Neonatal Clinical Trials
Neonatal Clinical Trials 2
280 - Multimodal monitoring of hemodynamics in Extremely Low Birth Weight preterm infant in a Canadian tertiary level unit- Non-Blinded Randomized Control Trial (RCT)-MUSE Trial
Publication Number: 280.428
- RL
Renjini Lalitha, MBChB, M.Med
Assistant Professor
The University of Western Ontario - Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry
London, Ontario, Canada
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Current approaches for the evaluation and treatment of transitional circulatory issues in preterm infants based primarily on blood pressure (BP) may be harmful. Hence, it is essential that these approaches are adequately investigated. This study tests a detailed hemodynamic approach with a multimodal assessment to standard approach using Vasoactive Ventilation Renal score (VVR) that incorporates inotrope use, ventilation support and renal function reflecting cardiorespiratory-renal health.
Objective:
To determine whether multimodal hemodynamic monitoring will improve cardiorespiratory-renal health as evidenced by decreasing VVR in preterm infants at one week of life.
Design/Methods: Randomized Control Trial in preterm infants born < 29 weeks gestational age admitted to a tertiary neonatal intensive care unit, between 15 Feb 2019 and 31 Dec 2021. Eligible infants were randomly assigned for the first 72hours of life to multimodal arm consisting of early Targeted Neonatal Echocardiogram, continuous cerebral Near Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS) and clinical-biochemical data or to standard arm using clinical-biochemical data only. A comprehensive study guideline was used for hemodynamic assessment in the multimodal arm. Univariate and multivariate analysis compared the two arms.
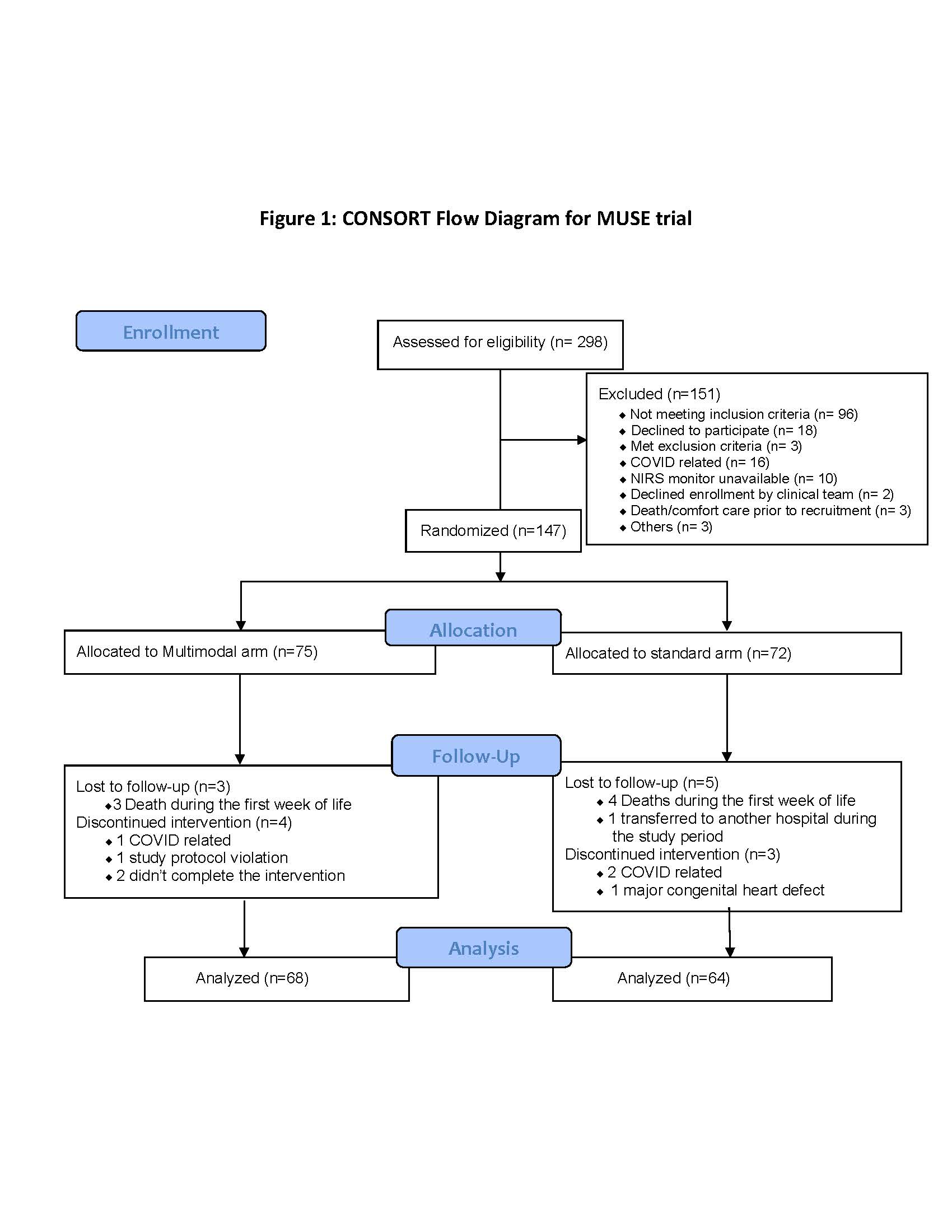
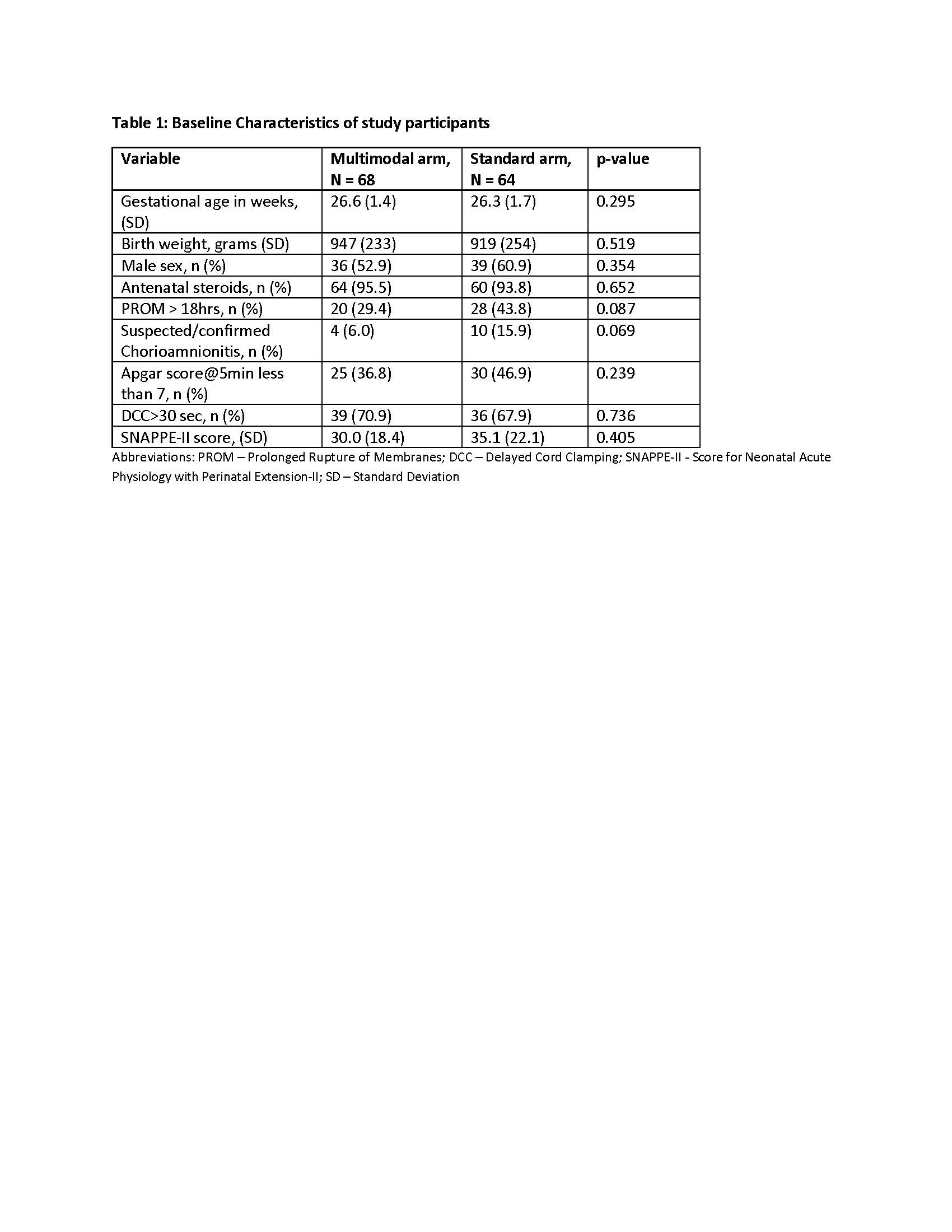
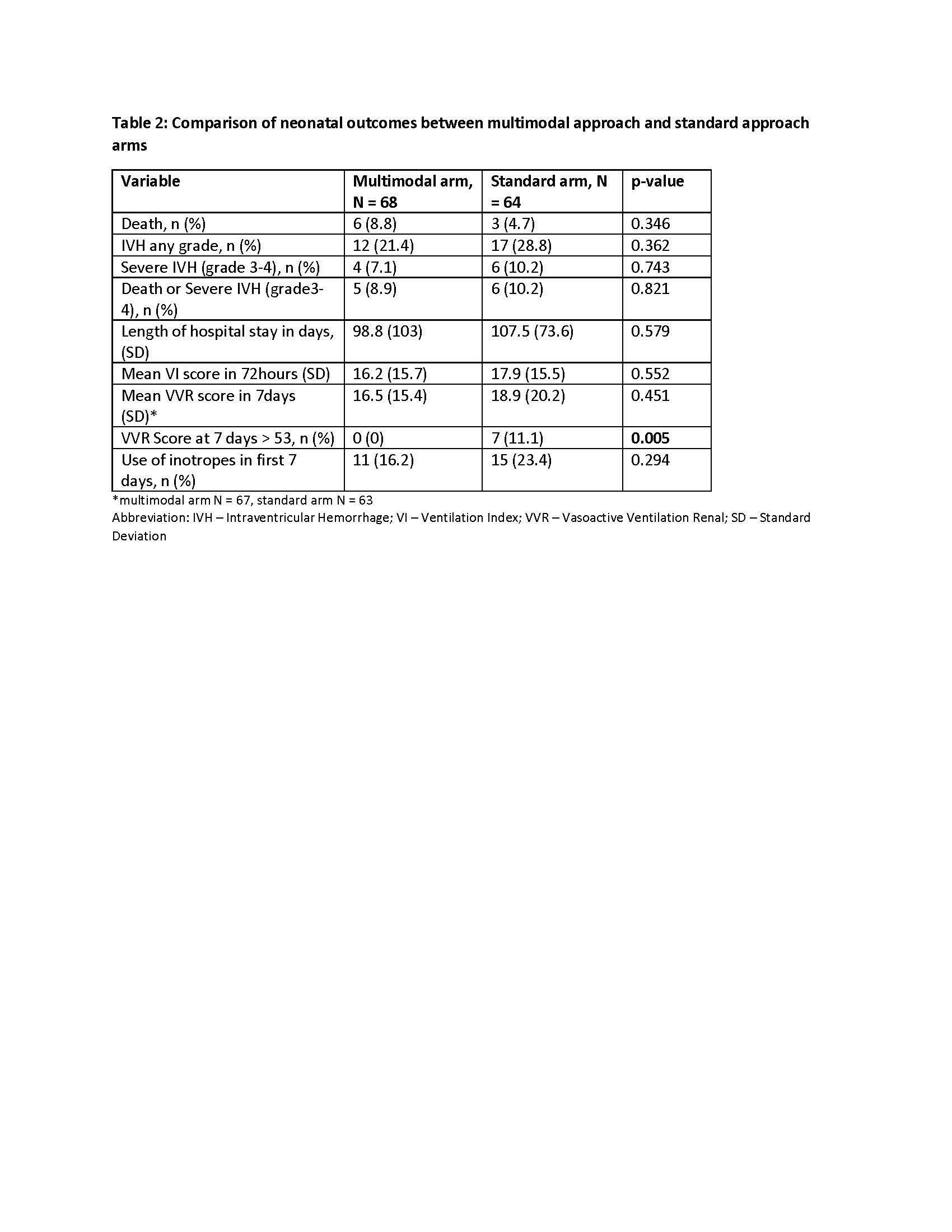
Results: 298 infants were screened during the study period and 147 were randomly assigned (75 multimodal arm, 72 standard arm). 68 in the multimodal and 64 in the standard arm were included in the preliminary analysis (Figure 1). Baseline characteristics were similar in both arms (Table 1). The mean VVR score within 7 days of life were 16.5(SD 15.4) and 18.9(SD 20.2) in the multimodal and standard arm respectively(p=0.451) while mean Ventilation Index score in the first 72hours of life were 16.2(SD 15.7) and 17.9(SD 15.5) respectively (p=0.552, Table 2). Peak VVR score >53 at 7 days were significantly higher in standard arm (11.1%) than the multimodal arm (0%), p= 0.005. Outcomes of death, severe Intraventricular Hemorrhage and length of hospital stay were not statistically different. However, there was a trend towards decreased inotrope use in the multimodal arm compared to standard arm (16.2% Vs 23.4% respectively, p=0.294).
Conclusion(s): In preterm infants, multimodal hemodynamic assessment during the transitional period was not associated with decreased VVR scores that signify improved cardiorespiratory-renal health but led to lower incidence of VVR score greater than 90th centile and decreasing trend in inotrope use in the first week of life.