Neonatal Cardiac Physiology/Pathophysiology/Pulmonary Hypertension
Neonatal Cardiac Physiology/Pathophysiology/ Pulmonary Hypertension 2
233 - Myocardial Deformation Assessment in Neonates: A Comparison Between Automated Function Imaging and EchoPAC Clinical Workstation Software
Publication Number: 233.33
- SA
Sean Armstrong, MB BCh BAO (Hons) MRCPI MRCPCH
Neonatal Specialist Registrar
Rotunda Hospital
Dublin 8, Dublin, Ireland
Presenting Author(s)
Background:
Deformation imaging of the left (LV) and right (RV) ventricle in neonatal intensive care is an area of increasing interest. The modality can characterize myocardial function in various disease states, monitor treatment response and predict outcomes. Automated function imaging (AFI) facilitates measurement of deformation at the bedside using a semi-automated method on the ultrasound machine. Its reliability and reproducibility is well established in the adult population when compared to offline assessment of strain using dedicated software (General Electric EchoPAC). To date, there are no studies assessing the reproducibility of the AFI technique and its agreement with offline EchoPAC in the neonatal population.
Objective: To assess the reproducibility of the AFI technique and its agreement with offline EchoPAC in the neonatal population in a prospective observational study.
Design/Methods:
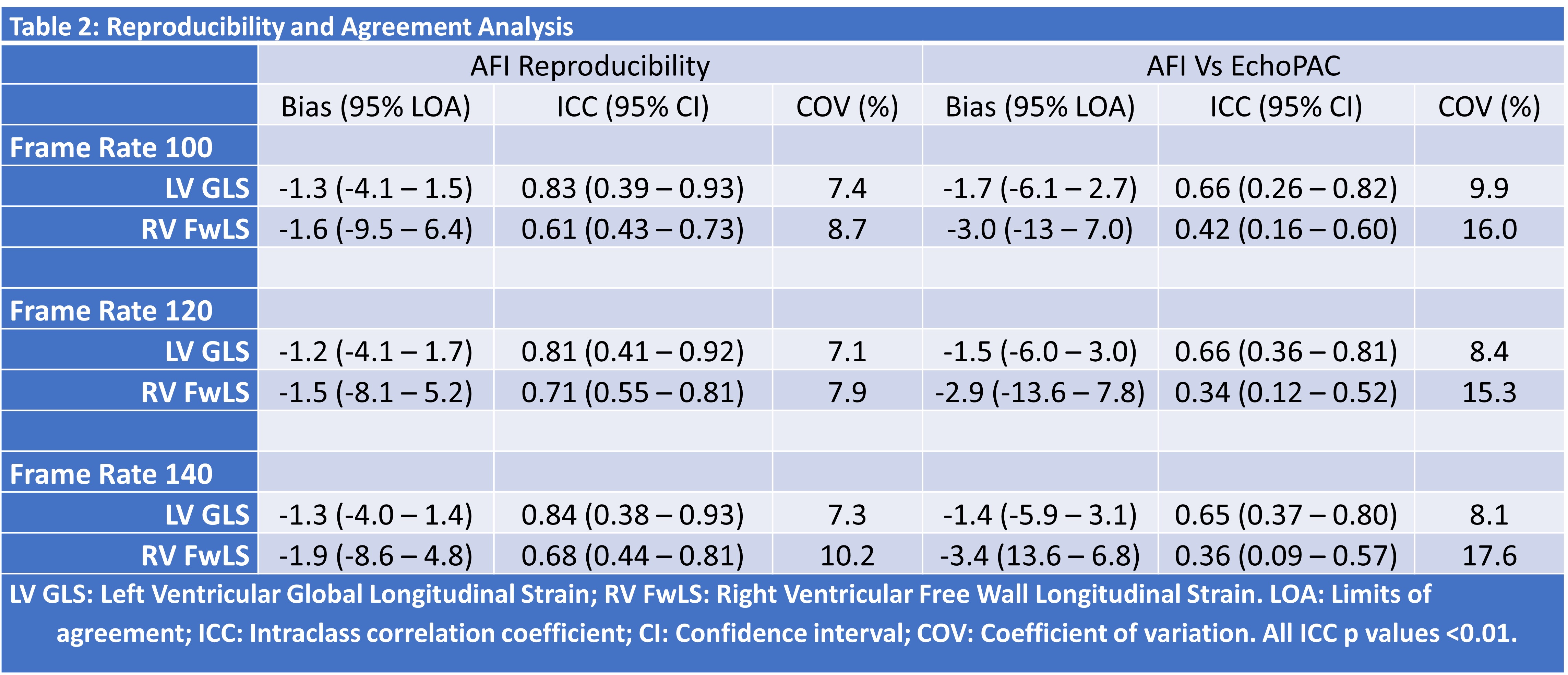
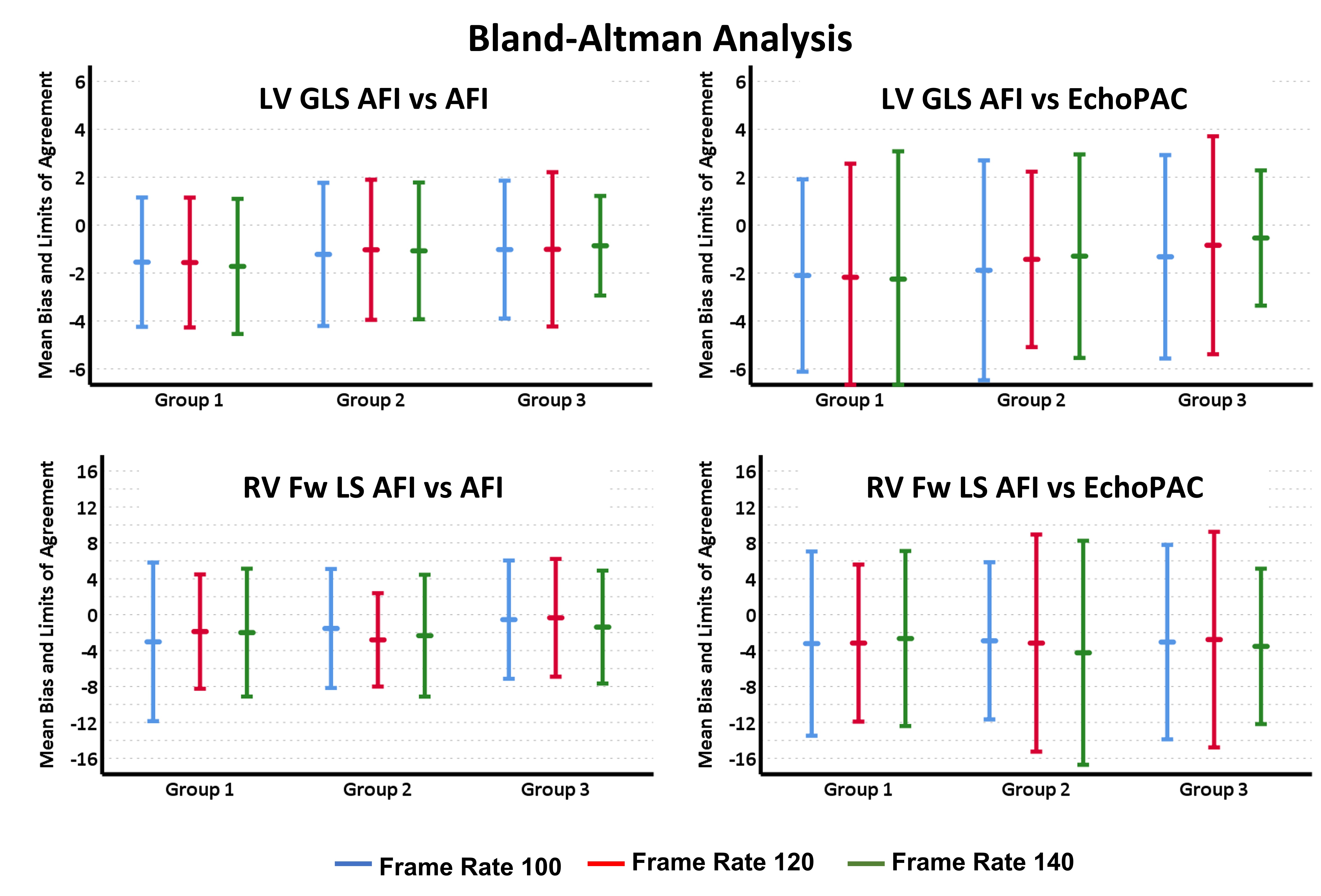
Imaging was obtained using the Vivid E95 system (Version 4; General Electric). Four, two, and three chamber images of the LV were obtained from the apical view. RV free wall focused imaging was also obtained at three different frame rates: 100, 120 and 140 frames per second. AFI reproducibility was assessed by comparing measurements performed by one investigator (SA) four weeks apart to avoid recall bias. Agreement between AFI and EchoPAC was assessed by comparing one set of AFI measurements obtained by the investigator with those obtained by the same investigator using EchoPAC, who was blinded to the original results. The reproducibility and agreement analyses were based on a combination of (1) Intraclass correlation (ICC); (2) Bland- Altman analysis; and (3) Coefficient of variation (COV).
