Neonatal Quality Improvement
Neonatal Quality Improvement 1
643 - Adherence to guidelines for the use of rapid sequence during neonatal intubation: A quality improvement project
Publication Number: 643.138
- TN
Tetyana H. Nesterenko, MD, MSHS (she/her/hers)
Clinical Associate Professor of Pediatrics, Neonatologist, Quality Improvement Officer
Cleveland Clinic Children's Hospital
Cleveland, Ohio, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background:
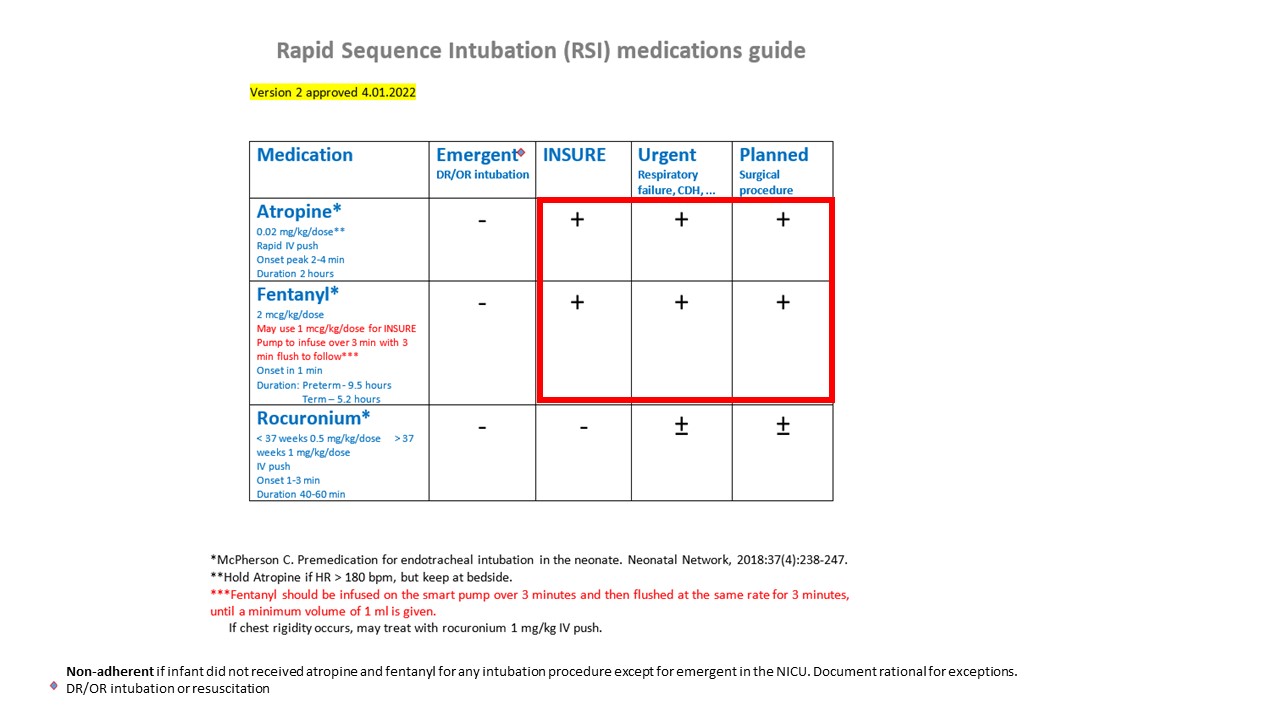
The use of atropine and fentanyl before tracheal intubation, also known as rapid sequence intubation (RSI), is associated with higher odds of successful intubation on the first attempt. At Cleveland Clinic Children’s Hospital, a quality improvement project for the implementation of a modified RSI medication guideline was started in December 2020. Evaluation during the first PDSA cycle, 6 month-period, revealed low adherence to RSI guideline. It was deemed essential to develop processes and structures to assist our caregivers with improving adherence to the RSI medication guideline and further customize it to better serve our patients and improve overall intubation outcomes.
