Neonatal Nephrology/AKI
Neonatal Nephrology/AKI 1
224 - Nephrotoxic Medication Exposure in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit and Early Acute Kidney Injury: Results from the AWAKEN Study
Publication Number: 224.242
- DS
David Selewski, MD, MSCR
Associated Professor
Medical University of South Carolina
Mount Pleasant, South Carolina, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Nephrotoxic medications (NTXm) exposures and associations with acute kidney injury (AKI) in critically ill neonates remain understudied.
Objective: We aimed to describe the epidemiology of NTXm exposure and investigate associations with AKI in the first postnatal week in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) utilizing a large, multi-center cohort.
Design/Methods: In a secondary analysis of the AWAKEN cohort, NTXm receipt (acyclovir, amphotericin B, aminoglycosides (AG), piperacillin-tazobactam, vancomycin, ibuprofen, indomethacin) during the first postnatal week was recorded. NTXm exposure was quantified: no NTxm, NTXm excluding AG, AG alone, AG with another NTXm. Associations with early AKI defined by the modified neonatal KDIGO creatinine criteria were evaluated using time-varying Cox proportional hazard regression models.
Results:
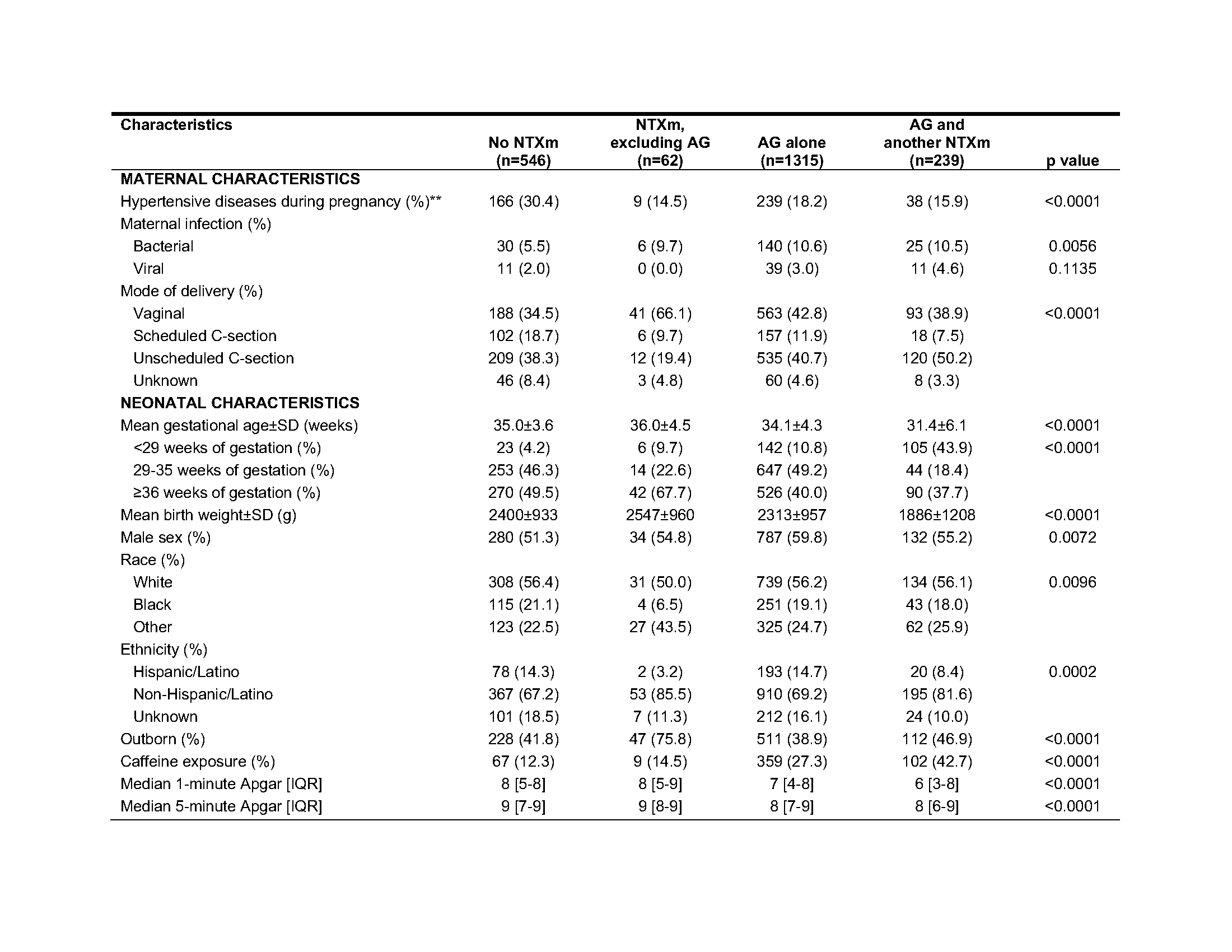
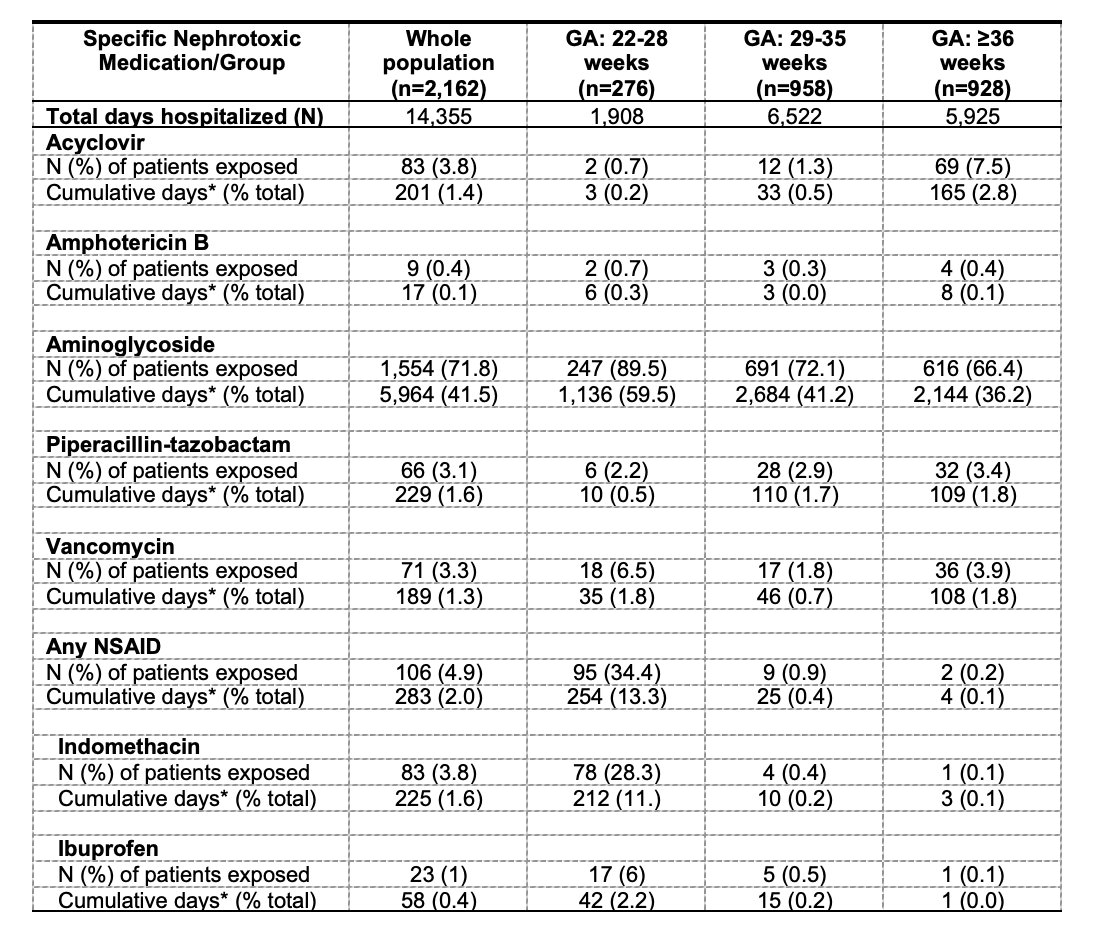
Of 2162 neonates, 75% were exposed to NTXm in the first postnatal week (no NTXm 25.3%, NTXm excluding AG 2.9%, AG alone 60.8%, AG with another NTXm 11.1%). Baseline maternal and neonatal characteristics varied by NTxm exposure group (Table 1). AG’s were the most commonly administered NTXm (72%). When examining NTXm exposure by gestational age, neonates born at 22-28 weeks of gestation were most frequently exposed to each NTXm (except acyclovir and piperacillin-tazobactam, Table 2).
