Adolescent Medicine: Substance Use
Adolescent Medicine 2
6 - Content and Persuasion Elements in Electronic Cigarette Cessation/Prevention Videos
Saturday, April 29, 2023
3:30 PM - 6:00 PM ET
Poster Number: 6
Publication Number: 6.2
Publication Number: 6.2
Jacqueline C. Sii, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, WI, United States; Reese Hyzer, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, WI, United States; Megan A. Moreno, UW Madison, Madison, WI, United States

Jacqueline C. Sii (she/her/hers)
n/a
University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health
Madison, Wisconsin, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: From 2015 to 2019, prevalence of e-cigarette use among youth and adolescents increased from 24.0% to 32.7%. Subsequently, tobacco prevention campaigns created vaping cessation/prevention videos (shown as advertisements) to deter youth from vaping. Little is known about the content of vaping cessation/prevention videos and whether there are differences across major channels.
Objective: The purpose of this study was to compare the presence of 1) content, 2) persuasion elements and 3) views of vaping cessation/prevention videos across two tobacco prevention campaigns on YouTube.
Design/Methods: In this content analysis study, vaping cessation/prevention videos were recruited from two popular tobacco prevention channels — The Real Cost and Truth — on YouTube that have published content for more than 8 years, using keywords: vape, e-cigarettes, or nicotine. Measures include a developed codebook with an inductive/deductive approach to evaluate 1) content related to people (youth and mature adults), vaping devices, video message; 2) persuasion elements (pathos, ethos, logos); and 3) video views. Analyses included chi-square and t-tests to evaluate differences between channels.
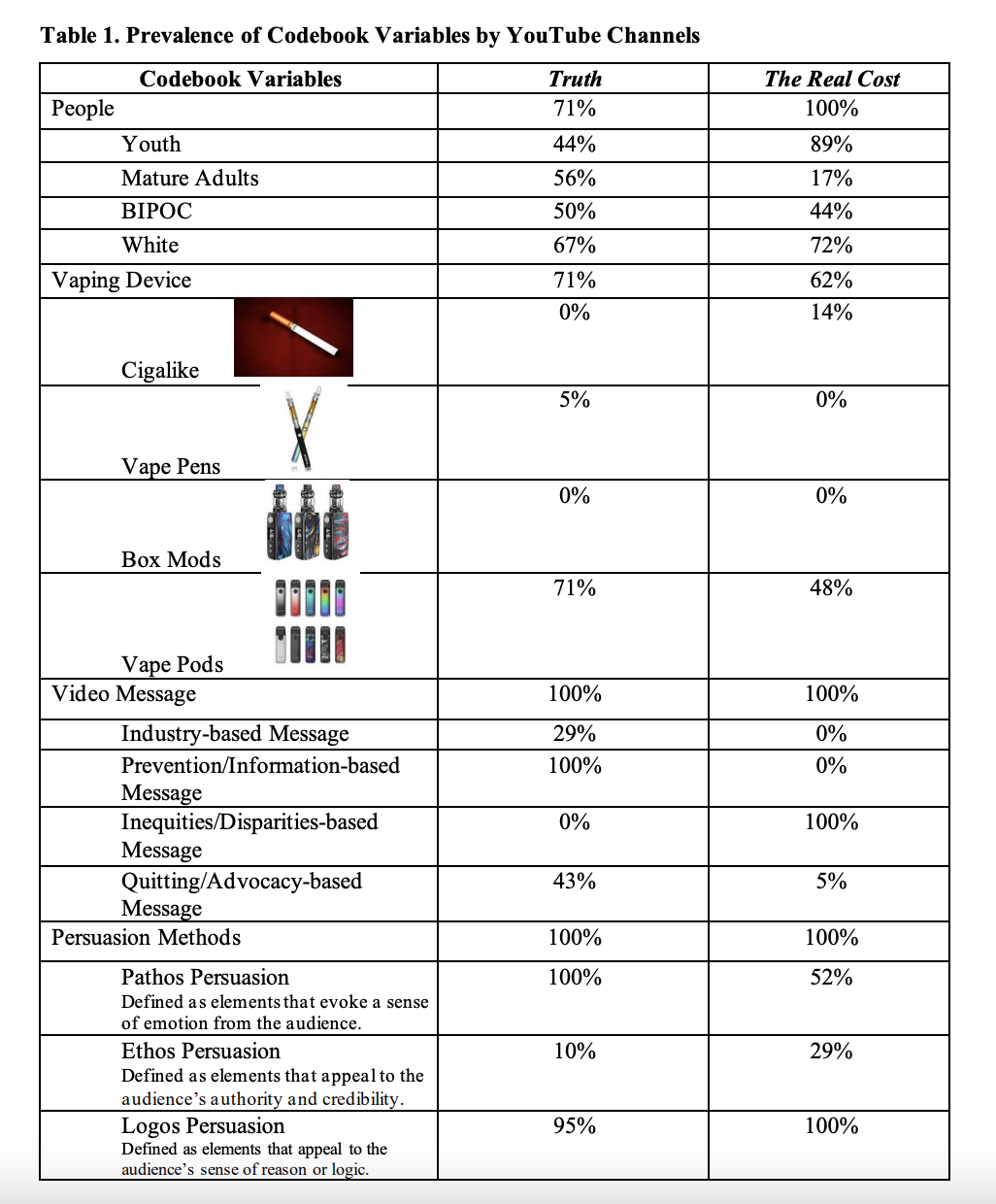
Results: A total of 40 videos were evaluated; 20 from the channel The Real Cost and 20 from the channel Truth. Prevalence of content and persuasion element for both channels are depicted in Table 1. Videos from Truth were more likely to include mature adults present (56%) than The Real Cost (17%) p = 0.016. Videos from The Real Cost were more likely to have youth present (89%) than Truth (44%) p = 0.005. Truth videos were more likely to have pathos persuasion (100%) than The Real Cost (52%) p < 0.001. The Real Cost videos had more views (M = 8729447.10, SD = 10162512.38) than Truth videos (M = 1151902.76, SD = 2572013.249, p = 0.003.
Conclusion(s): Vaping cessation/prevention videos from The Real Cost involved more people and youth and had more views than Truth. Persuasion methods of pathos, ethos, and logos were present in both channels. Future studies could examine how elements displayed in vaping/cessation prevention videos influence youth perspective on e-cigarette use.