Neonatal Quality Improvement
Neonatal Quality Improvement 7
220 - A Multidisciplinary Team Approach to Implementing the Neonatal Early-Onset Sepsis (EOS) Calculator in the Nursery
Publication Number: 220.441

Alice Han, MD
Instructor
Children's Hospital at Montefiore/Albert Einstein College of Medicine
New York, New York, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background:
AAP supports use of a multivariate risk assessment with a neonatal EOS calculator that synthesizes objective risk factors with an evolving clinical exam to predict individual risk of EOS. Nurseries have used the calculator with an associated reduction in blood culture evaluations, antibiotic use, and increase in clinical observation. Few studies have reviewed the multidisciplinary changes needed for EOS calculator implementation.
Objective:
To implement the Kaiser EOS calculator for newborns >35 weeks’ gestation admitted to an urban perinatal center with a multidisciplinary team.
Design/Methods:
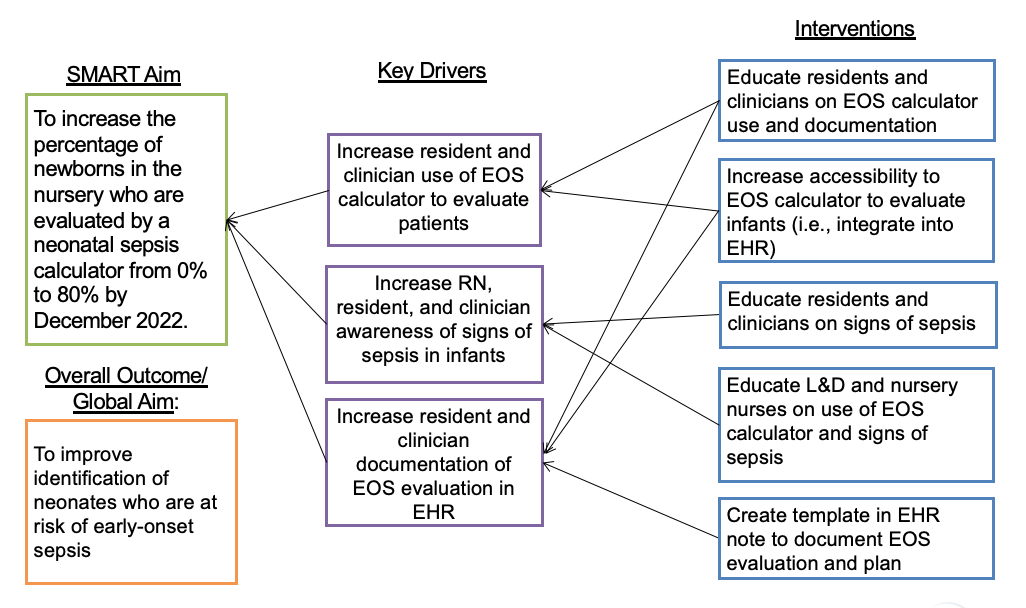
Retrospective chart review included admitted newborns >35 weeks’ gestation from 1/2022 to 11/2022. A key driver diagram helped structure the project (Fig. 1). In 6/2022, the calculator was integrated into the EHR. In 8/2022, clinicians and residents were educated on using the calculator, documenting the result, and signs of neonatal sepsis. Nurses were educated on changes in management due to the calculator and signs of neonatal sepsis. The primary outcome measure was the percentage of sampled newborns (every 5th newborn) evaluated with the calculator. Secondary outcome measures evaluated all newborns pre-and post-EOS calculator implementation: 1) percentage of newborns evaluated with a blood culture, and 2) percentage of newborns initiated on antibiotics for presumed EOS. The process measure was the percentage of nurses trained about the calculator. Balancing measures included 1) percentage of newborns transferred from nursery to NICU, and 2) percentage of readmissions within 7 days of life with culture-positive sepsis or meningitis. Run charts were used to evaluate the measures.
