Breastfeeding/Human Milk
Breastfeeding/Human Milk 1: Human Milk in the NICU
368 - Donor Human Milk Access and Utilization within Military Neonatal Intensive Care Units and Well Newborn Nurseries
Publication Number: 368.101

La'Toya I. James-Davis, MD (she/her/hers)
Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine Fellow
Brooke Army Medical Center
Fort Sam Houston, Texas, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background:
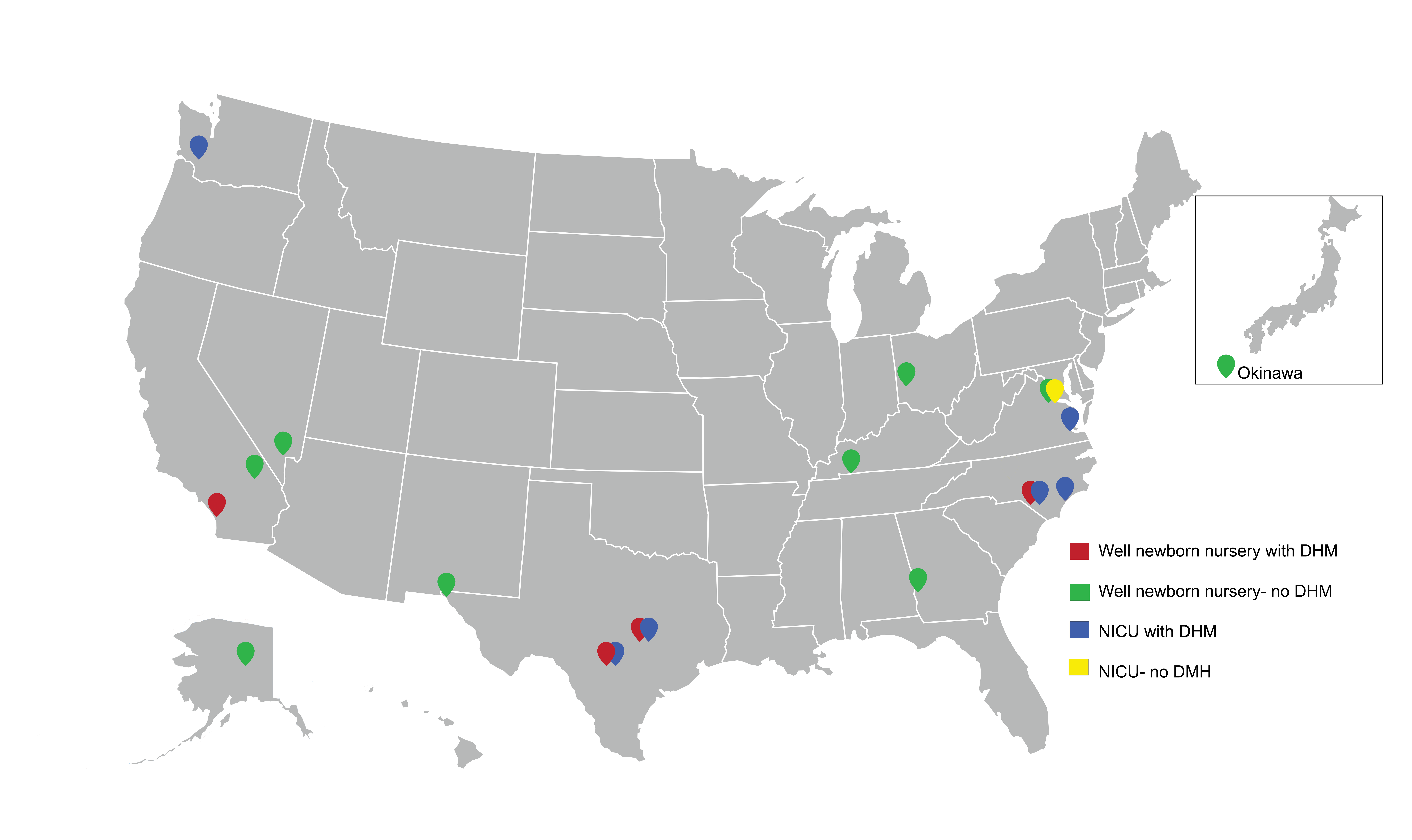
Donor human milk (DHM) use is increasing within well newborn nurseries and neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) across the U.S. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends use of DHM for high-risk infants (birth weight less than 1500 grams, premature infants and those with intestinal diseases), but recently expanded the recommendation for use in late preterm and early term infants if DHM is available. At present, there are 28 Human Milk Banking Association of North America milk banks across the U.S. Given differences in regional availability and access, as well as funding and insurance reimbursement, there are likely practice variations in the use of DHM. Military beneficiaries benefit from a no-cost universal health care system that provides services to support breastfeeding. Examination of DHM practices within the military health system offers a unique perspective on regional variability.
Objective:
Describe DHM practices amongst military well newborn nurseries and NICUs and identify potential disparities in DHM usage.
Design/Methods:
Through an online survey, we polled military well newborn nursery and NICU medical directors on DHM availability and utilization. Medical directors were specifically surveyed regarding location of unit, criteria/policies in place for use of DHM and type of DHM available.
Results:
This survey yielded 22 responses, (36% response rate) Of the respondents, 25% of military well newborn nurseries and 85.7% of NICUs utilize DHM. All well newborn nurseries with access to DHM were associated with a NICU. Most units (75%) with access to DHM have a policy for its use. Eligibility criteria for DHM vary widely, with the majority of policies including gestational age (< 30-37 weeks), medical condition criteria (e.g., hypoglycemia, gastrointestinal disease, weight loss, etc.) or provider discretion. Few units (27.2%) have a formal policy for discontinuation of DHM. Two-thirds of all units surveyed allow DMH use in healthy term newborns. No correlation was found with baby-friendly designation and use of DHM.
Conclusion(s):
DHM access and use is not uniform across military installations. Military well newborn nurseries without an associated NICU are unlikely to have access to DHM. There are variations in practice based on criteria for use of DHM with most units reliant upon gestational age or medical condition criteria. This survey provides insight into the regional variability of DHM within the military. We suspect that within the civilian sector where there is not universal healthcare, there likely exists even greater variability in DHM access and use.