Neonatal GI Physiology & NEC
Neonatal GI Physiology & NEC 3: Gut Health Clinical Research
76 - Dolichocolon: a very rare congenital colonic redundancy in three infants with intermittent intestinal obstruction
Publication Number: 76.235
- LK
Loay Khateeb, MD
Pediatric Resident
Richmond University Medical Center - MG
Melissa Grageda, MD (she/her/hers)
Richmond University Medical Center
Staten Island, New York, United States
Presenting Author(s)
First Author(s)
Background: Dolichocolon is a very rare congenital redundant colonic anomaly with unknown pediatric prevalence.
Objective: We present 3 neonates with intermittent abdominal distention and obstipation secondary to dolichocolon with clinical intermittent volvulus.
Design/Methods:
Case 1: A full-term male infant presented at 2 weeks of age with abdominal distention and bilious vomiting. Upper gastrointestinal series ruled out malrotation. He improved with conservative management, but returned at 5 weeks of age with 2 weeks duration of obstipation, abdominal distention, vomiting and dehydration. Imaging studies showed dilated bowel loops, markedly redundant sigmoid colon consistent with dolichocolon. At exploration, dilated redundant sigmoid colon was resected with primary anastomosis. At 4 years of age, the child is asymptomatic and thriving well.
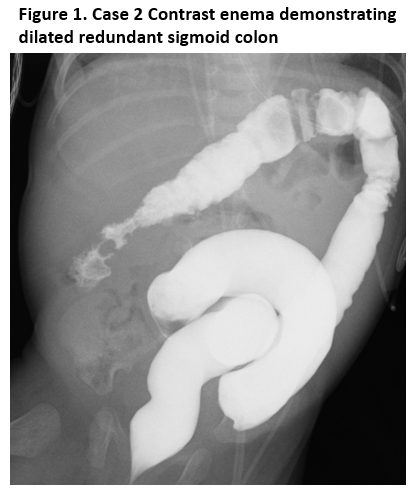
Case 2: A premature female infant (28 weeks gestation) presented with intermittent feeding difficulties since birth, with abdominal distention and dilated bowel loops on imaging, and was treated conservatively. Contrast enema at 6 weeks of age demonstrated a redundant sigmoid colon, consistent with dolichocolon. Progressive abdominal distention and dilated bowel loops raised concerns for intermittent obstruction from volvulus. At exploration, dilated redundant sigmoid colon was resected with primary anastomosis. At 2 years of age, the child is doing well.
Case 3: A preterm female (32 weeks gestation) presented with feeding difficulties during the first week of life, with intermittent abdominal distention, obstipation and nonbilious vomiting. Imaging demonstrated distended loops of bowel and redundant sigmoid colon. Dilated redundant sigmoid colon was resected at 3 weeks of age, with satisfactory post-operative course. At 1 year of age, the child is thriving well.
Results:
Dolichocolon may present in neonates with obstipation and abdominal distention. In our series, all patients had redundant sigmoid colon requiring surgical intervention.
Conclusion(s): A high index of suspicion for dolichocolon causing intermittent volvulus in otherwise healthy babies leads to expeditious diagnosis and treatment.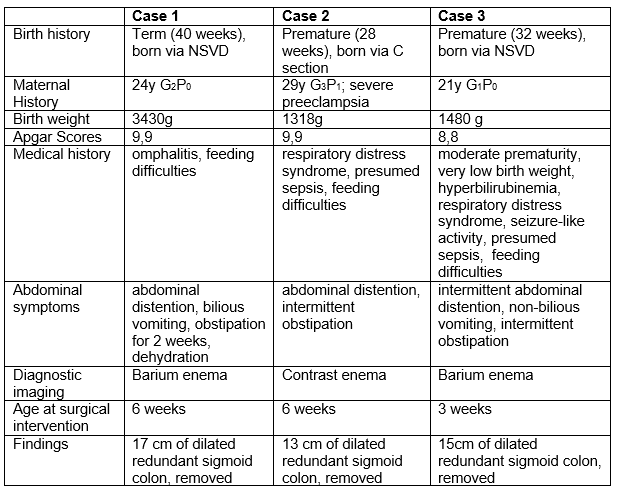
.png)
