Injury Prevention
Injury Prevention 1
143 - The Injury Equity Matrix: An Innovative Working Tool to Address Injury Inequities
Publication Number: 143.121
- SK
Sadiqa Kendi, MD, MPH (she/her/hers)
Associate Professor
Boston Medical Center
Boston, Massachusetts, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background:
Injuries are the number one cause of death in children and young adults between 1 and 44 years of age. The prevalence of some injuries have reduced over time, however there has been an uptick in three of the most prevalent injury mechanisms, including MVCs, drowning and firearm injuries. In addition, inequities in injury outcomes have persisted and in some cases worsened over the past decade despite years of data documenting inequities. We have created a framework to outline the complex multifactorial contributors to injury inequities. The Injury Equity Framework displays the relationship of various factors to each other, and how those factors build on each other to lead to inequities. We recognized through a review of the evidence how much crossover there is amongst factors that lead to injury inequities regardless of intent or specific injury.
Objective: Our goal was to develop a companion working tool to the Injury Equity Framework for use by teams to assist with the development of equity focused recommendations to address injury inequities, and the translation of those recommendations to concrete actionable next steps.
Design/Methods: Using implementation science methods, we developed and optimized a tool to meet the objectives listed. Feedback on the tool was collected from the team conducting the review as well as the research team. Six reviews were conducted total, and updates to the Injury Equity Matrix were made after each review. The tool was updated through several iterations based on the feedback collected.
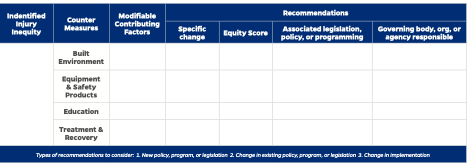
Results: We have developed two companion working tools to the Injury Equity Framework. The first is the Injury Equity Matrix for Modifiable Factors, used to assist in the identification of modifiable factors which impact injury inequities, and recommendations to address each factor. The second is the Injury Equity Matrix for Recommendation Refinement, used to refine recommendations as equity focused SMART goals with specific next steps.
Conclusion(s): We have developed the Injury Equity Matrices to address the challenge of better identifying the underlying causes of inequities, developing effective interventions, and demonstrating concrete next steps for implementation and dissemination of those interventions..png)