Neonatal Respiratory Assessment/Support/Ventilation
Neonatal Respiratory Assessment/Support/Ventilation 2: Physiology 1
326 - Intra-amniotic LPS and intramuscular Betamethasone decrease plasma and lung levels of budesonide in preterm lambs ventilated after combination of surfactant with budesonide
Publication Number: 326.345

Noah Hillman, MD
Professor of Pediatrics
Saint Louis University School of Medicine
St. Louis, Missouri, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: The combination of surfactant and budesonide may decrease BPD rates and severity in preterm infants. Budesonide is detectable in plasma of preterm sheep and infants after intra-tracheal administration. Many preterm infants are exposed to chorioamnionitis and/or antenatal corticosteroids, and it unknown how these may affect the distribution of pharmacokinetics of budesonide.
Objective: To evaluate the effects of antenatal steroids and intra-amniotic LPS on plasma and lung levels of budesonide after mechanical ventilation.
Design/Methods:
Date-mated Ewes at 123±1 day gestational age received either intra-amniotic (IA) saline or IA E. Coli LPS 10 mg and/or Intramuscular (IM) betamethasone 0.25 mg/kg 48 hours and 24 hours prior to delivery at 125±1 day. Lambs were ventilated with injurious ventilation for 15 minutes then normal tidal volume ventilation for 4 hours. At 15 min, lambs received 0.25 mg/kg of budesonide mixed in 200 mg/kg Curosurf via ET tube. Plasma was collected at 15 min after dose, 1 hour, 2 hours, and 4 hours. Budesonide levels were determined from plasma and the lung tissue at end of ventilation with LC-MS. Analysis of tissues after hydrolysis is underway.
Results:
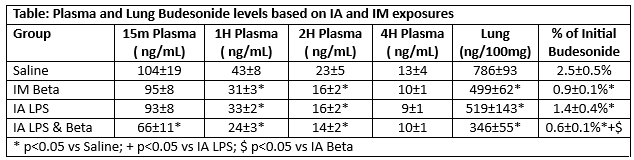
Budesonide was detected in the plasma within 15 minutes of intra-tracheal administration in surfactant (Table). The combination of LPS and Beta decreased plasma levels at 15 min compared to IA Saline, and plasma levels were lower in IM Beta and IA LPS animals at 1H and 2H. Budesonide levels in lung tissue was lower at end of 4 hours with IA LPS and/or IM Beta. The percent of initial Budesonide dose was lowest in the animals receiving IA LPS and Beta. IA LPS and IM Beta had similar decreased levels with additive effects found.
Conclusion(s): Budesonide is detected in plasma within 15 min in all groups. IA LPS or IM Betamethasone decreased plasma budesonide level throughout ventilation period, but less unaltered budesonide is present in the lung at end of ventilation. Analysis of budesonide esters is underway.