Neonatal Quality Improvement
Neonatal Quality Improvement 3
723 - Multi-disciplinary Quality Improvement Initiative To Increase Skin-to-skin care Duration In Preterm Neonates
Publication Number: 723.342

Palanikumar Balasundaram, MD (he/him/his)
Fellow, Neonatal Perinatal medicine
The Children's Hospital at Montefiore
Bronx, New York, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background:
Skin-to-skin (STS) care is given by holding an infant with ventral skin-to-skin contact, typically upright on the parent's chest. STS is highly effective in improving neonatal outcomes, particularly among preterm neonates in the first month of life. STS care strongly correlates with better sleep organization, advanced maturation of thermoregulation, better neurobehavioral performance, increased maternal milk production, and enhanced parent-child bonding. Even in units where STS care is routinely practiced, the number of STS hours remains low for preterm in the first four weeks of life, mainly when they are sick.
Objective:
We aim to increase the duration of STS care during the first four weeks of life from a baseline of 12.8 minutes per eligible patient day to 30 minutes per eligible patient day for neonates born less than 35 weeks gestation admitted to the Montefiore Weiler NICU from June 2021 to October 2022.
Design/Methods:
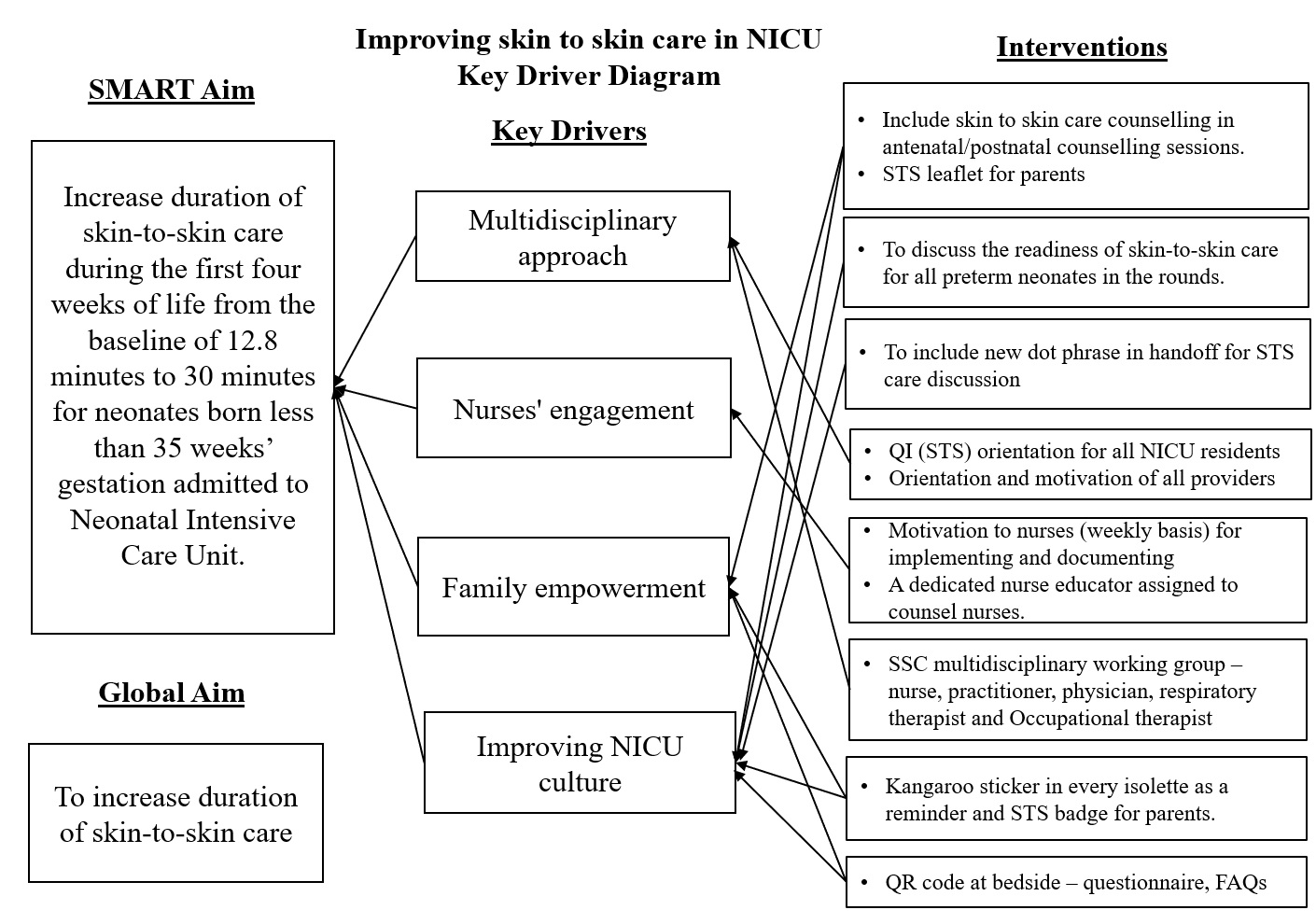
Baseline data collection was performed, and a staff survey was conducted to determine attitudes and knowledge of STS care. A Key Driver Diagram (Figure 1) was created to identify interventions to be tested using multiple “Plan, Do, Study, Act” (PDSA) cycles. The primary outcome measure is the mean duration of STS per eligible patient day. Process measures include documentation of eligibility for STS care in EMR. Balancing measures include adverse events such as apnea, bradycardia, desaturation, hypothermia, and inadvertent dislodgement of central lines and endotracheal tube. Run charts and statistical process control charts were created using QI Macros for Excel.
