Neonatal Fetal Nutrition & Metabolism
Neonatal GI Physiology & NEC 4: Gut Health, Enteral Nutrition and Oral Feeding
92 - Timing of introduction of complementary feeds in infants born preterm less than 35 weeks gestation: a randomized control trial
Publication Number: 92.236
- SN
Sushma Nangia, MBBS, MD, DM (she/her/hers)
Professor
Lady Hardinge Medical College & Kalawati Saran Children's Hospital
New Delhi, Delhi, India
Presenting Author(s)
Background:
Evidence regarding the optimal timing of introduction of complementary feeding in preterm infants is scarce. Some studies have reported different anthropometric parameters and their changes with the timing of weaning, but whether the complementary feeds need to be initiated at 6 months corrected or chronological age still remains unresolved.
Objective:
To study effect of initiation of complementary feeding in preterm infants (< 35 weeks GA) at 6 months of Corrected age versus 6 months of Chronological age on anthropometric parameters after 6 months of weaning.
Design/Methods:
This open-label, randomized trial, enrolled preterm infants (< 35 weeks GA). Eligible infants were tracked from birth and were randomly assigned to two groups. Infants in Group A were initiated of complementary feeding at 6 months corrected age whereas infants in Group B were initiated on complementary feeds at 6 months chronological age. Following arthrometric parameters (e.g. WAZ, HAZ, WHZ, HCZ, MUAC-Z & TSFZ as per WHO Multicentre Growth Reference Study growth standards) were recorded after 6 months of the introduction of complementary feeding. Trial registration CTRI/ 2022/ 09/ 045682.
Results:
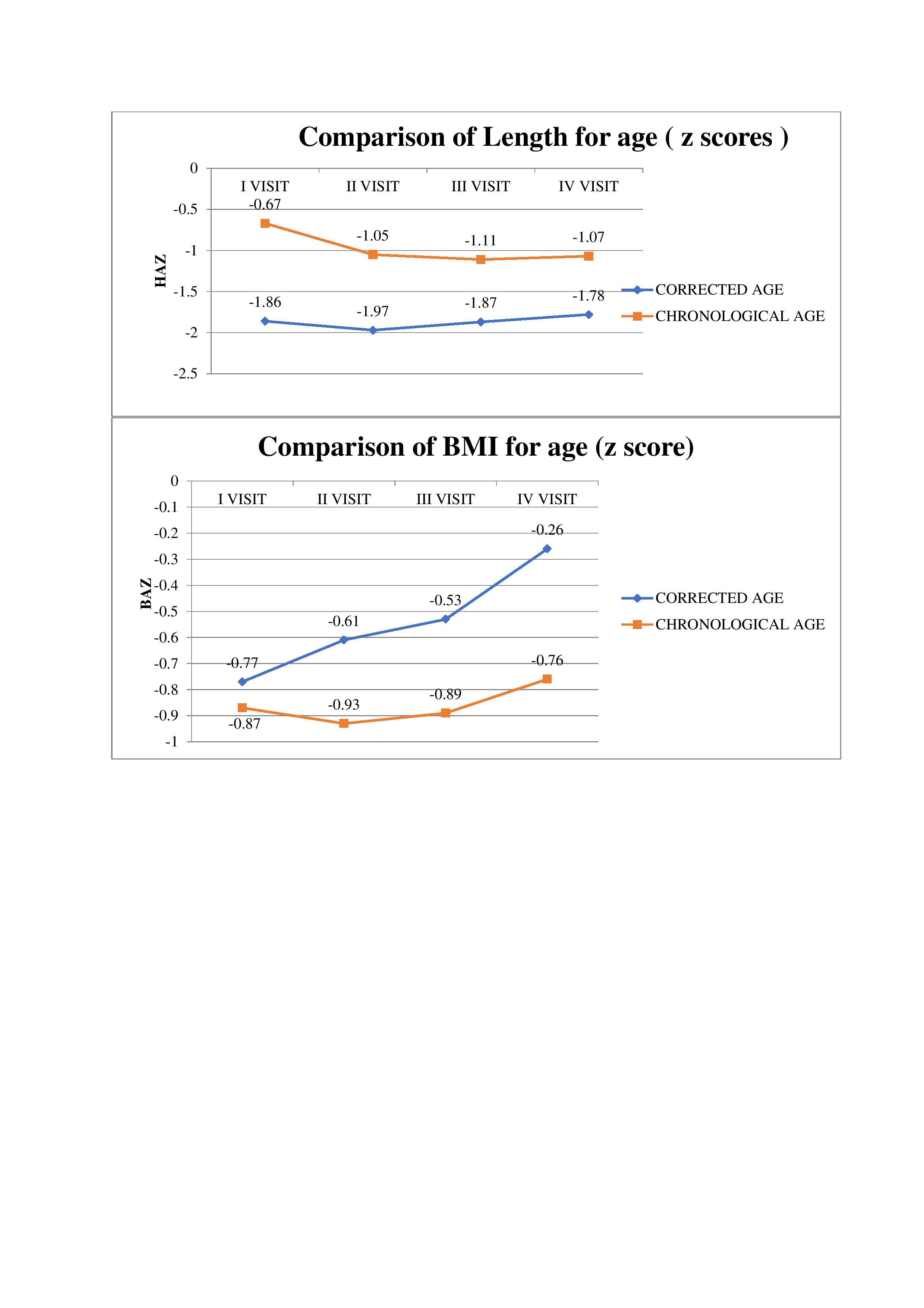
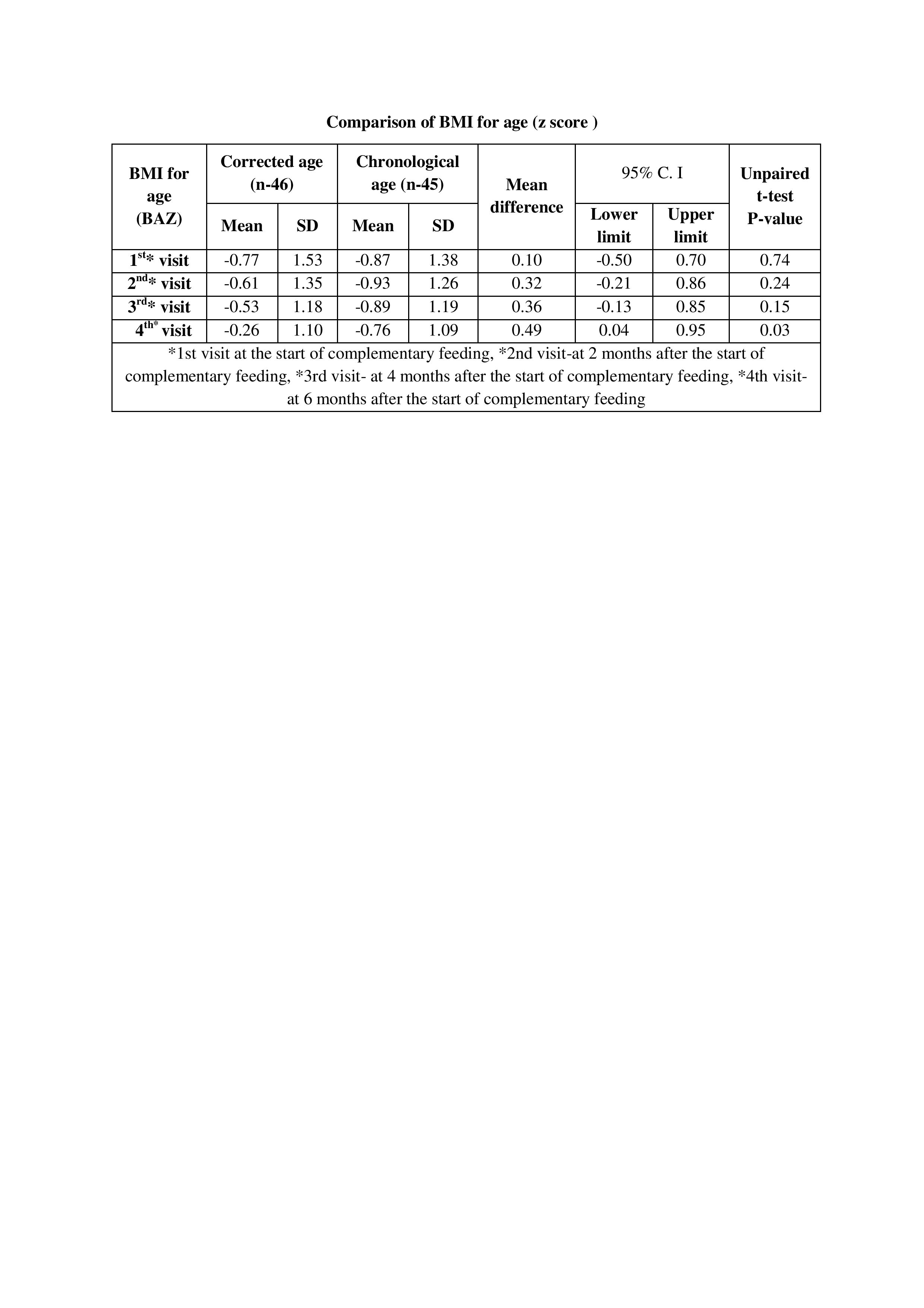
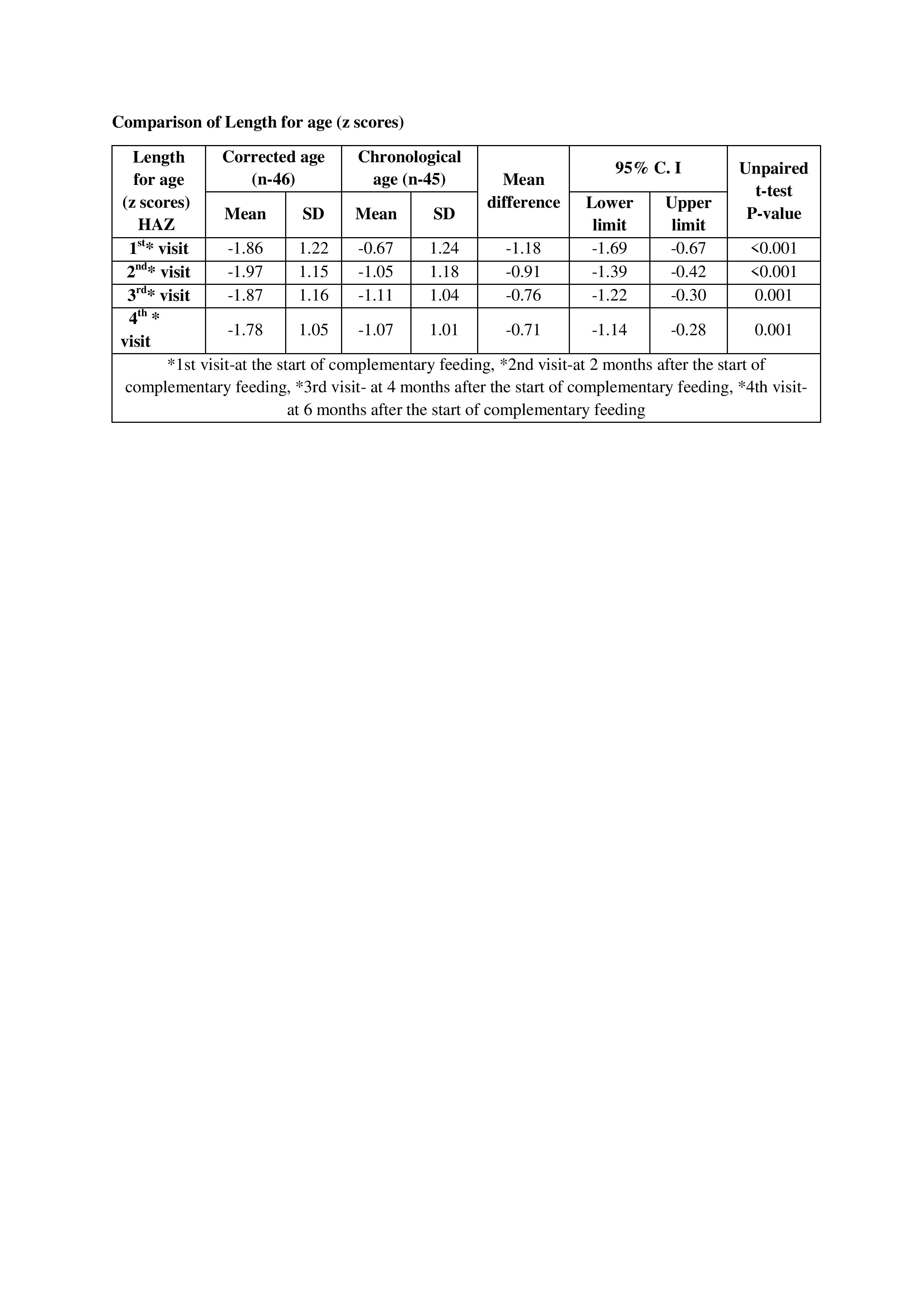
The present study enrolled and randomized 91 infants between 26 0/7 weeks to 34 6/7 weeks of gestation. Of these, 46 were randomized to the corrected age group (Intervention group-A), while 45 to the chronological age group (Control group-B). Infants in the chronological age group had significantly better WAZ scores at the start of complementary feeding [z score in the corrected age group was (-1.66z), compared to (-1.02 z) score in the chronological age group(p-0.02)] ,but there was no significant difference after 6 months of complementary feeding. The babies in the chronological age group had a significantly better length for age z score (HAZ) scores at the start of complementary feeding [MD(-1.18)] & after 6 months of complementary feeding[MD (-0.71)]. Although the mean difference in both the groups gradually decreased with each follow-up visit but remained statistically significant throughout (p-0.001). At 6 months of complementary feeding, babies in the corrected age group had a significantly higher BMI z-score[MD (0.49)]which was a consequence of increasing weight but no appreciable gain in length in this group of infants (p-0.03). No significant difference was detected in the rate of re-hospitalization and or other outcome parameters.
Conclusion(s):
Preterm infants between 26 0/7 weeks to 34 6/7 weeks of gestation started on complimentary feeding at 6 months chronological age achieve better linear growth & sustained weight gain.