Neonatal Clinical Trials
Neonatal Clinical Trials 2
285 - Effect of Kangaroo Mother Care Transport in Preventing Moderate Hypothermia In Low Birth Weight Babies While Being Transported Home After Discharge: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Publication Number: 285.428

Somashekhar M. Nimbalkar, MD
Professor of Neonatology
Bhaikaka University
Karamsad, Gujarat, India
Presenting Author(s)
Background: The transport of neonates is often neglected, which has resulted in high mortality of neonates during transport.
Objective: To determine the effectiveness of kangaroo mother care (KMC) in terms of hypothermia prevention during transport from hospital to home for low birth weight neonates.
Design/Methods:
Study design: Randomized controlled trial
Participants: A total of 152 low birth weight neonates (Between 1 kg and 2.5 kg at birth) being discharged from the neonatal intensive care unit of our hospital between March, 2021 to August, 2022.
Intervention: Neonates in the study group (n=76) received KMC during transport from the hospital to home, while the control group (n=76) received routine care during transport. Axillary temperature was recorded in both groups at the time of discharge, every 5 minutes during transport, and on reaching home.
Travel distance was considered within 30 km radius with the expectation of reaching home within 30 min. All the newborns were transported in a close vehicle (ambulance or car). During transport, newborns were breastfed on demand in both groups. Mothers wore traditional clothes (gown or saree) during transport. No external heating (warming) device was used in either group.
