General Pediatrics: Primary Care/Prevention
General Pediatrics 2
118 - Validation of a “Novel” Numeracy Screening Tool (The Number Farm)
Publication Number: 118.115

John S. Hutton, MS MS (he/him/his)
Assistant Professor
Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center
Cincinnati, Ohio, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background:
Numeracy is a developmental process from basic knowledge about quantity to formal math concepts. Early skills can be learned via home activities. Numeracy is vital in the global economy with wide disparities in achievement and environmental and genetic contributors. The AAP recommends developmental screening to support school readiness. A book-based approach to literacy screening is validated for preschool-age children. Numeracy screening tools are not currently integrated into pediatric practice.
Objective: To describe development of The Number Farm (TNF), a book-based approach to numeracy screening for preschool-age.
Design/Methods:
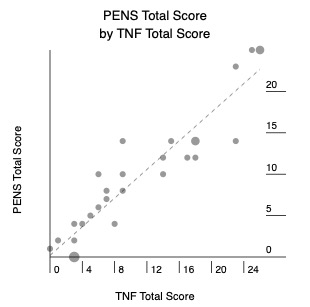
The TNF conceptual model involves skills selected via literature review in collaboration with experts (Table 1). A mockup of TNF (front/back covers, 7 page spreads) was developed with K-level, rhyming text and illustrations featuring barnyard animals (Figure 1a). This was first informally shown to parents to ensure clarity. Actual screening used an 11-item, scripted assessment based on the mockup. Points are for correct answers, max 28. The Preschool Early Numeracy Screener (PENS; Figure 1b) is a 25-item, normed measure with similar components validated for 3-5 years old, used as the gold standard. This pilot was at Cincinnati Children’s primary care clinics during well-visits, all aspects by pediatric residents. Inclusion criteria: gestation >34 wks, age 36-59 mos, no developmental disorder, fluent in English, no illness. Families received a gift card. After consent and demographics, TNF and PENS were administered in random order to the child, noting screening time and barriers. Post-screening, the parent and child completed a Likert impression survey. 31 children were screened, mean age 50 months (+4; 36-71), 17 boys, 14 girls. Barriers were rare, most often interruption by clinic staff. Admin time < 10 min. Mean TNF score was 11 (+3; 0-26), and PENS score was 10 (+3; 0-25), positively correlated (Pearson r=0.94, p< 0.001; Figure 2). All but 1 TNF item had >10% density per response option (10). Item-measure correlations were positive (0.53-0.85). Cronbach’s alpha was 0.89. TNF may be an efficient, reliable, useful and fun way to screen numeracy skills at preschool-age during well-visits. Further studies are needed to expand validation and guide TNF refinement, including a children’s book version.
Results:
Parent impression of TNF was favorable: 100% helpful at a doctor visit, 75% Just Right time spent, 94% learned about child’s skills (66% had been worried), 69% surprised by score, 97% inspired to work with child at home. 97% of children reported TNF as Fun.
Conclusion(s): 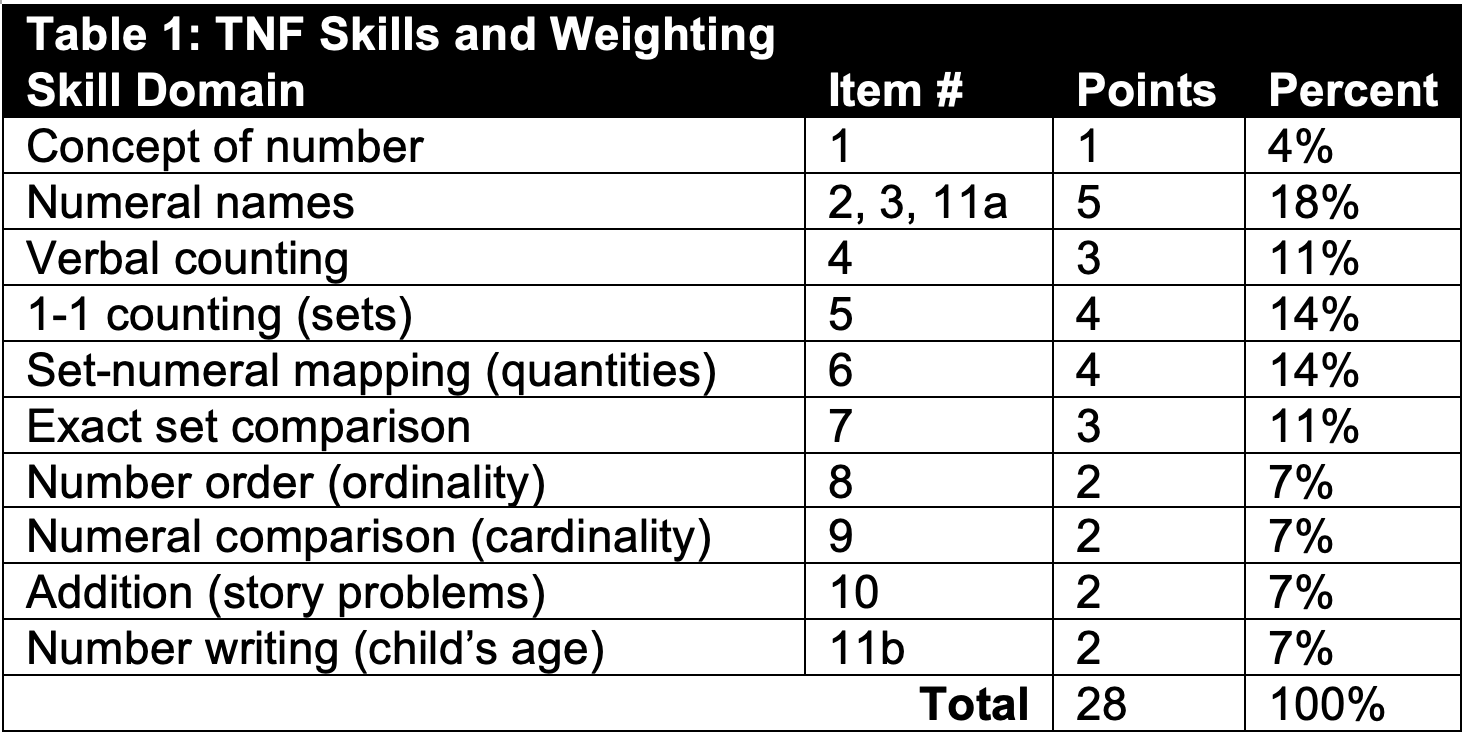
.png)