Neonatal Cardiac Physiology/Pathophysiology/Pulmonary Hypertension
Neonatal Cardiac Physiology/Pathophysiology/ Pulmonary Hypertension 1
212 - Contemporary Outcomes of Patent Ductus Arteriosus Closure in Very Low Birth Weight Preterm Infants
Publication Number: 212.329

Arpit Gupta, MD, FAAP (he/him/his)
Attending Physician
New York Medical College/Metroplitan Hospital Center
NYC, New York, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) carries substantial morbidity and mortality in very low birth weight (VLBW) preterm infants. Controversy exists regarding the management approach after failed pharmacologic treatment.
Objective: We sought to investigate the outcomes of surgical ligation (SL) compared to percutaneous closure (PC).
Design/Methods:
A retrospective review of premature infants with birth weight < 1500 g and < 32 weeks of gestation diagnosed with PDA from Kids’ Inpatient Database in 2009, 2012, 2016, and 2019 was performed. PDA was found in 30,920 patients, of them 4,100 patients (13.3%) had SL [mean age 20.4±28 days, 48.2% males], and 323 patients (1%) required PC [mean age 17.7±29.7 days, 57.6% males]. Outcomes were analyzed between both groups.
Results:
The incidence of PC has increased across the years (from 0.1% in 2009 to 0.3% in 2019) and SL has decreased (from 26.9% in 2009 to 5.2% in 2019). Overall in-hospital mortality was not different in the two groups (5.8% in PC group vs 6.4% in SL group, p=0.7). Iatrogenic pneumothorax was higher in SL patients (1.6% vs 0%, p=0.01). Other complications including acute kidney injury, chylothorax, recurrent laryngeal nerve injury, and bleeding were comparable (p >0.05). Length of hospital stay was similar (101.3±62.5 days in PC group vs 101.4±52.6 days in SL group, p=0.9).
Conclusion(s):
The incidence of SL has declined across the years and PC rate continues to increase. PC can be a reliable alternative to SL in these patients with comparable morbidity and mortality. These results can be considered in decision-making and family counseling. 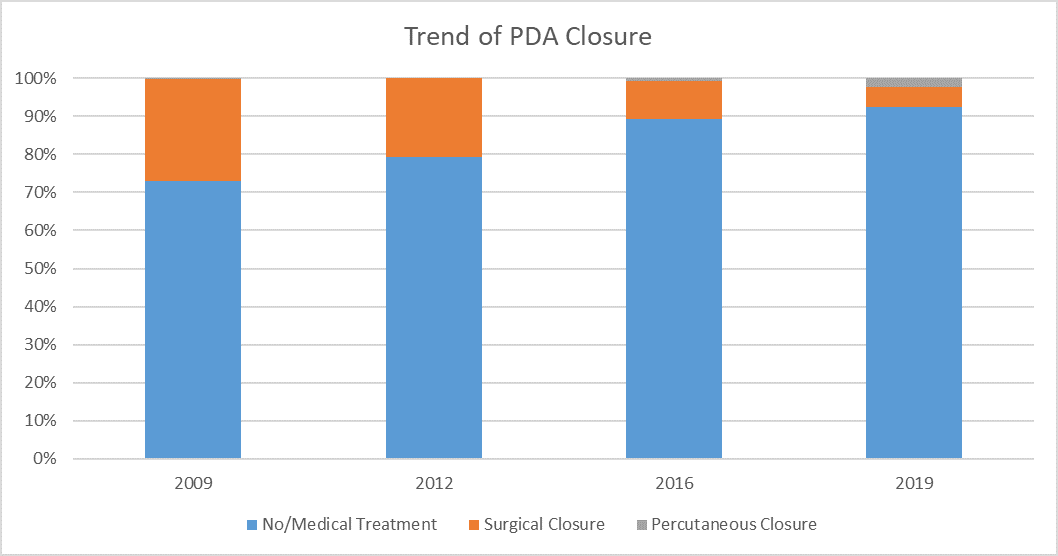
Table-1.jpeg
Table-2.jpeg
