Neonatal Quality Improvement
Neonatal Quality Improvement 6
211 - Improvement in daily weight gain in preterm infants after introducing standardized feeding guidelines
Monday, May 1, 2023
9:30 AM - 11:30 AM ET
Poster Number: 211
Publication Number: 211.44
Publication Number: 211.44
Dhruv Gupta, Pediatrix Medical Group of El Paso, El Paso, TX, United States; Marcella T. Mascher-Denen, Other, El Paso, TX, United States; Marryam Khan, Pediatrix Medical Group, El Paso, TX, United States; Fernando Najar, The Children's Hospital at Providence, El Paso, TX, United States; Jenifer Gehlsen, Pediatrix Medical Group of El Paso, El Paso, TX, United States; Mia M.. Guerrero, Pediatrix Medical Grouo, El Paso, TX, United States; Lilliana E. Meza, Pediatrix Medical Group, El Paso, TX, United States; Gregory Welch, Pediatrix, EL PASO, TX, United States

Dhruv Gupta, MD, FAAP
Medical Director
Pediatrix Medical Group of El Paso
El Paso, Texas, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Nutrition and optimal weight gain are essential in preterm infants. Poor nutrition and impaired weight gain in preterm infants is associated with higher rates of cerebral palsy and adverse neurodevelopmental outcomes in later life. Comparison of outcome data from the Pediatrix® clinical data warehouse showed that the median daily weight gain in first 28 days for infants with birth weight ≤ 1500gms from 2018-2019 in the neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) covered by our practice group was in the lowest 33rd percentile.
Objective: This quality improvement project sought to improve the median daily weight gain in first 28 days for infants with birth weight ≤ 1500gms, by instituting standardized feeding guidelines across all the NICUs covered by our practice group by at at least 30%.
Design/Methods: This study included all infants with birth weight ≤ 1500 g, born across seven different NICUs in El Paso, TX and Las Cruces, NM from 2018- 2022 and were in the NICU on their 28th day of life. These NICUs are covered by the same neonatology practice group. The study was divided into 3 periods: 1, baseline (2018-2019); 2, initial changes based on cycles of Plan-Do-Study-Act (2020); and 3, post full implementation of the feeding guidelines (2021-2022). The feeding guidelines included feeding advancement protocols and milk fortification protocol for different weight categories along with weekly documentation of weight gain. It also included multivitamin and iron supplementation guidelines. As a balancing measure, necrotizing enterocolitis rates were measured as well, in the different study periods. The primary outcome was median daily weight gain in first 28 days for infants with birth weight ≤ 1500gms. The other outcome measure included rates of necrotizing enterocolitis.
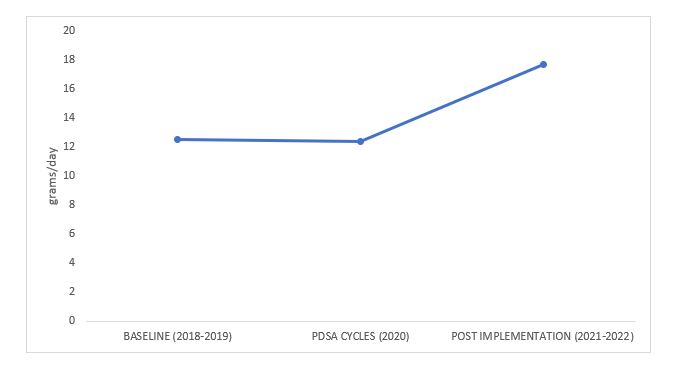
Results: The study population over the 3 periods included 601 infants. Out of these, 248 infants were included in the baseline data (2018-2019), and 231 infants were included in the data post full implementation of the feeding guidelines (2021-2022). Median daily weight gain in first 28 days in infants with birth weight ≤ 1500gms, improved significantly after the feeding guideline implementation, from 12.5 grams per day to 17.7 grams per day (P value 0.007). During the same time period, the necrotizing enterocolitis rate remained stable at 1.2% (2018-2019) to 0.75% (2021-2022).
Conclusion(s): Standardized feeding guidelines successfully improved median daily weight gain in preterm infants, with no significant difference in the rates of necrotizing enterocolitis.