Neonatal Pulmonology
Neonatal Pulmonology 3: BPD Clinical and Translational
282 - Reduced pulmonary gas exchange in small-for-gestational-age preterm infants
Publication Number: 282.341

Alessio Correani, MSc, PhD (he/him/his)
Research fellow
Università Politecnica delle Marche
Ancona, Marche, Italy
Presenting Author(s)
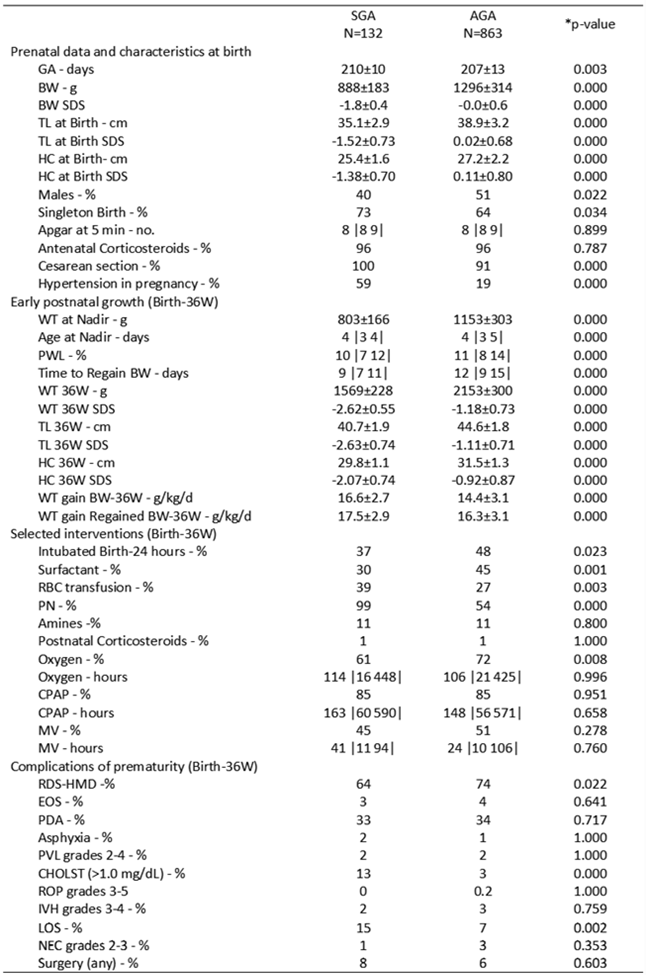
Background: Small-for-gestational-age (SGA) preterm infants are at increased risk of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD). Given (a) the marked over-representation of SGAs in preterm infants with BPD and (b) the rather variable incidence of BPD among preterm infants understanding the impact of SGA status on lung development, independently from BPD, remains a challenge. To date, limited information is available on pulmonary gas exchange of SGA preterm infants without BPD or with otherwise “normal lungs”.
Objective:
To compare pulmonary gas exchange of SGA with appropriate-for-gestational-age (AGA) preterm infants.
