Adolescent Medicine: General
Adolescent Medicine 3
510 - No Wrong Door-Implementing Suicide Screening in a Youth-centered Practice Focused on Sexual and Reproductive Health with BIPOC and LGBTQ Youth
Publication Number: 510.3

Katie Plax, MD (she/her/hers)
Division Chief Adolescent Medicine
Washington University in St. Louis School of Medicine
Saint Louis, Missouri, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Given the youth mental health crisis, the AAP recommends universal suicide screening for patients age 12 and up. The literature also highlights that race, sexual orientation and gender identity are factors of special consideration for suicide risk.
Objective: The goal of this study was to implement the Ask Suicide-Screening Questions (ASQ) screening instrument in a youth-centered practice that provides medical care, focused on sexual and reproductive health, and social services to BIPOC and LGBTQ youth.
Design/Methods:
Counselors and case managers were trained on the ASQ and a local suicide risk assessment pathway. The ASQ was added to the existing mental health screening workflow youth receive prior to medical visits and every 6 months when in counseling. Screening includes the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) for depression. The suicide risk assessment pathway had 3 categories of risk that correspond to the ASQ score: low risk (no to all questions), intermediate risk (yes to at least one question), and acute risk (yes response to imminent risk). Results of the ASQ were compared to PHQ-9 and endorsement of question 9 (frequency over the last two weeks of “thoughts that you would be better off dead or of hurting yourself in some way”). The study period was 5/25-10/31/22.