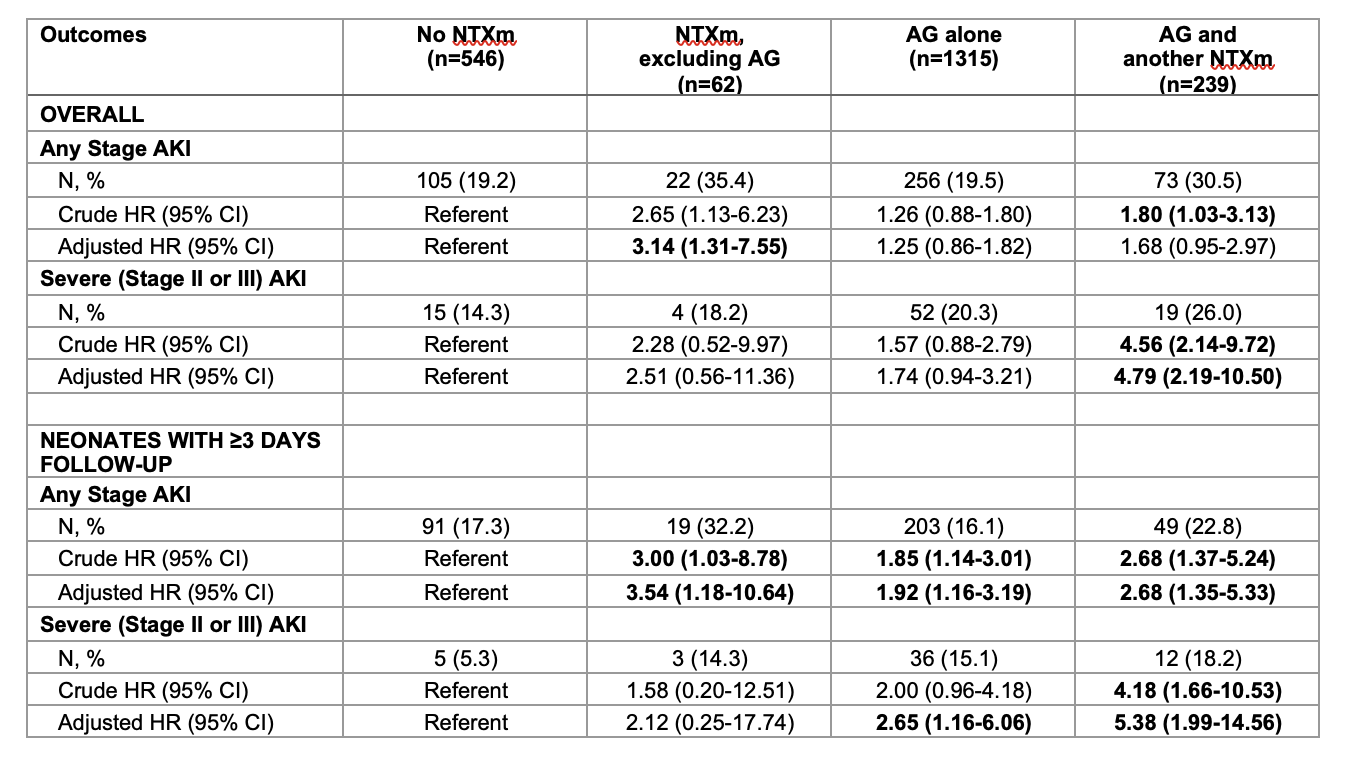
Early AKI occurred in 21% and was associated with NTXm exposure (no NTXm 19.2%, NTXm excluding AG 35.5%, AG alone 19.5%, AG with another NTXm 30.5%; p< 0.01). Stage 1 AKI (80.3%) was most common. After adjusting for confounders, NTXm excluding AG receipt was associated with increased risk of any early AKI (HR 3.14, 95% CI 1.31-7.55); AG with another NTXm receipt was associated with increased risk of severe early AKI (HR 4.79, 95% CI 2.19-10.50). In neonates with data available beyond day 3 of life, all NTXm exposure groups were independently associated with increased risk of any early AKI; AG alone and AG with another NTXm receipt were both independently associated with increased risk of severe early AKI (Table 3).
Conclusion(s):
During the first postnatal week, NTXm exposure in the NICU was frequent. AG receipt was most common. Specific NTXm exposure, principally AG with an additional NTXm, was independently associated with early AKI in critically ill neonates.