Objective:
The aim of the project was to increase adherence to RSI medications guideline from 17% to > 80% by the end of 2022 in neonates who require non-emergency intubation.
Design/Methods:
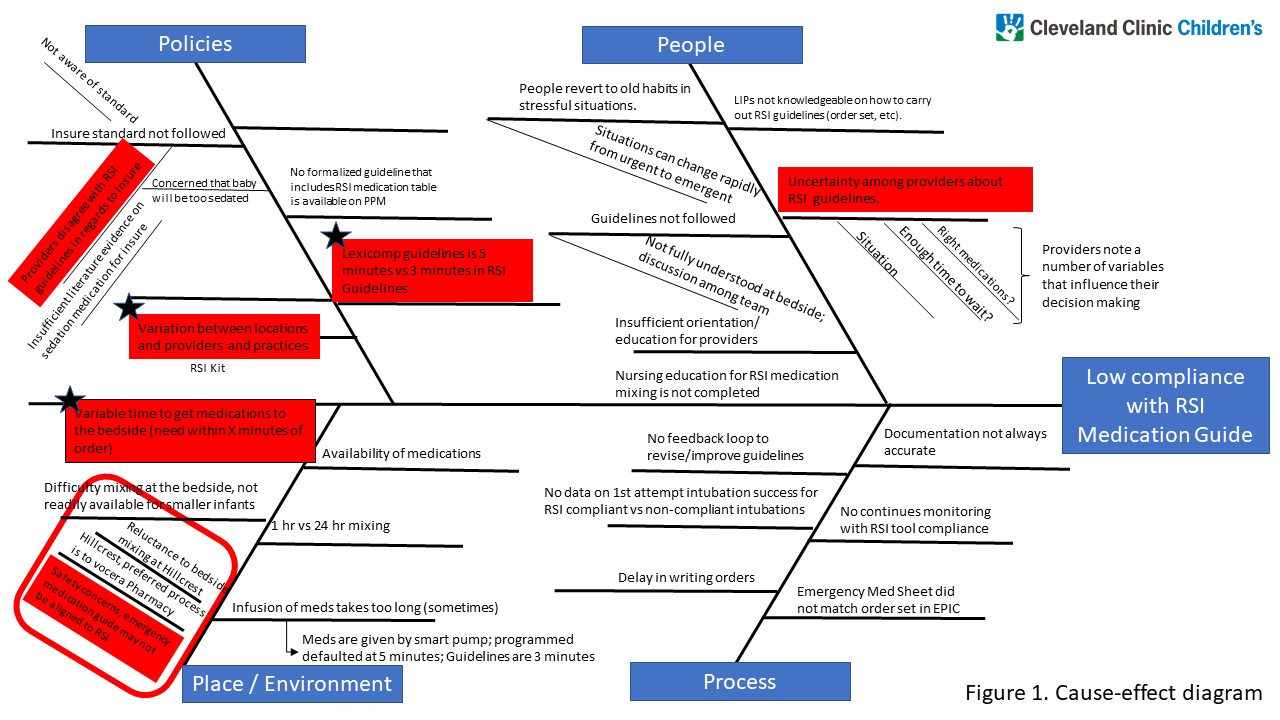
Our approach centered on the model for improvement methodology. Initial RSI medication guideline was developed based on literature review and expert consensus. Baseline data on adherence to guideline was collected from all non-delivery room intubations. Next, cause-effect analysis was undergone in the form of a fishbone diagram, which identified targeted areas for improvement including policy and environmental factors (Figure 1). This projects included 3 PDSA cycles: PDSA cycle 1- where qualified caregivers received formal education on the importance of RSI; PDSA cycle 2- where electronic order set for guidelines of RSI medication was introduced; and PDA cycle 3- non-adherent intubation events were reviewed and presented as safety stories during department staff meetings biweekly. A behavioral chart (p-chart) for the average RSI adherence rate was presented to all staff monthly.
