Health Equity/Social Determinants of Health
Health Equity/Social Determinants of Health 9
579 - Can the Electronic Health Record Increase WIC Enrollment & Improve Provider Communication for Medicaid or Uninsured Children Under Age 5? A Mixed Methods Study
Publication Number: 579.413

Kimberly Montez, MD, MPH, FAAP (she/her/ella)
Assistant Professor, Associate Program Director, Vice Chair JEDI
Wake Forest University School of Medicine
Winston-Salem, North Carolina, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: WIC participation has numerous health benefits; yet many eligible families do not enroll. Little research exists about referrals and care coordination between healthcare providers and WIC.
Objective: We sought to determine: (a) whether electronic health record (EHR)-based referrals result in WIC enrollment and (b) to evaluate patient perspectives on communication between healthcare and WIC providers.
Design/Methods:
This cross-sectional study was part of a larger mixed methods study. WIC staff in 3 counties were granted secure, limited online access to the health system’s EHR, allowing users to view medical charts, send/receive secure messages with healthcare teams, and receive WIC referrals. For children aged 0-4 years with uninsurance or Medicaid, a Best Practice Advisory (BPA) fired during well visits prompting medical staff to screen for WIC participation and assess interest in referral if not participating. Automated BPA referrals were sent directly to WIC’s EHR in-basket to begin enrollment. To determine program effectiveness, structured data were extracted monthly for all BPA results November 2021-October 2022. WIC referral dispositions were verified by WIC staff via their internal records and were summarized across the study period using descriptive statistics. To understand perspectives, 100 caregivers of children < 6 yrs who attended 1 of 8 participating clinics, received WIC benefits within 1 yr, and underwent BPA screening were recruited March-July 2022 for an interviewer-administered phone survey. Results were analyzed using descriptive statistics. Comparisons between demographics were evaluated using the Chi-Square test or t-test.
Results:
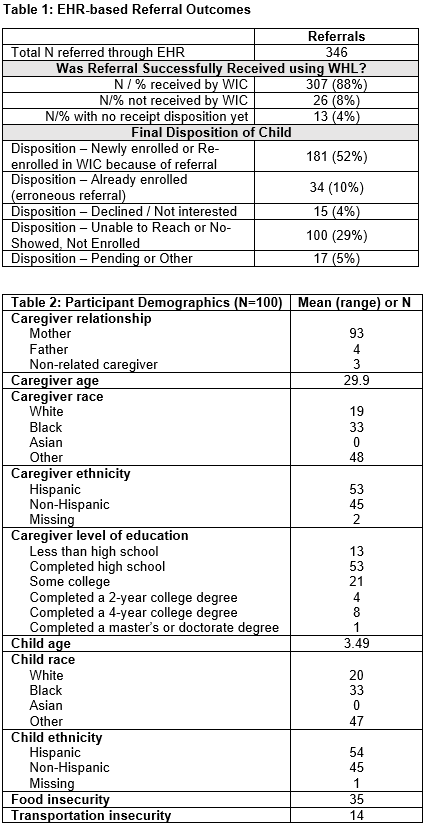
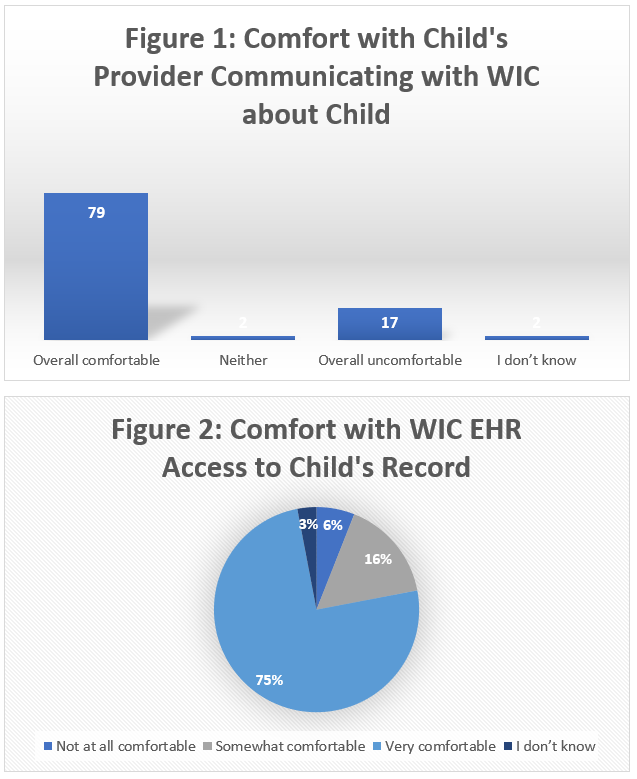
358 patients agreed to WIC referral using BPA screening. Of these, 59.2% (212) were enrolled in WIC (Table 1). Most survey respondents were mothers (93%). Respondents had a mean age of 29.9 years, self-identified as Black (33%), Other (48%), or White (19%), and Hispanic (53%); 53% completed high school (Table 2). The mean child age was 3.5 yrs; 35% reported food insecurity; 72% reported running out of benefits by month’s end. 79% were overall comfortable and 17% were overall uncomfortable about their child’s doctor communicating directly with WIC (Figure 1); 91% were overall comfortable and 6% not at all comfortable about WIC accessing their child’s EHR (Figure 2). Caregiver race, ethnicity and age were not associated with reported comfort with information sharing between WIC and the health system.
Conclusion(s):
Providing secure EHR access to WIC and EHR-based WIC referrals has the potential to improve communication and access to services.