Results:
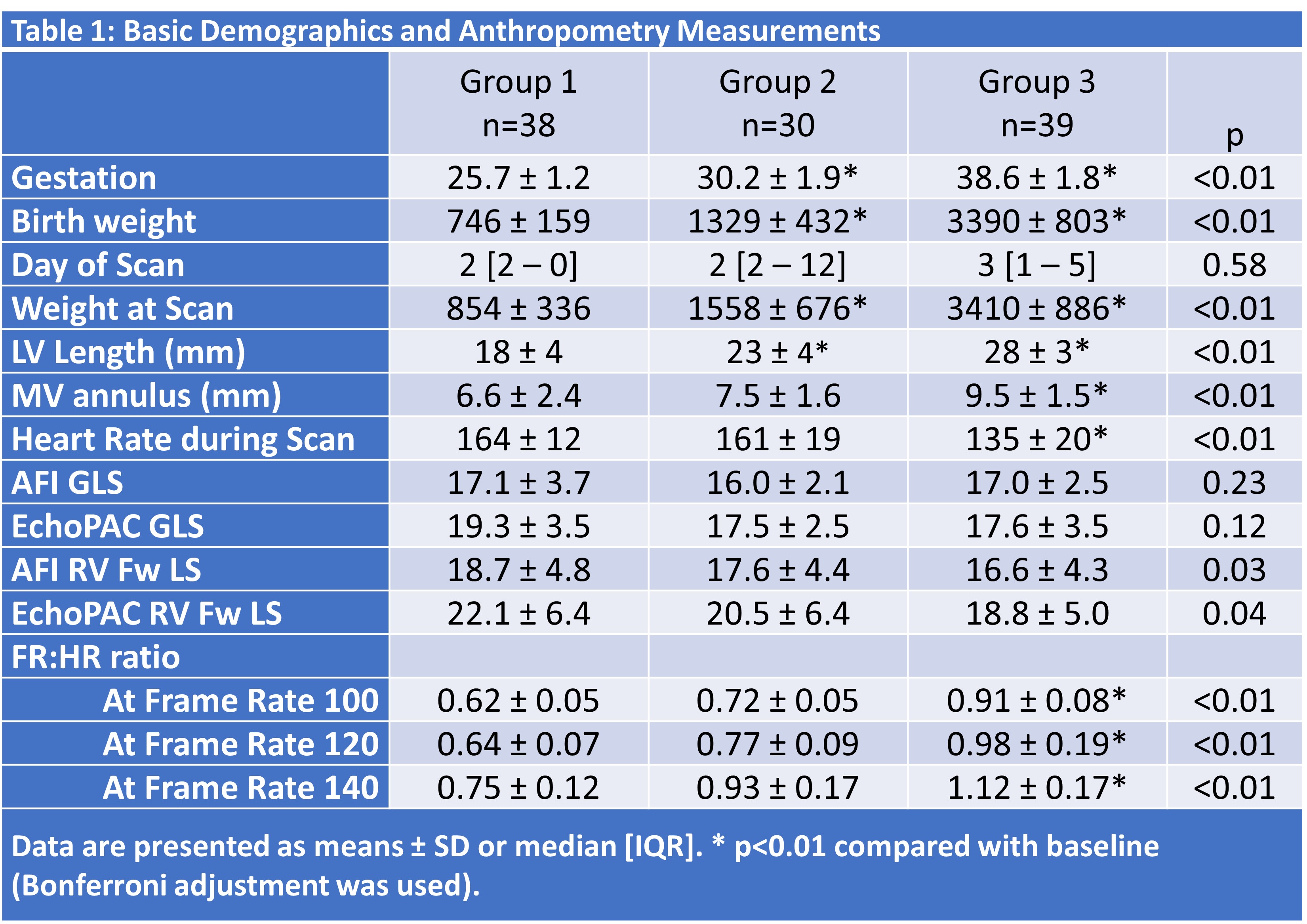
107 infants were recruited– with 3 subgroups created for analysis based on gestational age (Table 1). Examining LV strain measurements, AFI demonstrated acceptable reproducibility – with acceptable median ICC and COV values across different frame rates (Table 2, Figure 1). Agreement between AFI and EchoPAC was poor throughout all frame rates. Bias and COV values were acceptable. RV strain measurements exhibited poor reproducibility and agreement throughout all frame rates. Bias and COV values strayed outside the limits of acceptability.
Conclusion(s):
Our study demonstrates that AFI has poor agreement with EchoPAC in either LV or RV measurements, and that caution should be applied when preforming online strain measurements at the beside in the neonatal population. Further improvements to AFI software are warranted to provide a viable alternative to offline measurements in this specific patient cohort.