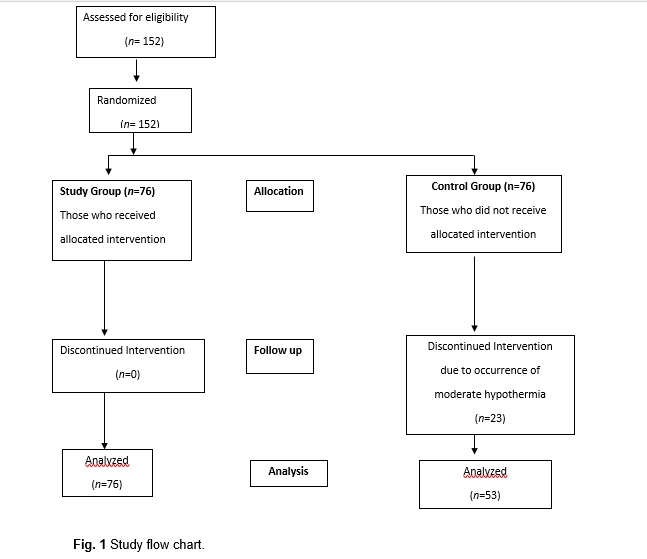
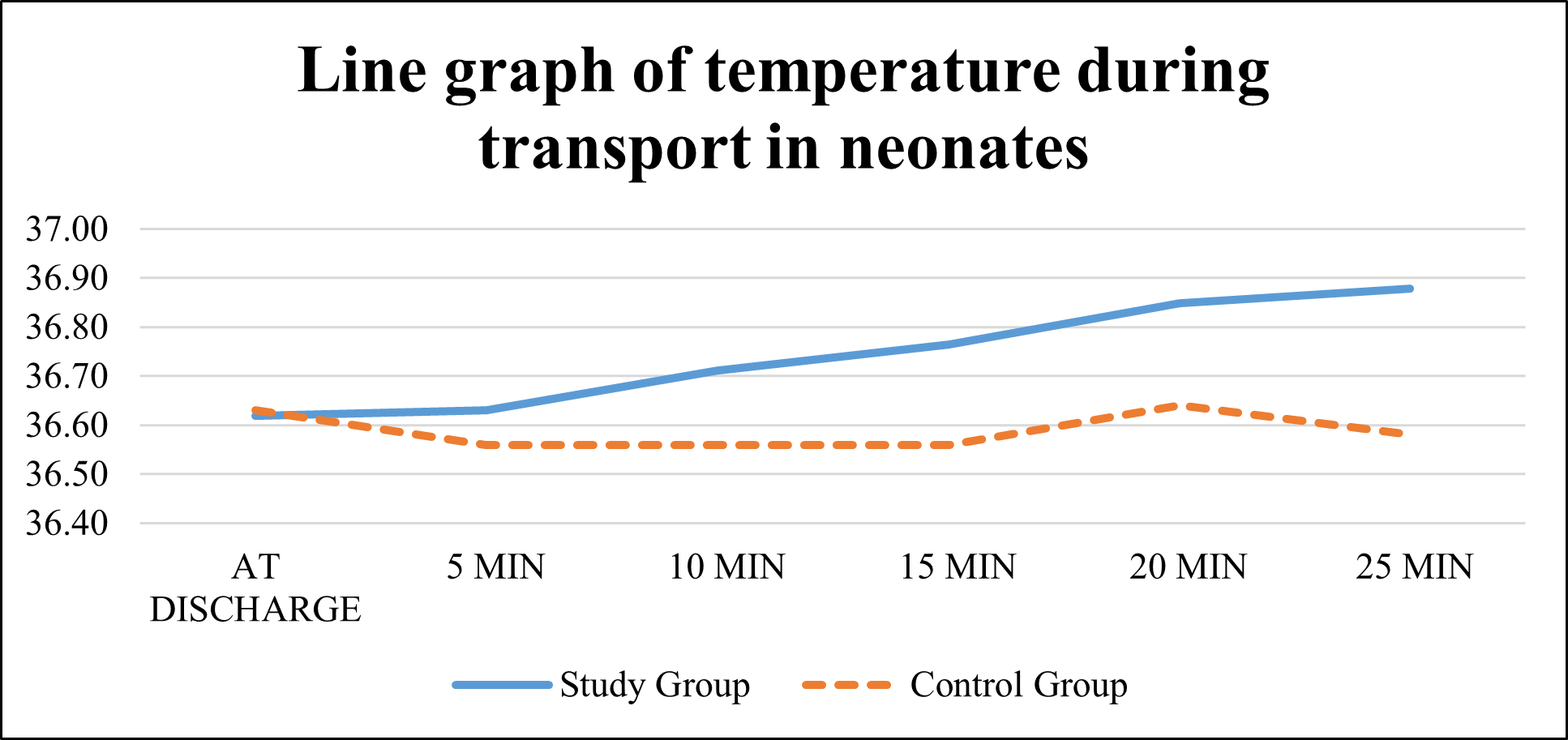
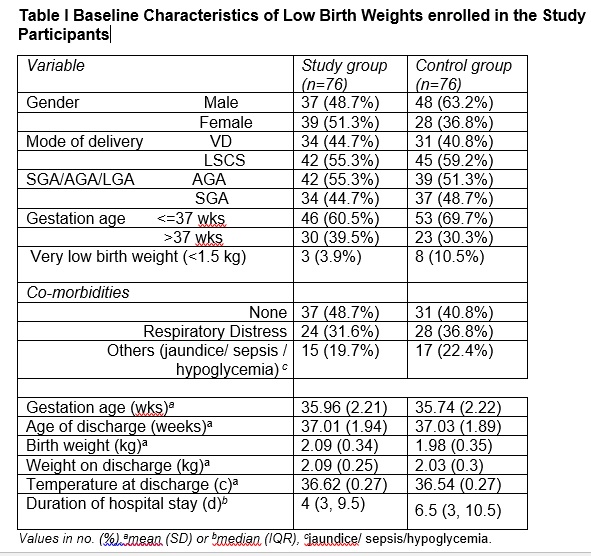
Outcomes: Hypothermia episodes in neonates while receiving KMC compared to neonates not receiving KMC. From March, 2021 to August, 2022, 152 neonates (76 in the study group and 76 in the control group) were randomized (Fig. 1). The baseline profile of the study participants is depicted in Table I. All the baseline characteristics were similar across the groups. The primary endpoint of the study was moderate hypothermia. In the first ten minutes of travel during transport, 23 neonates in the control group experienced moderate hypothermia, which was statistically significant [0% vs 30.26%; P< 0.001]. From 10 minutes of transport, till the neonates reached home, the mean (SD) temperature in the study group was significantly higher than in the control group. (Fig. 2). The number of mild hypothermia episodes was comparable across groups at discharge [21 (27.6%) vs 17 (22.4%);0.45] and at 5 minutes during transport [17 (22.4%) vs 26 (34.2%);0.10]. The control group has statistically significantly more mild hypothermia episodes than the study group from 10 minutes of transport to 25 minutes. Also similar result was noted when neonates reached at home [4 (5.3%) vs 22 (41.5%); p< 0.001].
Results:
Conclusion(s): Low birth weight Neonates receiving KMC showed optimal thermoregulation, whereas a high incidence of moderate hypothermia was seen among neonates receiving conventional care during transport.