Publication Number: 22.322
- KR
Krupal Rana, MLS, LSSGB (she/her/hers)
Enterprise Improvement Advisor
Children's Hospital of Phildadelphia
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background:
At Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP), only 2.2 % of children at high-risk of hypertension (HTN) under 3 yrs have Blood Pressure (BP) measured at Well Care visits. Per 2017 AAP guidelines, children at high-risk should have routine, accurate BPs. However, there are many barriers to obtaining BP in children under 3 yrs. So, BP is frequently not done and HTN is under-diagnosed.
Objective:
To promote awareness of the need to obtain BPs in high-risk children under 3; to provide appropriate tools and education to clinical team; to test and pilot a new standard of care for measuring BP; and to ensure follow up. Thereby improving the long-term health of children under 3 yrs at increased risk for HTN.
Design/Methods:
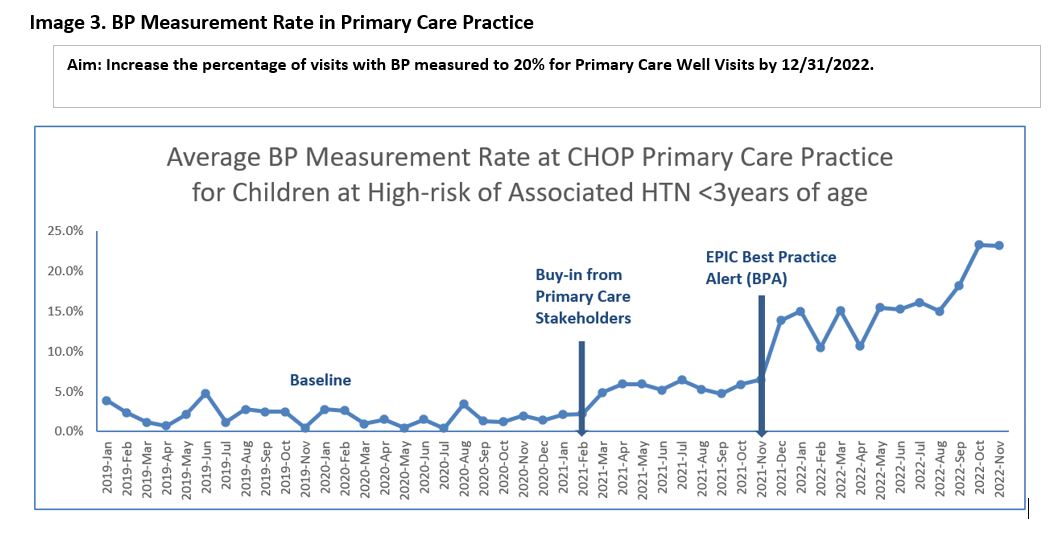
An automated Welch-Allyn®(WA) BP device was validated via a comparison trial with an automated GE® device by serial measurements in sedated patients. Then real-time data was collected from the Nephrology and Neurofibromatosis Clinics. The WA device was then rolled out for use in Primary care and Sub-specialty clinics. Age- appropriate distraction tools and educational materials were provided. A BP Best Practice Alert (BPA) was created and implemented throughout PCPs to identify the high-risk population, to recommend specialist referrals, and to recognize normotensive patients. A robust dashboard was created to graphically establish the BP baseline and to monitor outcome progress (Figure 1).
Results:
BPs from 58 sedated patients under 3 yrs were compared between WA and GE devices and gave similar readings (Figure 2). Real-time data collected from the Nephrology and Neurofibromatosis Clinics showed results that were comparable or better than those when using the Dynamap. The WA device was then approved for use in children under 3 yrs. in CHOP Out-patient clinics. (Re-)education of all clinical staff occurred, totaling 366 RNs & MAs and 49 physicians. Since implementation of the BPA, total average BP measurement rate has increased from 2% to 11% across all PCP sites (Figure 3). Also, through targeted PDSA cycle, EPIC Nephrology Committee has introduced a national BP cut-off for children under 1 yr.
Conclusion(s):
The automated WA device is accurate, faster, and better tolerated for children under 3 yrs than the Dynamap. Appropriate education, implementation of Electronic Medical Record (EMR) tools and referral pathways are in place to improve care and outcomes in children under 3 yrs with high-risk of HTN conditions. Our long-term goals are to expand this initiative locally, regionally, and then nationally.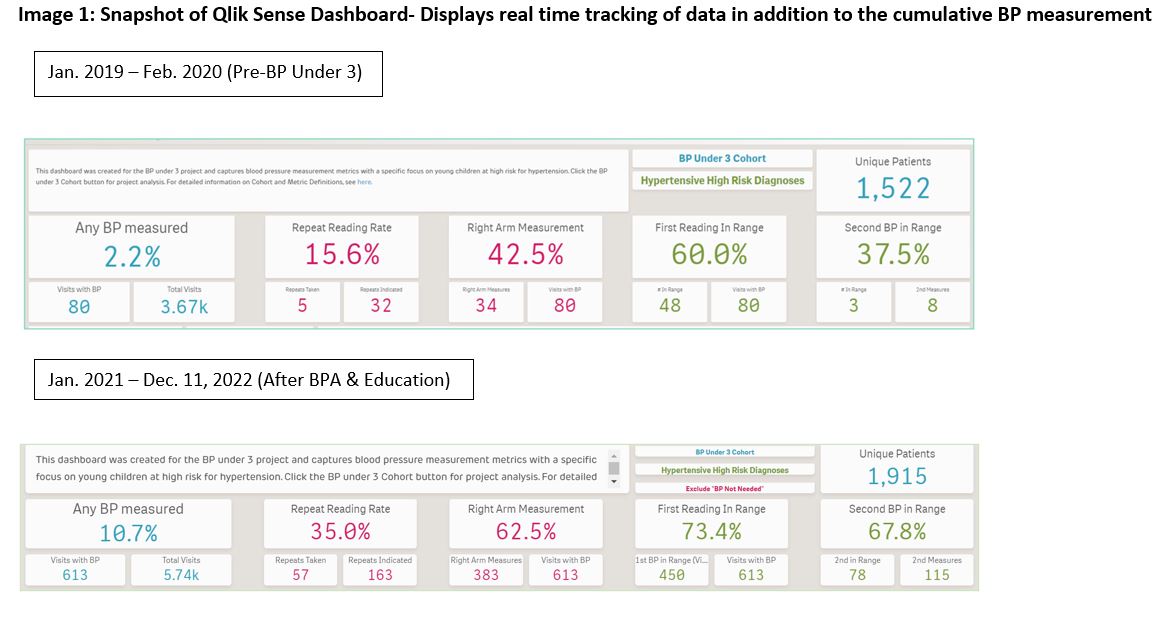
.jpg)