Neonatal Cardiac Physiology/Pathophysiology/Pulmonary Hypertension
Neonatal Cardiac Physiology/Pathophysiology/ Pulmonary Hypertension 5
122 - Left ventricular dimensions and function by three-dimensional echocardiography are associated with brain injury in neonatal encephalopathy
Publication Number: 122.427

Pierre Elias (he/him/his)
Student
McGill University Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences
Montréal, Quebec, Canada
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Despite therapeutic hypothermia (TH), many neonates with neonatal encephalopathy (NE) develop brain injury. These neonates often present with cardiac dysfunction in the first days of life.
Objective: To evaluate the association between brain injury on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and cardiac function of neonates with NE treated with TH, using three-dimensional echocardiography (3D-ECHO).
Design/Methods: Single-center prospective study of neonates with moderate to severe NE treated with TH between 2019 and 2021. 3D-ECHOs were performed on day of life (DOL) 2 (during TH). Left ventricular (LV) metrics were measured by 3D-Speckle Tracking Echocardiography and were compared between neonates with brain injury categorized by Barkovich score vs. without.
Results:
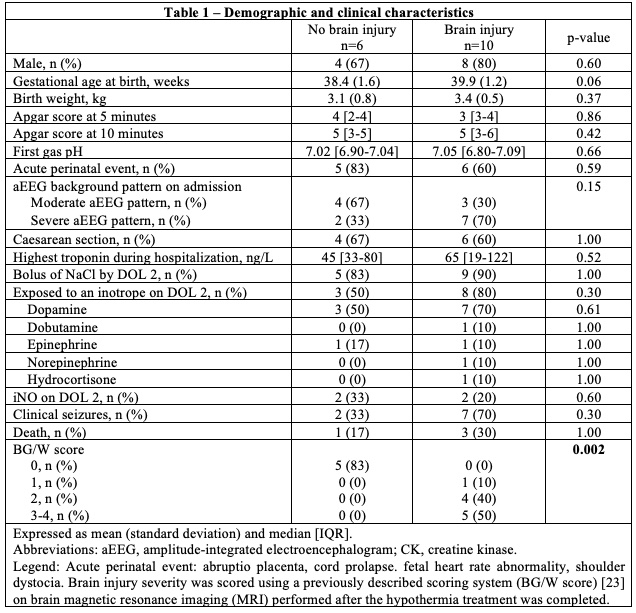
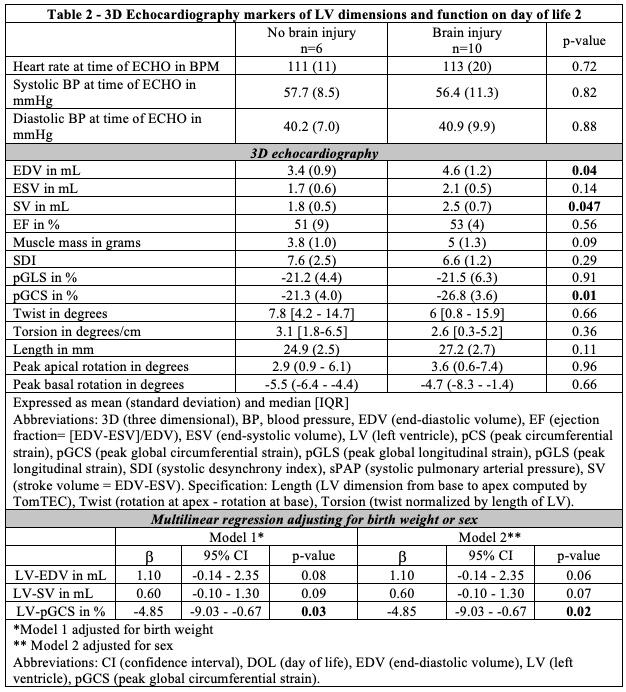
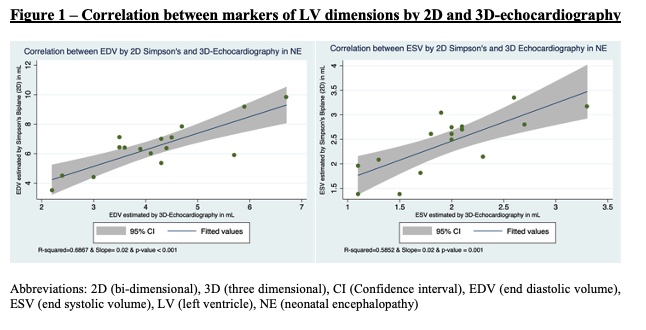
Out of 16 infants included in the study, ten had injury on brain magnetic resonance imaging. Demographic/clinical characteristics were similar between groups (Table 1). Neonates with brain injury had higher left ventricle end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) 4.6 [1.2] vs 3.4 [0.9] mL; p=0.04. They also had higher 3D-derived stroke volume (1.8 [0.5] vs 2.5 [0.7] mL; p=0.047) and higher peak global circumferential strain (-26.6 [3.6] vs –21.3 [4.0] %; p=0.01). We found a good correlation between 2D and 3D methods for EF assessment as shown in figure 1.
Conclusion(s): Neonates with moderate to severe NE developing brain injury despite TH had differences on their 3D-ECHO LV metrics on DOL 2 compared to neonates without injury. Future studies on early identification of these markers will be useful to determine the neonates at highest risk for brain injury and to optimize their hemodynamic management.