Results:
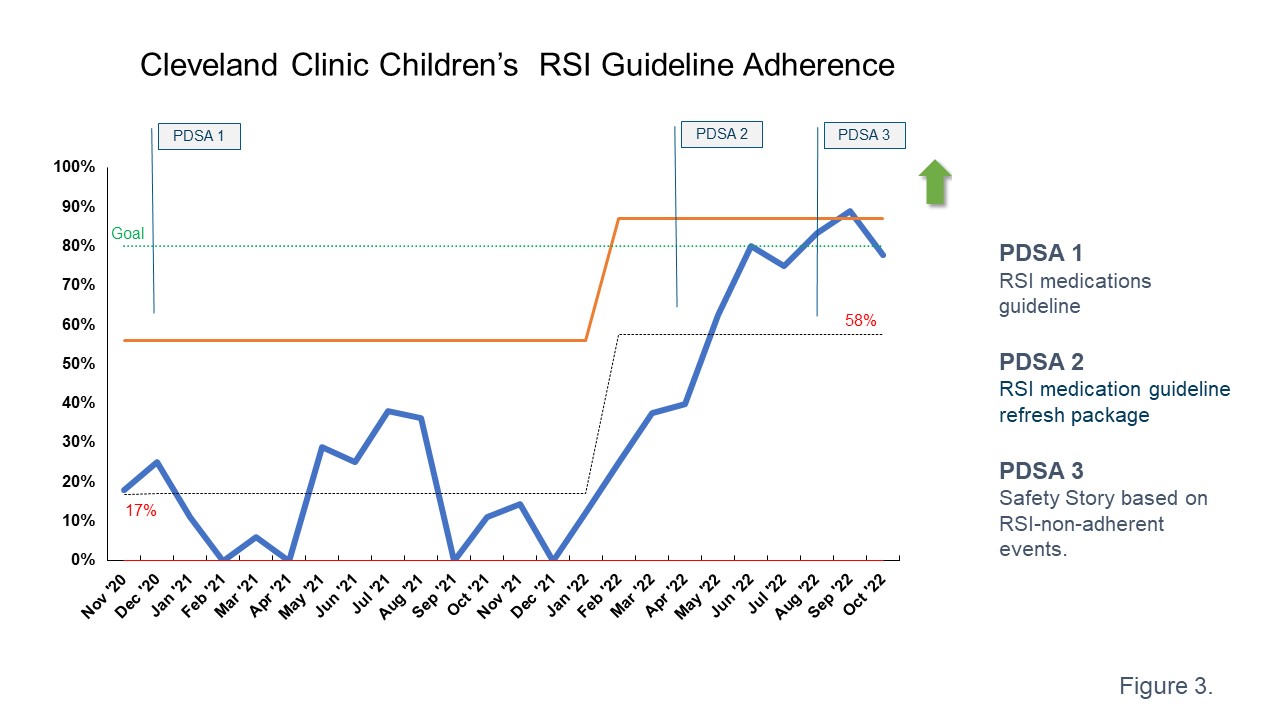
Analysis of the baseline data from November 2020 to July 2021 demonstrated adherence to the recommended pre-medications to be 17%.The survey on revised RSI medication guideline was completed by 35 out of 49 qualified caregivers (71%). Of them, 33 (94.3%) agreed with the guideline... Implementation of PDSA cycles 2 and 3 resulted in the upward shift of monthly average adherence rate from 17 to 58% with significant positive trend thereafter (Figure 3). Along with improved adherence to RSI, there was improvement in first attempt intubation success rate from 54% to 66%.
Conclusion(s):
Utilization of quality improvement methodology allows for enhancement of multidisciplinary adherence to a standardized guideline. Adherence to implemented guidelines and processes is essential in achieving high standards in patient care quality and safety.