Neonatal/Infant Resuscitation
Neonatal/Infant Resuscitation 1
308 - TeleVISION: Telesimulation Versus In-person Simulation Of Neonatal resuscitation skills
Publication Number: 308.347

Lakshmi Sridhar, MD (she/her/hers)
Neonatal-Perinatal Fellow Physician, PGY-6
University of Rochester, Golisano Children's Hospital
Rochester, New York, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Neonatal Resuscitation Program (NRP) instructors are not routinely available at all hospitals. Telesimulation (telesim) connects learners with an instructor virtually. Research is needed to compare learner experiences of acquiring kinesthetic skills via telesim vs. traditional in-person instruction.
Objective:
To explore learners' experiences of receiving instruction via telesim and their perspectives on telesim as an alternative to in-person led instruction.
Design/Methods:
In this single-center mixed-methods study, groups of 3-6 learners participated in a telesim facilitated by a NRP instructor over videoconferencing to learn 3 kinesthetic skills: bag-valve-mask ventilation (BVM), chest compressions (CC), and intubation (Intub). Learners completed pre- and post-telesim surveys on their technical skills and their experience participating in the session. In a semi-structured focus group, learners discussed audio-visual quality; benefits and challenges of using telesim; and using telesim to teach novice vs. experienced learners. Focus groups were conducted with an interview guide, audio recorded, and transcribed. Two investigators inductively analyzed transcripts using grounded theory. Two other investigators will audit the codes and themes.
Results: Advanced practice providers and resident physicians (n=45) participated in a total of 12 telesims and focus groups. At baseline, 8-14% of learners had prior telesim experience. Most learners reported performing these skills < 5 times in the past 2 years (BVM 64%, CC 100%, Intub 97%). Post-telesim, learners reported improved skills from novice to competent/advanced from 57 to 89% (BVM), 40 to 86% (CC), and 20 to 59% (Intub). Learners’ impressions that telesim would be effective for first-time learners increased from 35 to 70% (BVM), 46 to 75% (CC), and 24 to 59% (Intub). Learners’ impressions that telesim would be effective for repeat learners increased from 77 to 100% (BVM), 82 to 100% (CC), and 66 to 95% (Intub). Three major themes related to the benefits/challenges of using telesim emerged: technology, learner experiences and skill acquisition (Table). The derived theory focused on creating a successful learning environment and building a connection between the instructor and learner with technology as the interface while noting key factors (Figure).
Conclusion(s): Telesim may be used to learn the kinesthetic skills of neonatal resuscitation. Success is based on the development of an optimal learning environment, effective use of advanced technology, and possibly employing alternative educational strategies to improve learning for novice learners.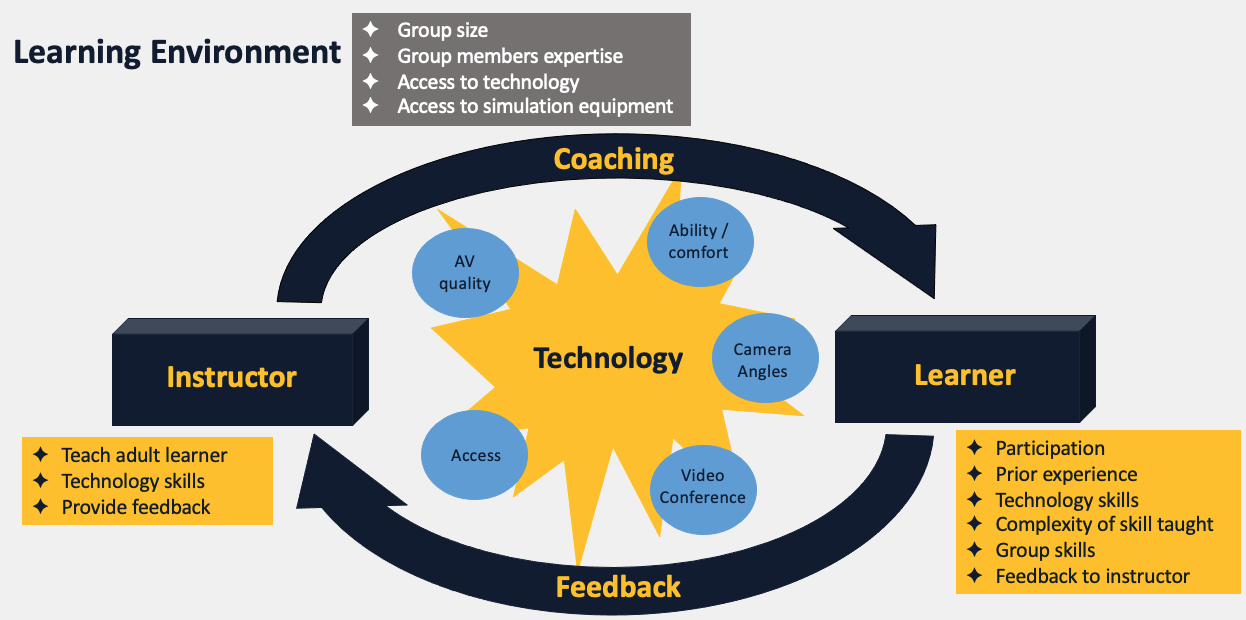
.png)
