Neonatal Follow-up
NICU Follow Up and Neurodevelopment 3: Impact of the Prenatal Environment on Development and Outcomes
231 - Fungal infection and neurodevelopmental outcomes at 18-30 months in preterm infants
Publication Number: 231.143

Qi Zhou (she/her/hers)
Neonatology
Children's Hospital of Fudan University
Shanghai, Shanghai, China (People's Republic)
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Invasive fungal infection (IFI) is associated with significant mortality and morbidity among preterm infants but there has been no population-based study of long-term neurodevelopmental outcomes.
Objective:
The objective of this study was to examine population-based incidence trends as well as mortality, short term in-hospital morbidity and long-term neurodevelopmental outcomes among preterm infants with IFI, non-IFI and no infections in Canada.
Design/Methods:
We conducted a retrospective cohort study of 8408 infants born at < 29 weeks gestational age (GA), admitted to Canadian Neonatal Network neonatal intensive care units (NICU) from April 2009 to Dec 2017, and followed up at 18-30 months corrected age (CA) in Canadian Neonatal Follow-Up Network clinics. We compared mortality, long term neurodevelopmental outcomes and short term in-hospital morbidity among 3 groups of infants (IFI, non-IFI, and no infections).
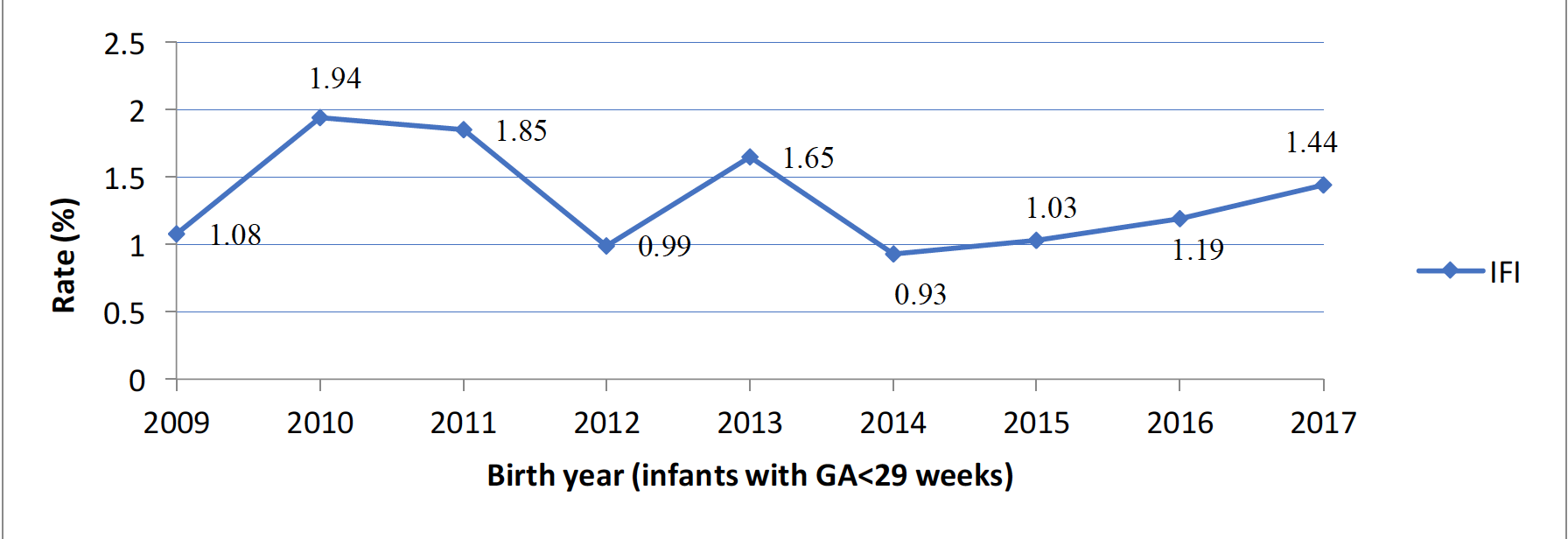
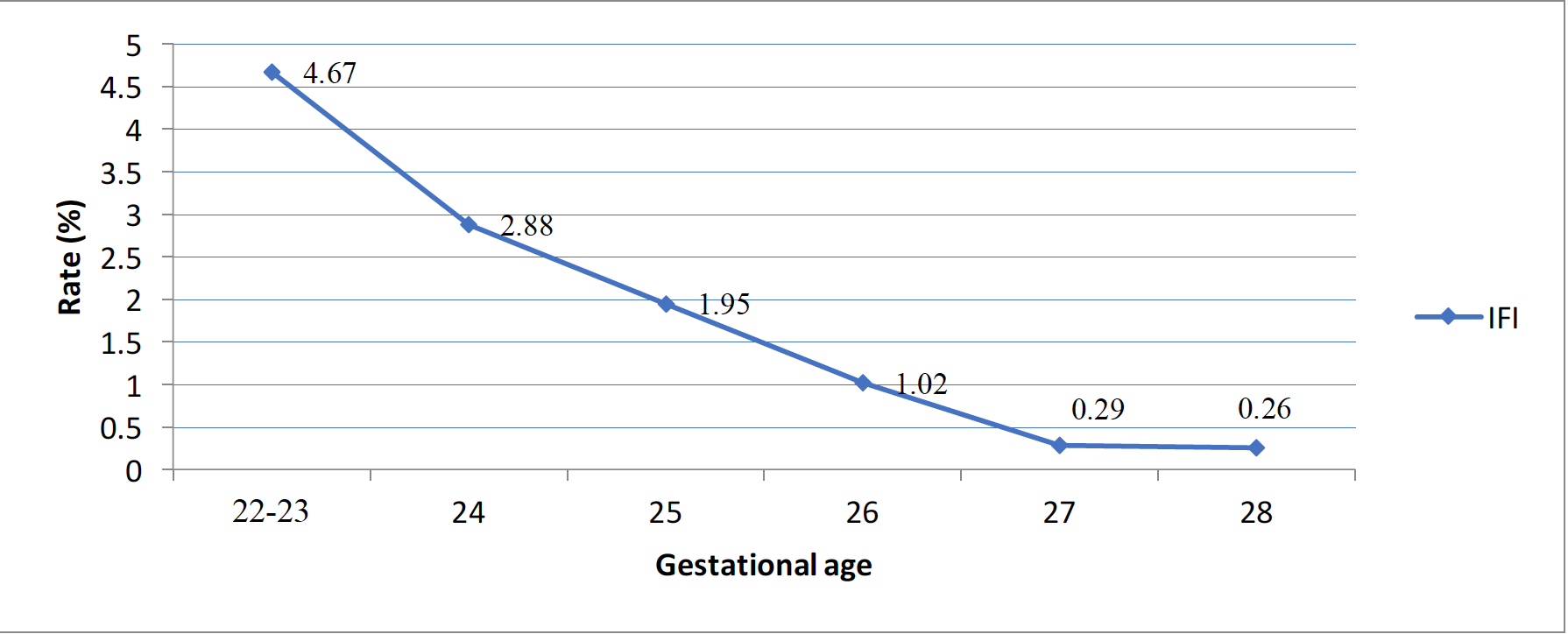
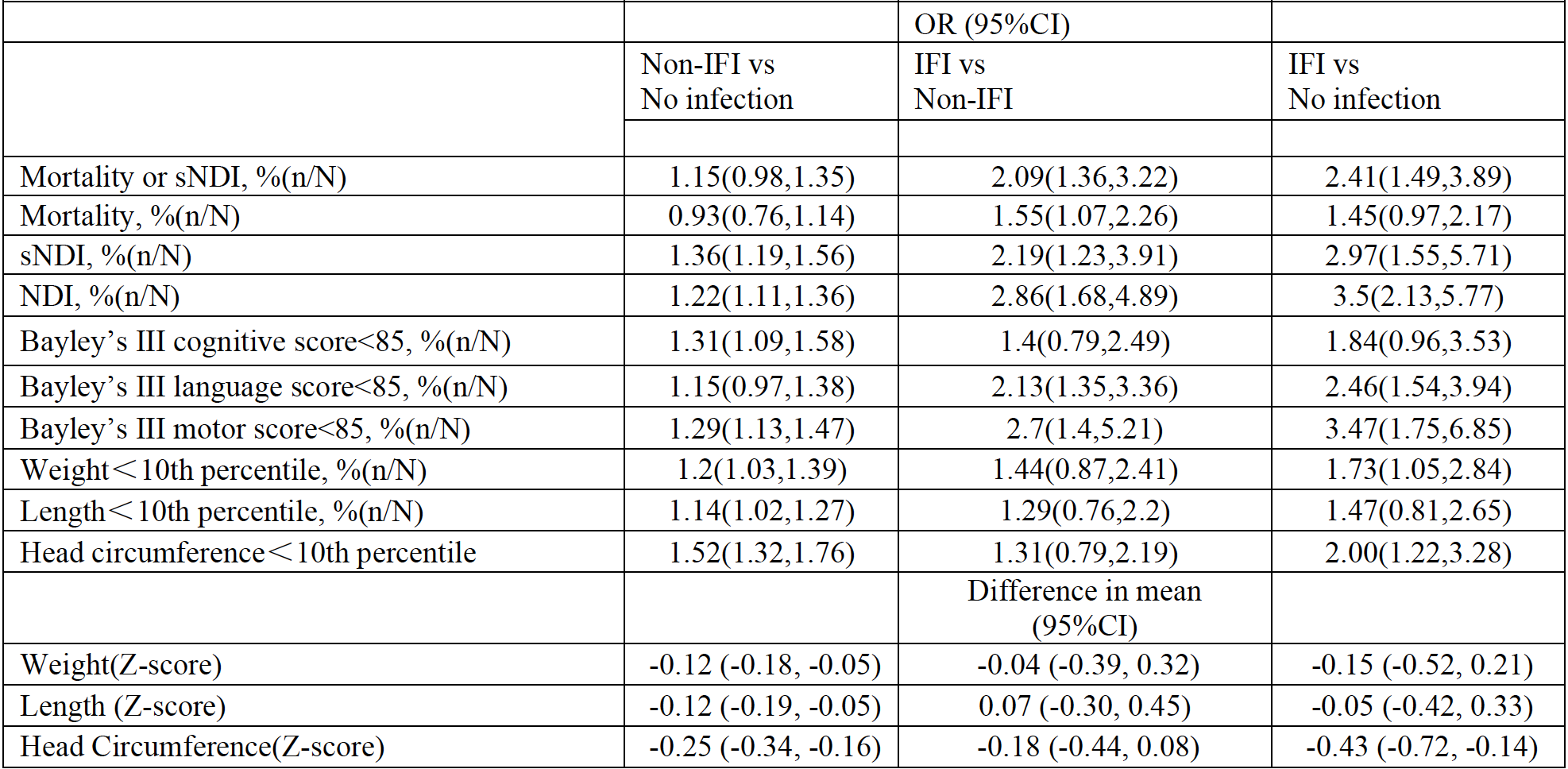
Results: The incidence of IFI was 1.3%, non-IFI 26.9% and no infections 71.7%. IFI incidence varied between 0.93-1.94% across the study period with no significant trend over time. Infants of higher gestational age were significantly (p< 0.01) less likely to have IFI. Among infants with no infection, non-IFI and IFI, the incidence of the significant neurodevelopmental impairment (sNDI) was 14.84%, 21.63% and 44.26% respectively, while mortality was 22.25%, 25.35% and 50% respectively. Even after risk adjustment for confounders (GA, Score for Neonatal Acute Physiology Version II, ruptured membranes >24 hours, maternal antibiotic treatment, antenatal steroid use, cesarean section), infants with IFI had significantly higher odds of sNDI than non-IFI (aOR 2.19; 95%CI1.23,3.91) or no infections (aOR 2.97; 95% CI 1.55,5.71).
Conclusion(s):
Preterm infants with invasive fungal infections have significantly higher incidence of mortality and adverse neurodevelopmental outcomes than those with non-invasive fungal infections and no infections.