Neonatal Cardiac Physiology/Pathophysiology/Pulmonary Hypertension
Neonatal Cardiac Physiology/Pathophysiology/ Pulmonary Hypertension 2
229 - Efficacy and Safety of Vasopressin in Newborns with Acute Pulmonary Hypertension
Publication Number: 229.33
.jpeg.jpg)
Audrey Hebert, MD, FRCPC
Neonatologist
Faculty of Medicine Université Laval
Quebec city, Quebec, Canada
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Acute pulmonary hypertension (aPH) in newborns can be life threatening and challenging to manage. Although inhale nitric oxide (iNO) is often recognized as first line therapy, up to 40% of newborns may be unresponsive to iNO. Vasopressin is a novel therapeutic avenue that may help in aPH due to its vasodilating action within the pulmonary vasculature, however there is currently a lack of sufficient evidence and safety profile for common use in newborns.
Objective:
To evaluate the efficacy and safety of vasopressin in newborns as an adjuvant treatment for aPH.
Design/Methods:
Retrospective single-center cohort study in newborns less than one month old who were treated with vasopressin for a minimum of one hour in the context of aPH in the neonatal and pediatric intensive care units of a tertiary university center between 2015 and 2022. Primary outcomes measures were oxygenation index, oxygen requirements, arterial oxygen pressure (PaO2) and blood pressure for efficacy of Vasopressin and liver function, renal function and sodium level for safety of Vasopressin prior to infusion of Vasopressin, at the start, at 12 hours, at 24 hours and at 48 hours.
Wilcoxon rank tests were used to compare continuous data and chi-square tests were used for categorical data comparisons. McNemar's tests were used for data dichotomized by periods with a significance level of p < 0.05.
Results:
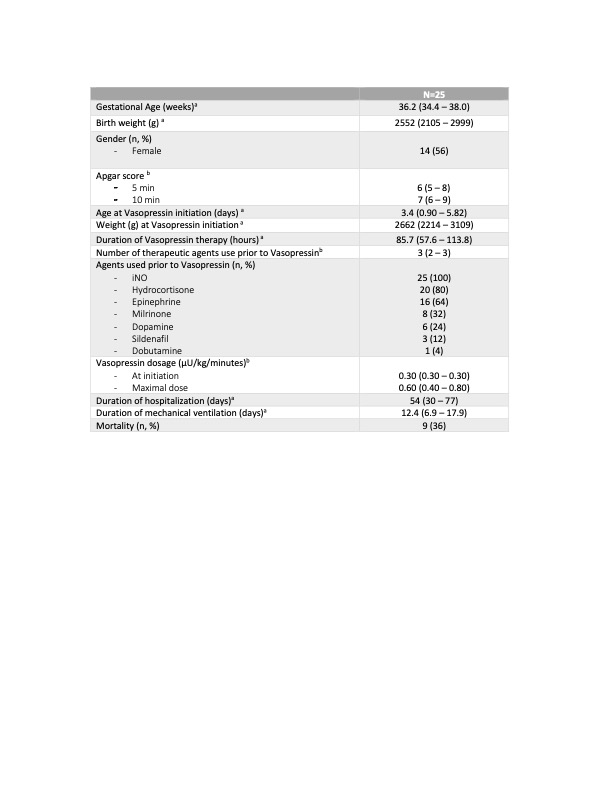
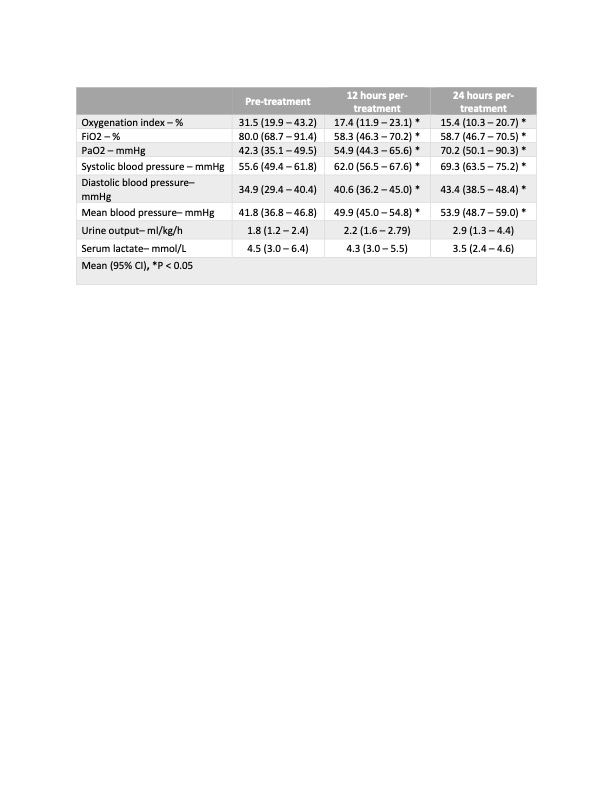
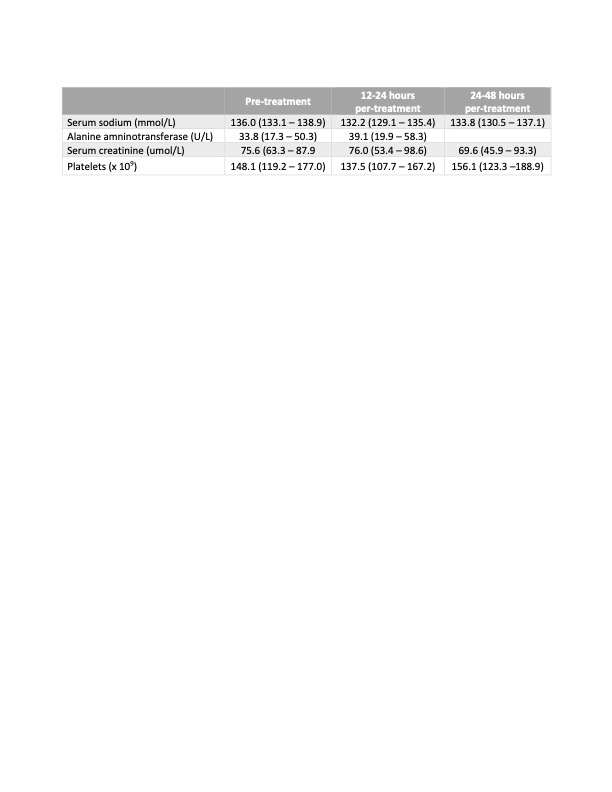
Twenty-five patients met inclusion criteria. The average gestational age was 36 weeks and birth weight ranged from 560 g to 4800 g. (Table 1) In patients who received vasopressin, there was a significant improvement in oxygenation index (31.5 to 15.4; p = 0.0003), PaO2 (42.3 to 70.2 mmHg; p = 0.0002) and oxygen requirements (FiO2) (82 to 58 %; p = 0.0008). There was also a significant improvement in their mean arterial pressure (41.8 to 53.8 mmHg; p = 0.001). (Table 2) In terms of safety, 68% of patients presented an episode of significant hyponatremia (minimum mean sodium level of 128.8 mmol) (Table 3) There were 3 patients diagnosed with necrotizing enterocolitis and 1 patient with spontaneous intestinal perforation within 7 days of vasopressin use. There was no impact on renal and liver function.
Conclusion(s):
The use of vasopressin seems promising to improve the oxygenation and hemodynamic status of neonatal patients with aPH refractory to initial therapy. Further prospective studies are needed to establish the safety profile of vasopressin in newborns.