Design/Methods:
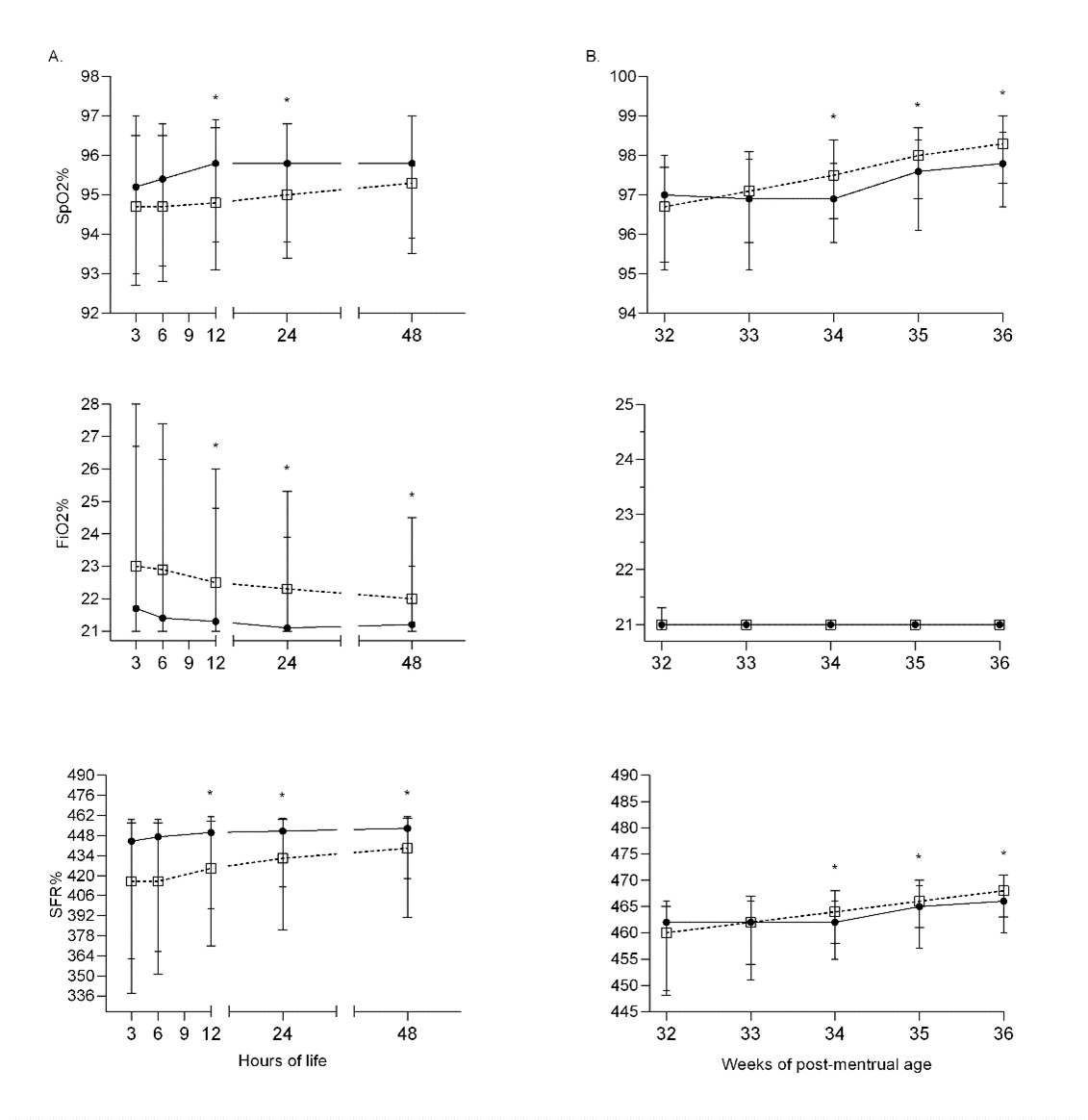
Preterm infants with gestational age (GA) between 24.0-31.6 weeks (W) without BPD were studied. SGA were match-paired for GA and gender with AGA infants. The oxygen saturation (SpO2) to the fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2) ratio (SFR) was chosen as a proxy for oxygen diffusion in lungs.
Results: We screened 1615 infants, 1189 met the inclusion criteria and were analyzed: 194 (16%) SGA and 995 (84%) AGA. The incidence of BPD was significantly higher in SGA (62/194 = 32%) than AGA (132/995 = 13%). Nine hundred ninety-five did not have BPD: 132 (13%) were SGA and 863 (87%) AGA (Table 1). The 132 SGA infants had significantly higher (better) SFR at birth, but lower (worse) at 33, 34, 35 and 36W than their AGA counterpart. At 36W, SFR was 465 |459 469| vs 468 |464 471| in SGA and AGA, respectively (p=0.010; Figure 1).
Conclusion(s): Among preterm infants born with GA between 24.0-31.6W and without BPD the SGA infants despite better oxygenation during the first days of life had poorer pulmonary gas exchanges at 36W in comparison with GA and gender match-paired AGA infants.