Neonatal Nephrology/AKI
Neonatal Nephrology/AKI 1
225 - Nephrology 3: Glomerular/Clinical and Basic Science
Publication Number: 225.242

Cara L. Slagle, MD (she/her/hers)
Assistant professor
Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center
Cincinnati, Ohio, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background:
Nephrotoxic medication exposure is common in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) and is a cause of acute kidney injury (AKI). Baby NINJA- Nephrotoxic Injury Negated by Just-in-time Action, is a surveillance process aimed to reduce high NTM (hNTM) exposure, AKI prevalence and intensity in the NICU, via daily serum creatinine (sCr) screening. Urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (uNGAL) has previously been associated with neonatal AKI and offers a less invasive alternative screening mechanism.
Objective: To compare differences between pre- and post- implementation of a less invasive screening pathway.
Design/Methods:
This single center study tracked use of an alternative pathway (Figure 1) for daily screening following patient triggering of Baby NINJA in June 2021 to July 2022. Providers were given the daily option for sCr monitoring or obtainment of uNGAL. If uNGAL is >=150 ng/mL than screening was transitioned to daily sCr until 2 days post hNTM termination. Screening compliance was tracked for quality metrics and was calculated by actual daily sCr or uNGAL obtained divided by days of hNTM exposure +2 days. Process control methods were used to determine trends from baseline. Statistical analysis included Mann-Whitney U Test.
Results:
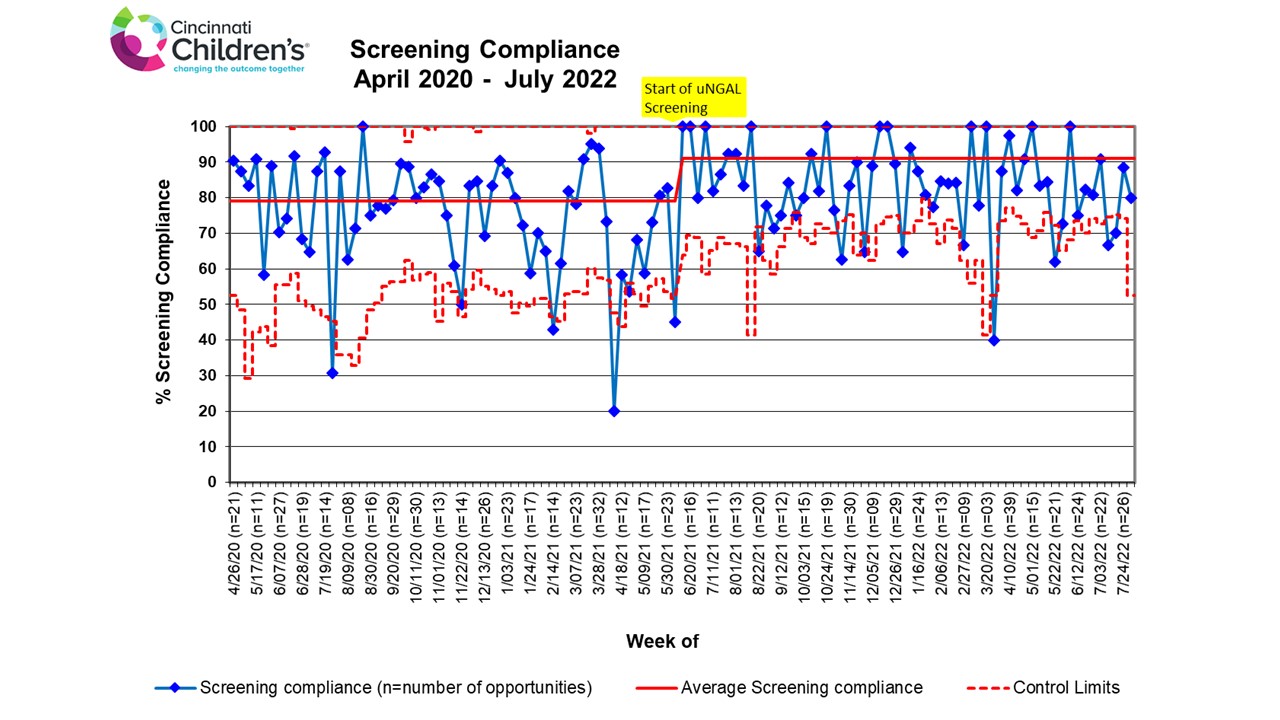
Daily screening compliance following initiation of the alternative screening pathway increased following implementation (pre =78% vs. post= 84%, p= 0.003) and is demonstrated by control chart, Figure 2. 37% of daily screening following implementation occurred by uNGAL. Following 99 new hNTM exposures, there were 21 conversions to daily sCr monitoring. Rates of hNTM exposure per 1000 patient days decreased from 8% to 6%, p=0.0003. AKI rates and intensity did not differ between the two time periods. Median uNGAL concentration that triggered conversion was 263 ng/mL (IQR: 195-825 ng/mL). Median birth gestational age of those that converted was 30 weeks (IQR 25-35 weeks). Following implementation, 8 subjects experienced a combined total of 18 days of AKI during hNTM exposure. Five subjects had AKI prior to Baby NINJA trigger and continued daily SCr screening. Two subjects were triggered by uNGALs of 859 ng/mL and 2835 ng/mL. Five subjects had an outcome of death within 48 hours of meeting Baby NINJA criteria. One subject had urine NGAL trended during their AKI episode with a median concentration of 946 ng/mL [IQR: 594 – 2724 ng/mL].
Conclusion(s):
Urine NGAL offers a less invasive screening pathway for AKI from nephrotoxic medication exposure. .jpg)