Neonatal General
Neonatal General 2
275 - The Relationship Between Hip Ultrasound Result and the Diagnosis of Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip in Premature Infants
Publication Number: 275.131

Ahmed Osman, MD
Assistant professor of Pediatrics/ Attending Neonatologist
The Ohio State University/Nationwide Children's Hospital
Columbus, Ohio, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Screening hip ultrasound (HUS) for Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH) is frequently done in premature infants after breech birth presentation. HUS is also performed following clinical concern for DDH.
Objective: The study objective was to evaluate the relationship between the first HUS result and DDH diagnosis in premature infants. Additionally, we report the type of treatment (observation, Pavlik harness or surgical interventions) for premature infants diagnosed with DDH.
Design/Methods:
This is a retrospective chart review of infants born between 01/01/2009 and 12/31/2018 at < 37 weeks of gestation who had HUS in the first year of life. The following data were manually extracted: Patient characteristics, the indications and results of HUSs, the DDH diagnosis made by an orthopedic surgeon up to 2 years of age, and treatments for patients with DDH. Positive predictive value and negative predictive value for abnormal, equivalent and normal HUS results were calculated.
Results:
From 2,397 infants analyzed, 51% were females. Seventy-three infants (3%) were diagnosed with DDH. The mean gestational age for patients with DDH diagnosis was 33 weeks, while it was 31.5 weeks for those without. The majority (89%) of patients had normal HUS, with only 0.3% later diagnosed with DDH. From the 8% with equivocal results, 10% had subsequent DDH diagnosis. Table 1 presents the counts of first HUS results and DDH diagnosis, and the predictive values of the results.
The majority (56%) of patients diagnosed with DDH were treated with Pavlik harness. Surgical correction was performed in 35% of patients. Table 2 shows the distribution of interventions (surgical, Pavlik harness or no intervention) for patients with DDH.
Conclusion(s): A normal first HUS result in premature infants has an excellent negative predictive value for the diagnosis of DDH. Abnormal first HUS has a good positive predictive value. A significant number had an equivocal result and need close follow up. Most premature infants with DDH are successfully treated non-surgically.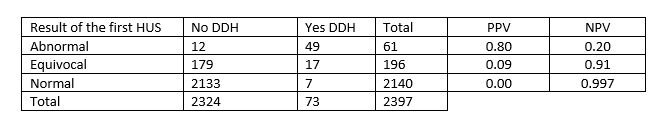
.png)
