Neonatal General
Neonatal General 4: GI-Nutrition-Growth
685 - Metabolomic profile in breastfed late preterm infants versus standard formula milk or postbiotic-supplemented formula milk
Publication Number: 685.232

Giuseppe De Bernardo, MD
Medical Director
Ospedale Buon Consiglio Fatebenefratelli
Napoli, Campania, Italy
Presenting Author(s)
Background:
Exclusive breast milk is recommended from birth to 6 months of life to promote the development of a balanced intestinal microbiota. Human milk provides several bioactive components, from natural probiotics such as Bifidobacterium spp. and Lactobacillus spp., to their metabolites which colonize the intestine of the newborn. However, if breast milk is not available or insufficient, it is used formula milk as a substitute. Infant formula can be supplemented with postbiotics to promote maturation of immune, metabolic and microbial components, similar to breast milk. Postbiotics are preparations composed of both microbial constituents and their metabolites, produced during fermentation.
Objective: The aim of the study was to detect the differences in the metabolome of the newborns fed with breast milk, standard formula milk or formula milk supplemented with 0,5 ml of SMART D3 MATRIX.
Design/Methods:
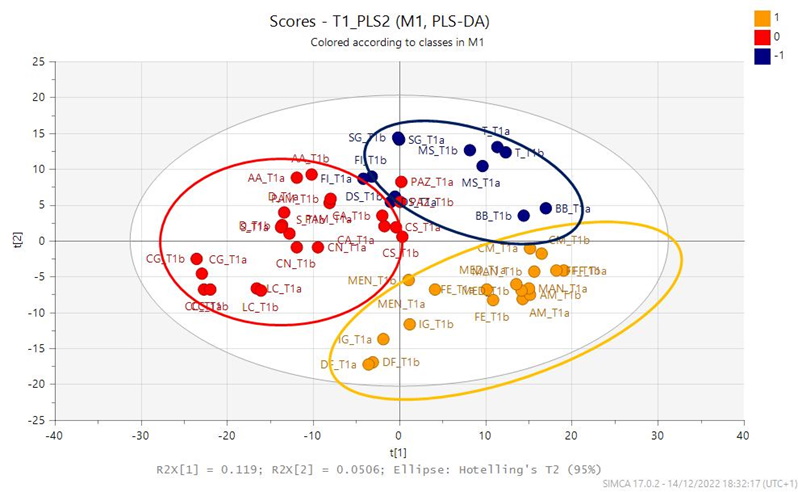
A prospective single-center observational cohort study was conducted from March to December 2022 at Buon Consiglio Fatebenefratelli Hospital. They were enrolled 27 late preterm newborns with body weight appropriate to gestational age. The patients were divided into 3 groups: group A formula + SMART D3 MATRIX feeding (7 patients), group B standard formula feeding (9 patients), group C breast feeding (11 patients). Stool samples for metabolome study were collected at T0 (5-7 days after birth) and T1 (1 month old). Stool samples were analyzed by Thermo scientific LTQ Orbitrap XL LCMS system, constituted of a quaternary Accela 600 pump and an Accela autosampler, connected to a linear Trap-Orbitrap hybrid mass spectrometer with electrospray ionization. LC-MS raw data of T0and T1 samples were processed separately using the software mzmine 2.53 obtaining two data matrix that were processed by SIMCA P software 17.0 (Umetrix AB, Umea Sweden) for the Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Partial least Square-Discriminant Analysis (PLS-DA).
Results: Metabolomics performed with untargeted approach relived at T0 and T1 a good separation between stool samples. In particular from PLS-DA score scatter plot of T0 and T1 samples (Figure 1 and 2), group B (in orange) are located in the right down part of the plot and really far from group C (in red) and group A (in blue).
Conclusion(s): Fecal metabolites of breast fed infants were closer and more similar to that of formula plus post biotic fed infants. .jpg)