Results:
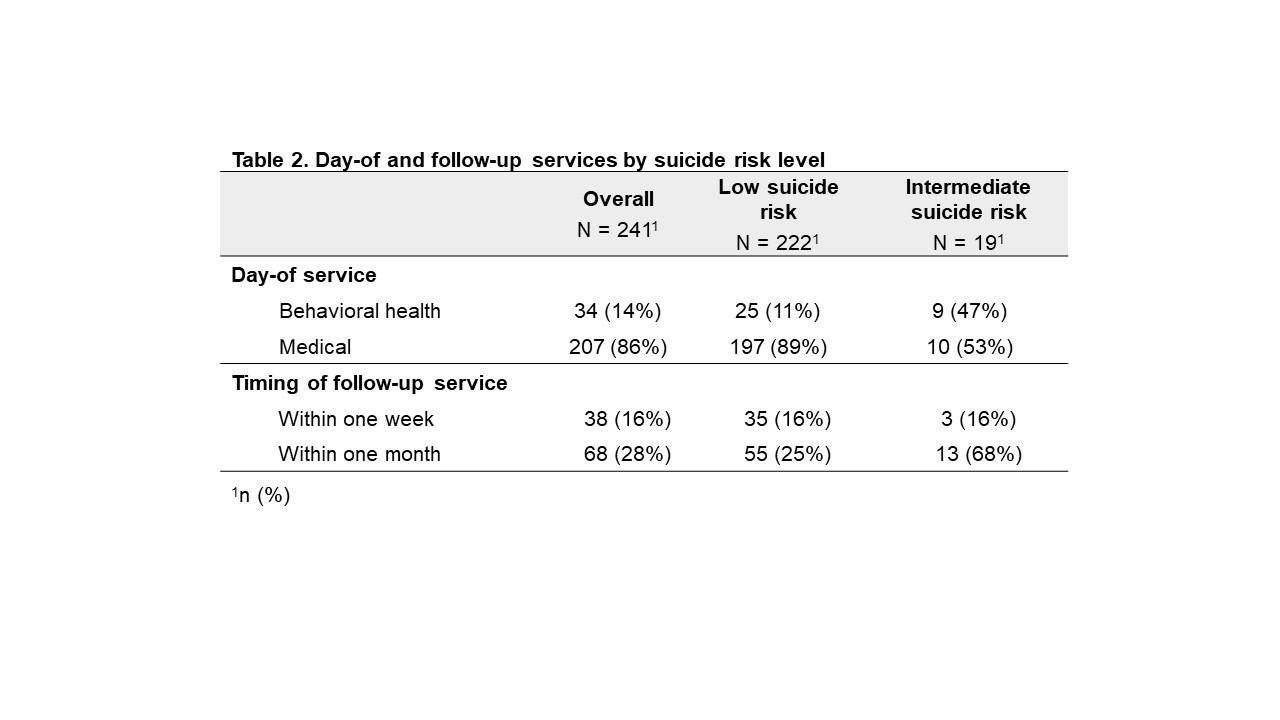
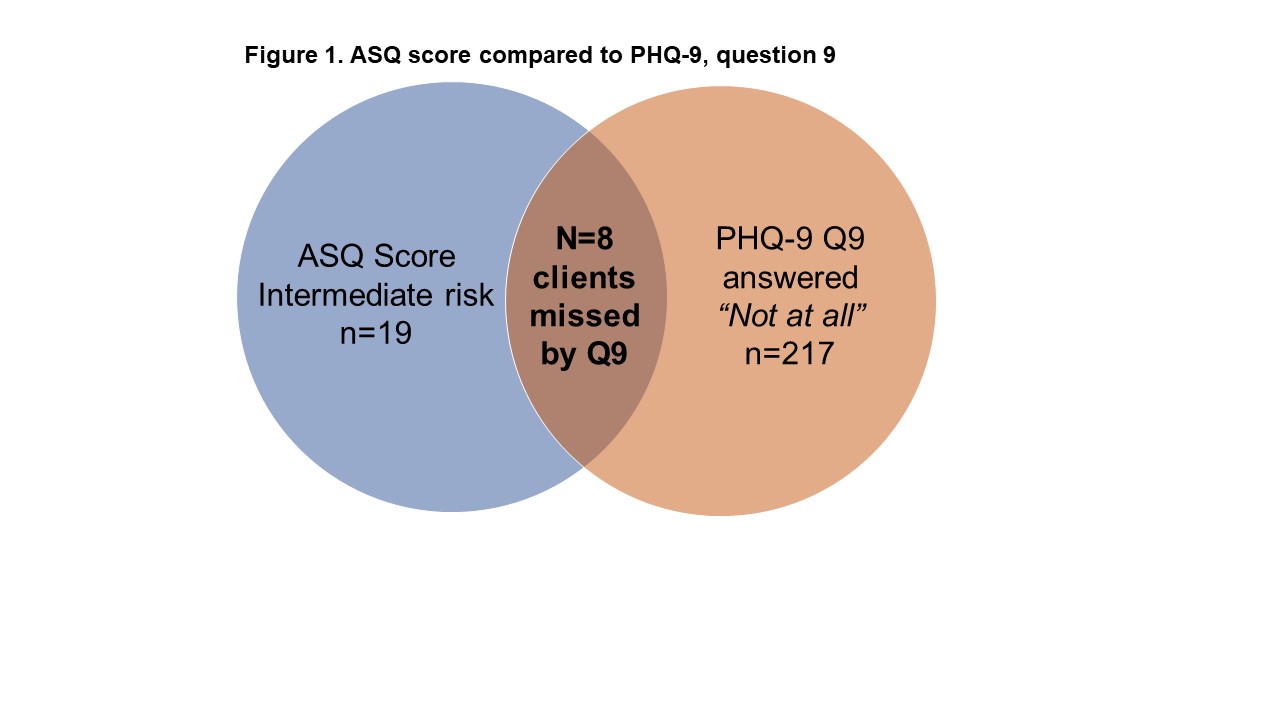
241 youth ages 14-26 were screened. The study population included 180 (75%) African American youth, 9 (4%) self-identified as gender diverse, and 61 (25%) a sexual orientation of lesbian, gay, bisexual, or queer/pansexual. 19 (8%) screened positive (intermediate risk); no youth endorsed acute risk of suicide. Comparing ASQ and PHQ-9 results, 7/19 (37%) scored less than 10 for depression screening and 8/19 (42%) endorsed “not at all” on question 9. All 19 received a suicide hotline number and, had further risk assessment with the screening staff. 13 (68%) had another appointment/follow-up within a month.
Conclusion(s):
In this youth center setting the ASQ and suicide risk assessment pathway was implemented within a diverse youth population. This study suggests that places where diverse youth seek sexual and reproductive care and treatment and social services are viable places to screen. This integrated care model with counselor/case manager clinicians doing screening worked well in a busy community setting and may also be a strategy for other clinical medical practices. The PHQ-9 overall and question 9 miss youth who screen positive for suicide risk with the ASQ. Models that involve other disciplines to achieve the suicide screening recommendation may increase achieving this goal..jpg)