2001–2005, 4thver.), II (2006–2010, 5th ver.), III (2011-2015, 6th ver.), and IV (2016–2019, 7th ver.). The primary outcome was the NM rate in each epoch, and the mortality rates were further sub-decided into the 3rd, 7th, 14th and 28th DOL. The secondary outcome is the neonatal mortality under each of the GA groups, including 22, 23, 24, and 25 wGA. Clinical covariates of NM were analyzed for each epoch changes with multi-regression analysis.
Results:
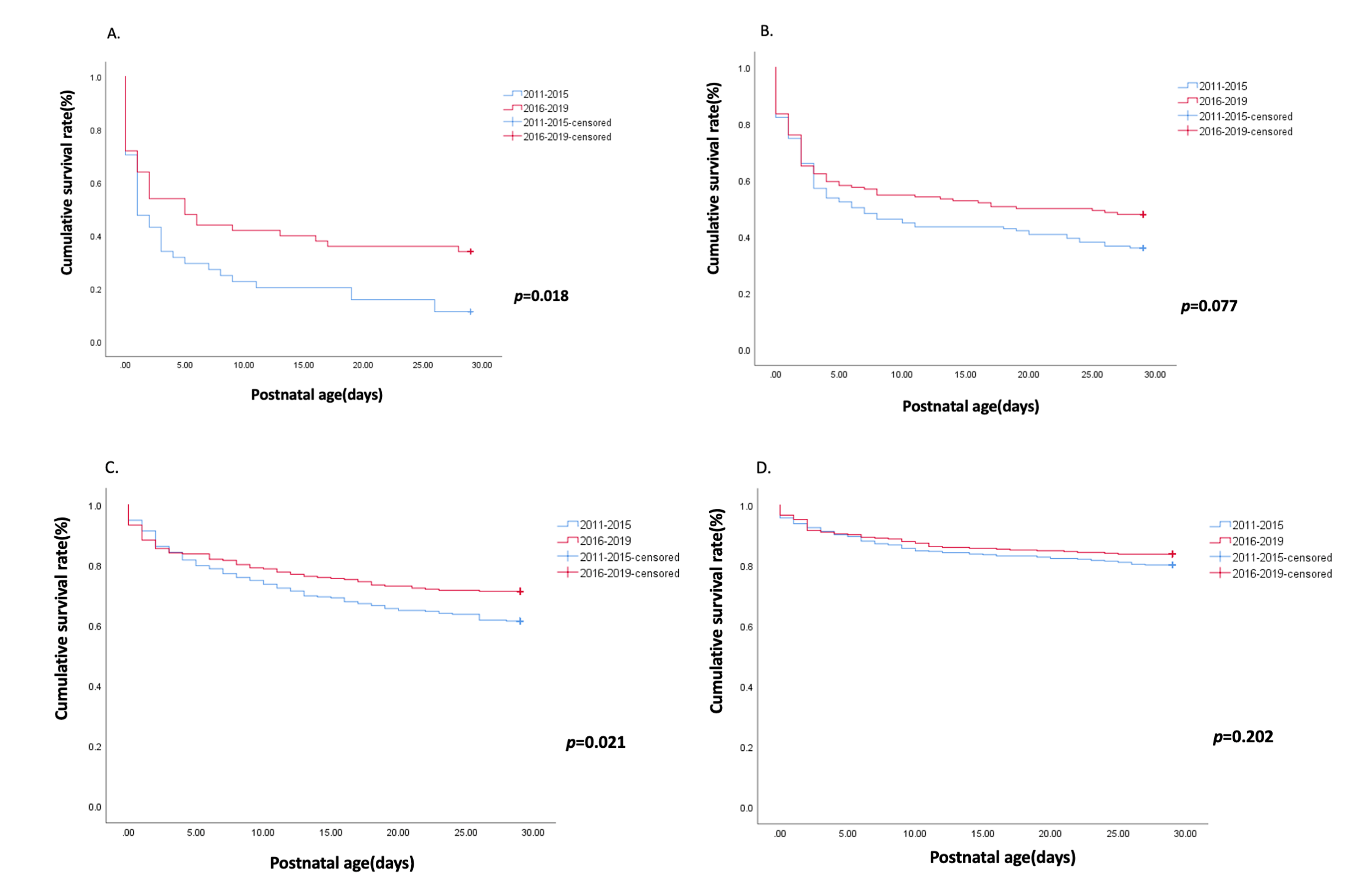
A total of 3125 PIs were enrolled and the demographic data in each epochs were listed (Table 1). Of the 4 defined epochs, Epoch IV which used the NRP 7th ver. had the lowest NM rate by 28th DOL (Figure 1). Compared to infants in Epoch III, lower mortalities were observed for Epoch IV infants with 22 wGA (p=0.018), 23 wGA (p=0.077) and 24 wGA (p=0.021) (Figure 2). In multivariate analysis, infants with 22-23 wGA born in Epoch IV had lower odds ratio(0.697) in NM (95% confidence interval 0.344–0.840, p =0.006) than infants born in Epoch III after adjusting sex, gestational age, antenatal steroid use, treated respiratory distress syndrome, and blood gas pH at admission.
