Breastfeeding/Human Milk
Breastfeeding/Human Milk 3: Human Milk Bioactives and Composition
26 - Longitudinal Analysis of Carotenoid Content in Preterm Human Milk
Publication Number: 26.201

Dror Mandel, MD (he/him/his)
Chief and Director of Neonatology
Dana Dwek Children's Hospital, Tel Aviv Medical Center
Tel Aviv, Tel Aviv, Israel
Presenting Author(s)
Background:
Accumulating evidence has shown that carotenoids are important for visual and cognitive development in infants. Carotenoids cannot be synthesized by humans and must be supplied by human milk (HM) to the infant.
Objective:
We aimed to evaluate the carotenoid content in preterm HM between week 1 and 6 post-partum.
Design/Methods:
In this prospective study, healthy exclusively lactating mothers of preterm infants born at gestational age 24+2 to 29+6 weeks or with birth-weight under 1500 grams were recruited along with their infants. Each participant provided up to 7 HM samples (2-10 ml) at day 0-3 and once a week until 6 weeks and a blood sample was collected from the infant at week 6 when available. Milk and plasma samples were stored frozen at -80°C, wrapped in aluminum foil to minimize light exposure, until analyzed by modified HPLC methodologies. HM concentrations of the major carotenoids, lutein, zeaxanthin, beta-carotene and lycopene, were assessed and compared with those in infant blood.
Results:
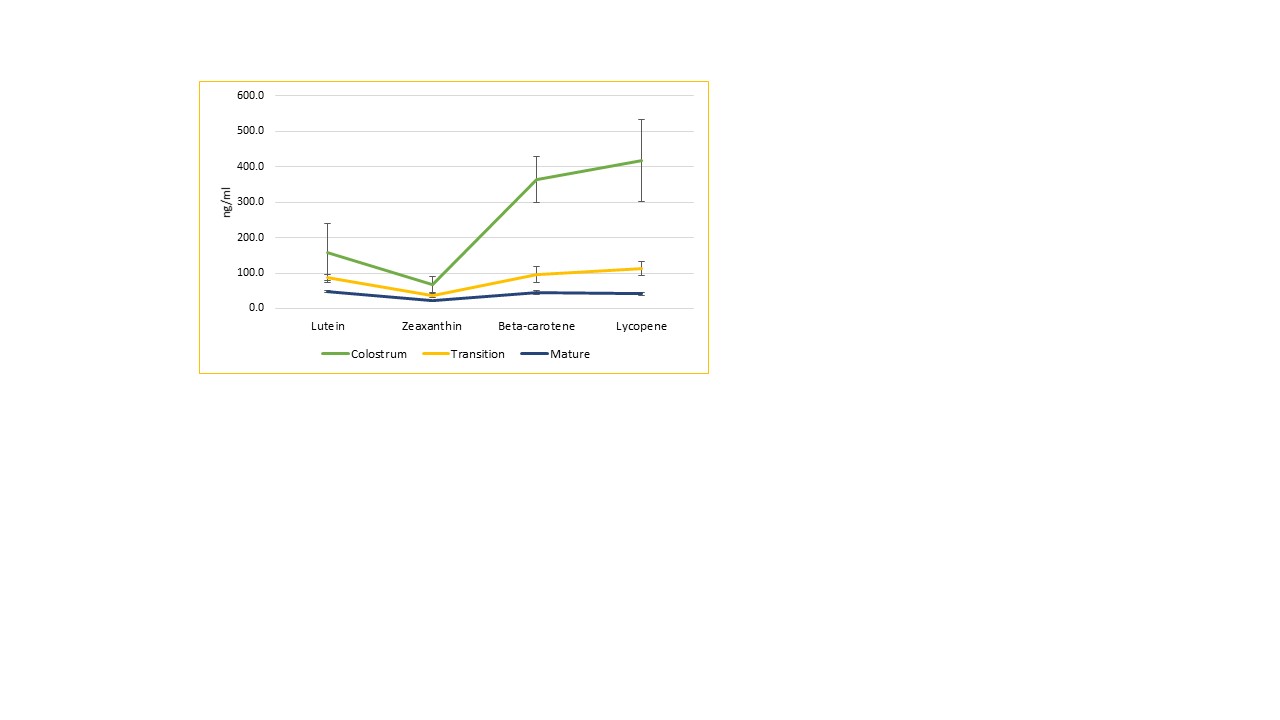
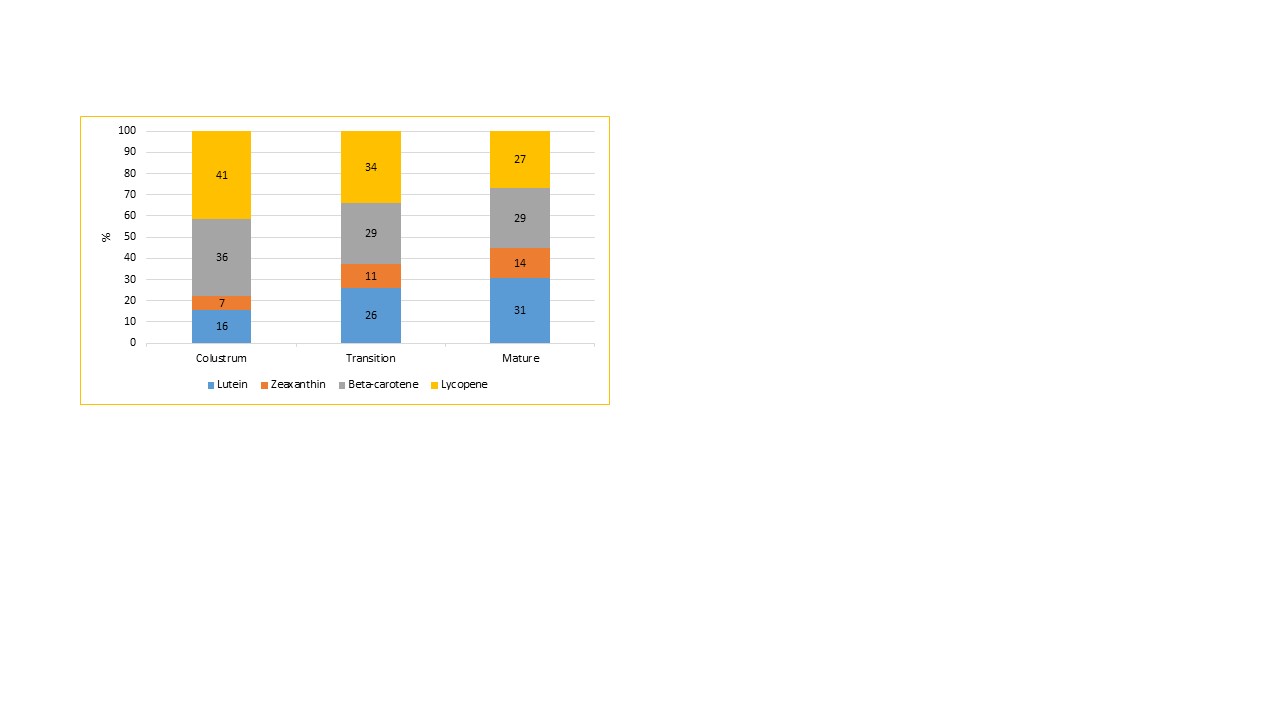
Thirty-nine mother-infant dyads were included and 184 HM samples and 22 plasma samples were collected. Lutein, zeaxanthin, beta-carotene and lycopene concentrations decreased as lactation progressed, being at their highest in colostrum, (Figure 1). HM displayed a great variability in its carotenoid content and distribution between mothers throughout lactation. Lycopene (41%) and beta-carotene (36%) were the predominant carotenoids in colostrum and up to 2 weeks post-delivery. Inversely, lutein and zeaxanthin increased with lactation to account for 45% of the carotenoids in mature HM, (Figure 2). Lutein accounted for 61% of the carotenoids in infant plasma and for only 30% in HM.
Conclusion(s):
Carotenoid content of preterm HM is dynamic and varies between mothers and as lactation progresses. Infant plasma displayed a distinct distribution of carotenoids from HM.