Neonatal/Infant Resuscitation
Neonatal/Infant Resuscitation 3
688 - Reference ranges for cerebral oxygen saturation in neonates during immediate transition after birth – Differences between devices
Publication Number: 688.444
- NB
Nariae Baik-Schneditz, MD, PhD (she/her/hers)
Pediatrician
Medical University Graz
Graz, Steiermark, Austria
Presenting Author(s)
Background:
Reliable, feasible and non- invasive brain monitoring in neonates during immediate transition after birth is of growing interest. There are different near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) devices measuring cerebral oxygen saturation using different algorithms. Immediate postnatal transition is accompanied by major changes in cerebral oxygenation and therefore it is crucial to define reference ranges for each device.
Objective:
The aim of the present prospective observational study was to define reference ranges for cerebral oxygen saturation (rSO2) during immediate transition after birth measured with Masimo (Root, O3 regional oxymetry, Masimo, USA) in stable preterm and term neonates without any medical support and compare them with already published reference ranges from other NIRS devices.
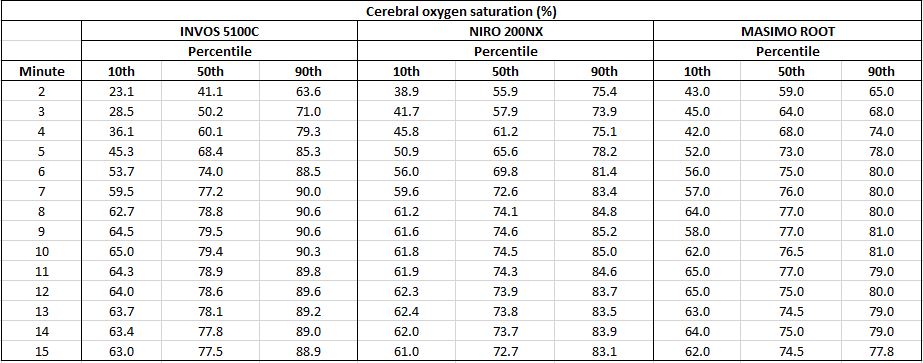
Design/Methods: The rSO2 was continuously measured with Masimo in neonates during the first 15 minutes after birth. The neonatal sensor was placed on the left frontoparietal side of the head and was fixed with a cap. Data of neonates after caesarean delivery without any medical support were included into the final analysis. Median values and 10th and 90th centile were calculated for each minute. These rSO2 values were compared to already published reference ranges of INVOS 5100C (Medtronic Corp, Troy, Michigan: crSO2) and NIRO 200NX (Hamamatsu, Japan: cTOI).
Results:
A total of 192 neonates were enrolled: 27 preterm and 165 term neonates after caesarean delivery. Due to respiratory support, 13 preterm and 57 term neonates were excluded. The data of 122 neonates (14 preterm/108 term) were analysed. rSO2 values measured with Masimo and the published cerebral oxygen saturation values of the INVOS 5100C and NIRO 200NX in every minute during the first 15 minutes after birth are presented in table 1. Compared to the established reference ranges, rSO2 values measured with Masimo have a similar course when compared to cTOI values measured with NIRO 200NX, whereas crSO2 values measured with INVOS 5100C are initially lower and increase during the first minutes after birth.
Conclusion(s):
The present observational study adds reference ranges of rSO2 measured with Masimo in stable neonates immediately after birth. As there are differences regarding reference ranges of various NIRS devices, it is important to consider this for future clinical use.