Results:
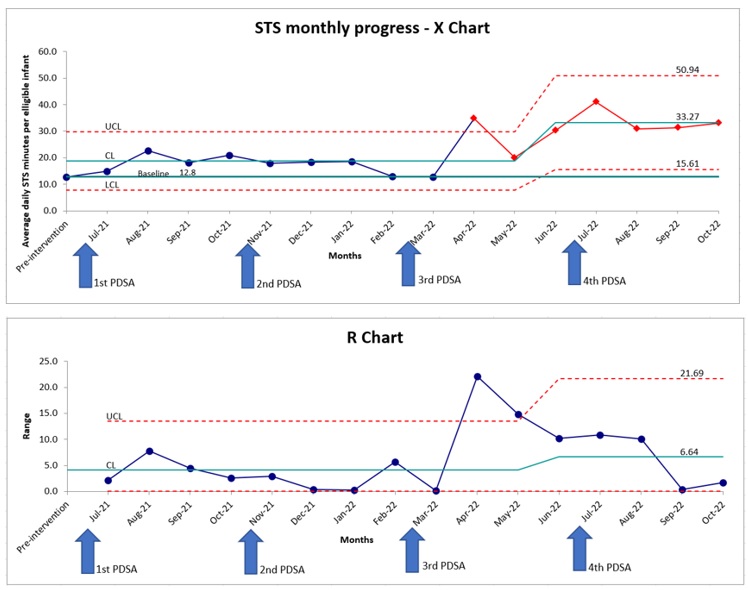
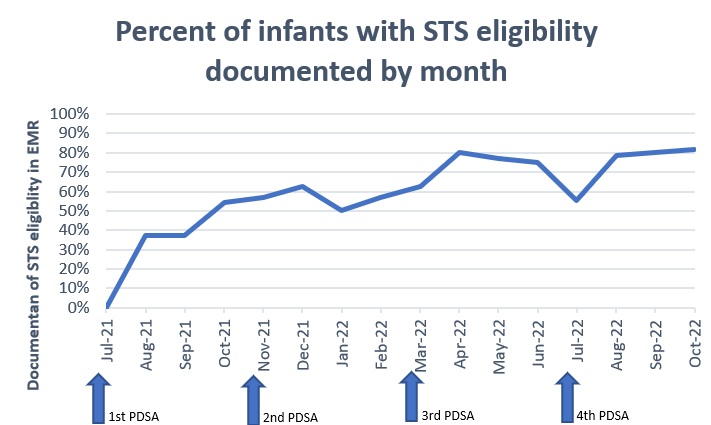
We included 154 eligible infants with a mean Gestational age of 29.1 weeks and a mean birth weight of 1000 grams. The mean STS duration per eligible patient day increased from a baseline of 12.8 minutes to 33.2 minutes (Figure 2). The median age at first STS care has improved from 13 to 8 days. Documentation of eligibility has increased from 0% to 81.8% (Figure 3). Adverse events reported were occasional apnea, bradycardia, and desaturations, but there were no episodes of hypothermia and no dislodged technology documented.
Conclusion(s):
The QI interventions we implemented have increased the duration of STS in preterm neonates. Provider education, motivation of bedside nurses, parental counseling, and the STS package (STS leaflets for parents, Kangaroo sticker, QR code for FAQs, and satisfaction survey) will be continued to sustain improvement.