Neonatal Quality Improvement
Neonatal Quality Improvement 5
190 - Improving On-Time Administration of the Initial Hepatitis B Vaccine in the NICU using a Quality Improvement Approach
Publication Number: 190.439

Michelle M. Gontasz, MD (she/her/hers)
Clinical Associate/Instructor
Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine
Cockeysville, Maryland, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Although the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) released updated guidelines in 2017 for universal administration of the initial hepatitis B vaccine for newborns, there continues to be practice variation and vaccine administration delays for universal routine prophylaxis in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU). Such delays can increase risks for perinatal acquisition and are associated with delays in future childhood immunizations.
Objective: This project aimed to increase the on-time administration of the birth dose of the hepatitis B vaccine from 46% to ≥ 70% by December 2020 at a level III and level IV NICU within the same health system.
Design/Methods:
This project utilized the Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) model for quality improvement (QI). In PDSA 1, a multidisciplinary stakeholder group reviewed data, constructed an aim, and identified key drivers for improvement (Fig. 1). The group developed and implemented unit guidelines to better define medical stability for the NICU population. In PDSA 2, the group developed and implemented an updated progress note template which prompts the provider with the AAP-recommended time for vaccine administration. Data review continued in PDSA 3. The outcome measure was the on-time administration rate for the initial hepatitis B vaccine for inborn NICU patients born to hepatitis B negative mothers, defined as administration within day of life (DOL) 1 for infants with birth weight ≥ 2 kg and within DOL 30 for those with birth weight < 2 kg. The process measure was the rate of on-time or valid reason to delay immunization in accordance with the guidelines. Measures were tracked using statistical process control (SPC) P-charts from January 2019 to May 2021. Patients were excluded if they were transferred or decreased prior to the date immunization was due.
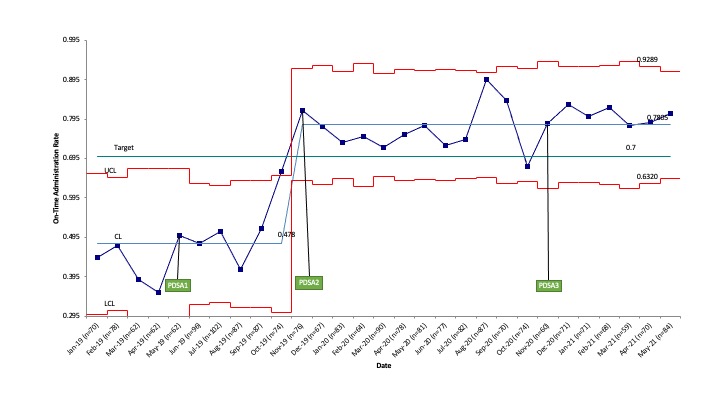
Results: There were 2,192 patients who met inclusion criteria. For the on-time administration rate, the SPC chart demonstrated an upward center line shift from 46% to 52% (Fig. 2). For the rate of on-time administration or valid reason to delay immunization, there was an upward center line shift from 48% to 78% (Fig. 3). Improvements were demonstrated in both birth weight groups and both locations.
Conclusion(s): This study used QI methods to identify barriers to delayed hepatitis B prophylaxis in the NICU and improve the timeliness of administration across two sites. The implementation of clinical guidelines tailored to this patient population and changes to the progress note template were successful in creating and sustaining change and may be beneficial at other NICUs. 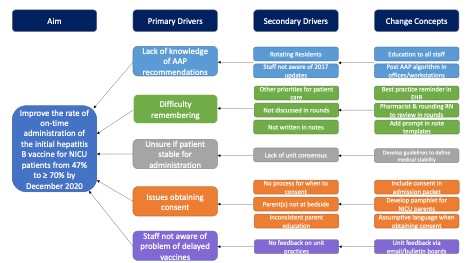
.jpg)