Results:
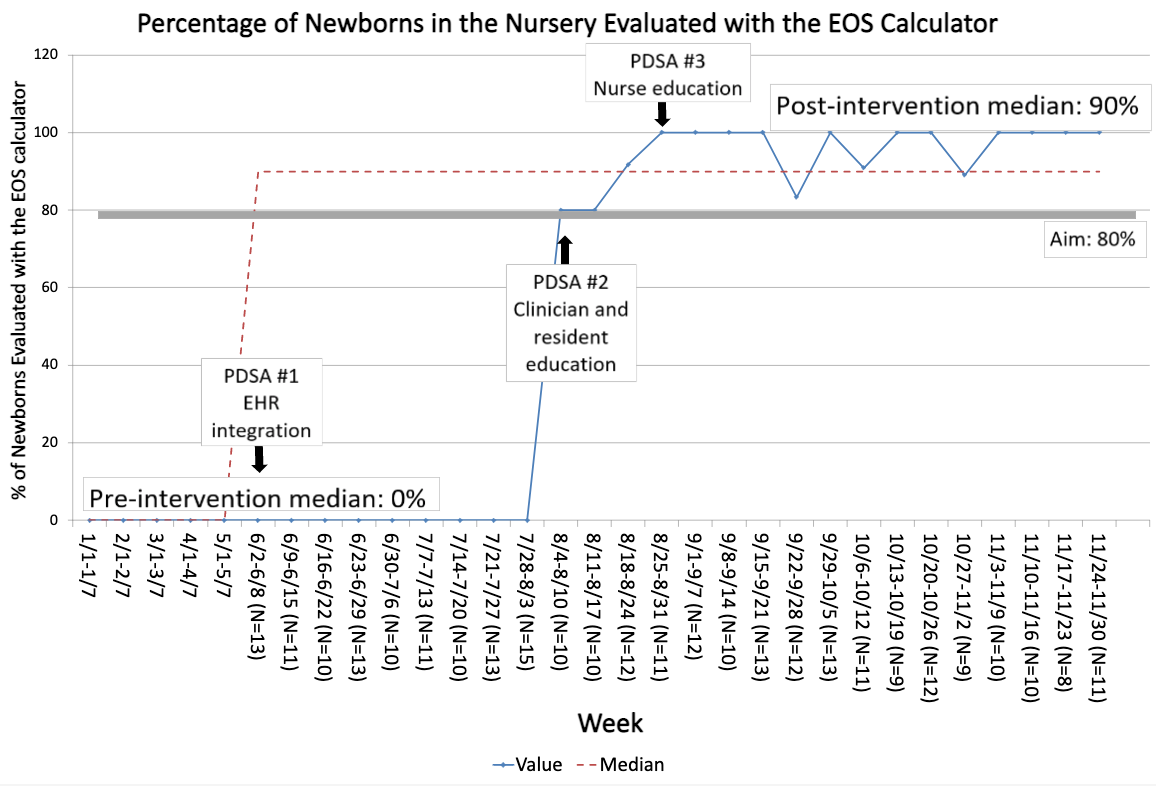
28 clinicians, 22 rotating residents, and 44 of 67 nurses received education. 1123 newborns were admitted from 1/2022-5/2022 (pre-EOS calculator). Among 1451 newborns born after 6/2022, a median of 90% of sampled charts were evaluated with the calculator (Fig. 2). Blood culture evaluations decreased from 11.5% (n=129/1123) to 7.4% (n=108/1451). Antibiotic use was stable at a median of 1.8% pre- and post-EOS calculator. Transfers from the nursery to the NICU were stable at a median of 4%. There were no readmissions within 7 days of life for culture-positive sepsis or meningitis pre- and post-EOS calculator.
Conclusion(s):
Widespread implementation of the EOS calculator is feasible with EHR integration and education of multidisciplinary team members. Blood culture evaluations declined after implementation of the EOS calculator. Antibiotic use did not change. Ongoing multidisciplinary education is needed to sustain implementation.