Conclusion(s):
Evolving NRP protocols may be associated with improved NM rate in PIs with 22–23 wGA in Taiwan.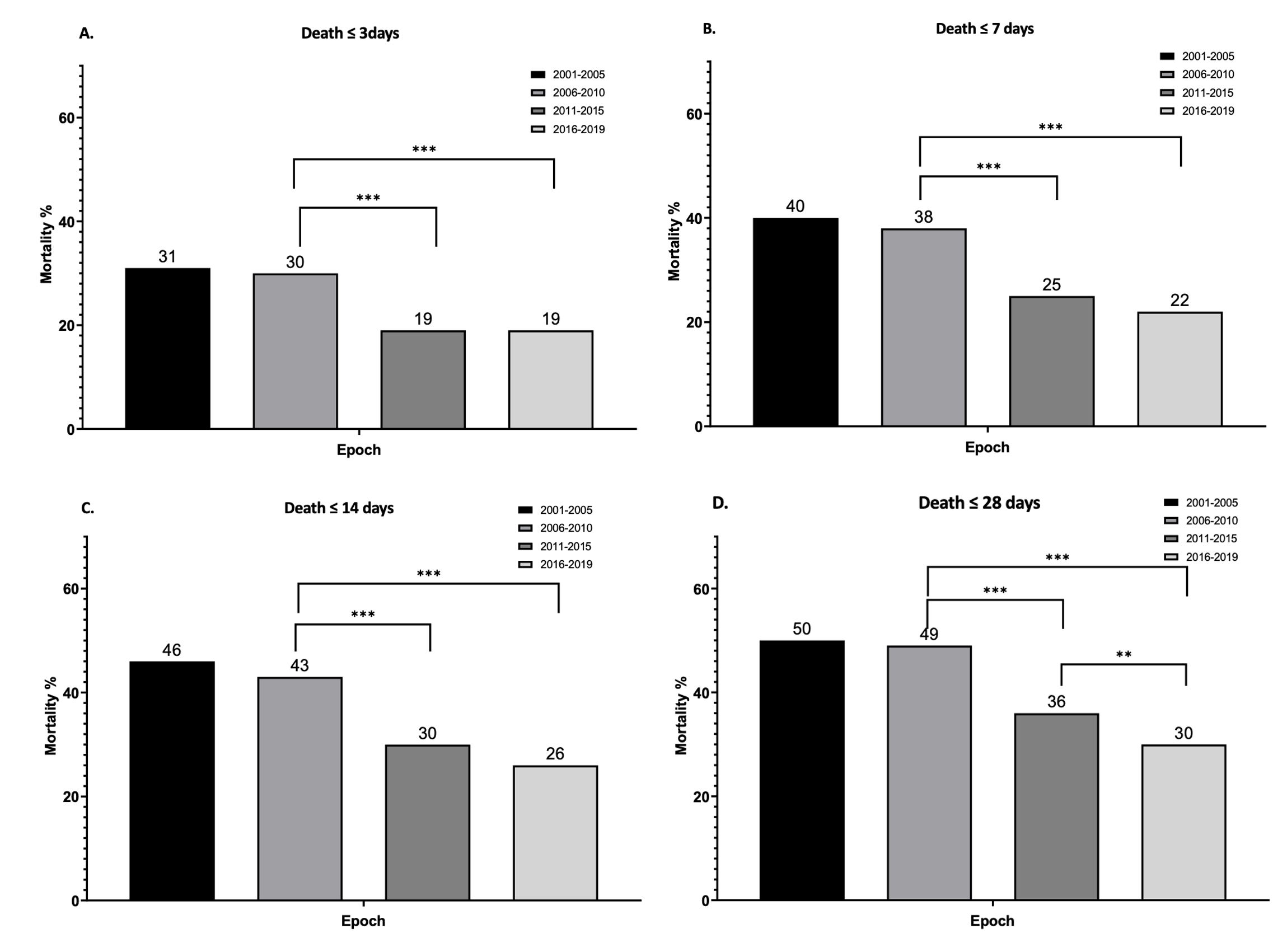
.png)
