Neonatal/Infant Resuscitation
Neonatal/Infant Resuscitation 4
701 - Comparison of Synchronized and Asynchronized Chest Compressions in the Term and Preterm Ovine Perinatal Cardiac Arrest
Publication Number: 701.445
.jpg)
Evan M. Giusto, RN (he/him/his)
Neonatal Transport Nurse
UC Davis Health
Sacramento, California, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Gas exchange is severely impaired during cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) during cardiac arrest despite chest compressions and ventilation with 100% O2.
Objective: To compare continuous chest compressions during ventilation with asynchronous compressions and ventilation (3:1 C:V) in term and preterm lambs.
Design/Methods: Time-dated preterm (~125d gestation; term~147d) and term (~141d) fetal lambs were instrumented and asphyxiated by umbilical cord occlusion until asystole for 5min and delivered. Lambs were randomized to 3:1 C:V following the neonatal resuscitation program (NRP) algorithm, or continuous chest compressions with ventilation provided asynchronous ventilation (CCaV group). Epinephrine was given at 3 minutes and repeated every 3 minutes until return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC).
Results:
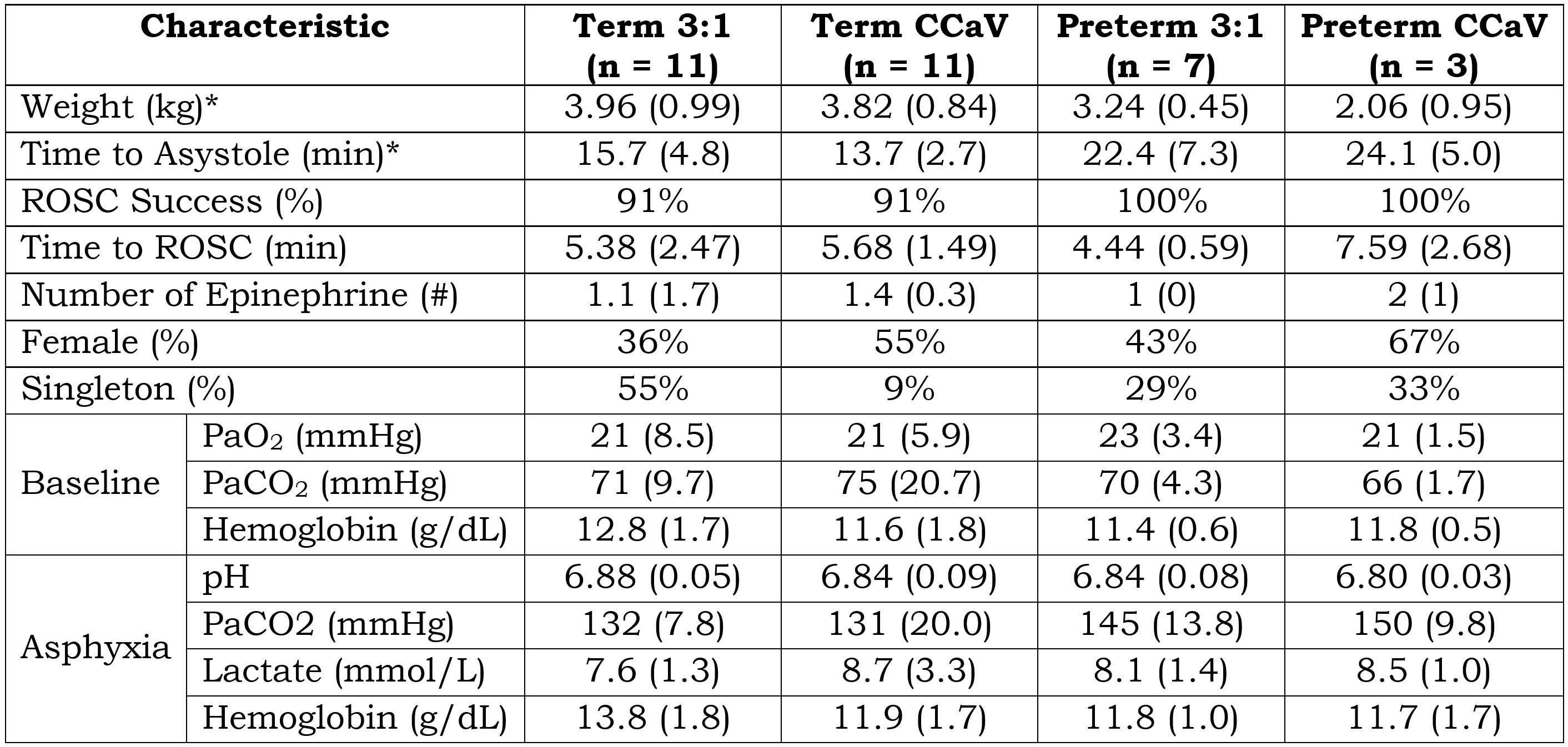
10 preterm lambs were studied and all achieved ROSC. The data gathered was compared to 22 term lambs (published-Vali et al., Pediatric Research 2021). Baseline characteristics, ROSC success, time to ROSC, and number of epinephrine given were similar. Time to asystole from the onset of umbilical cord compression was longer in preterm compared to term lambs (Table 1).
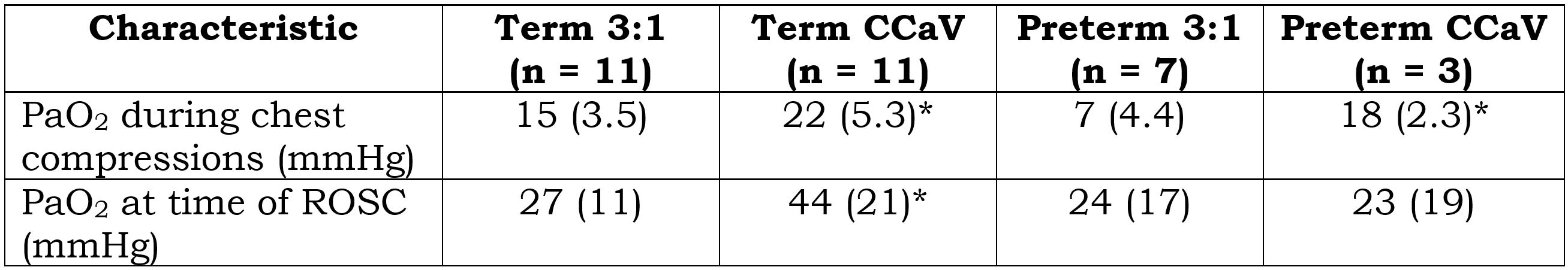
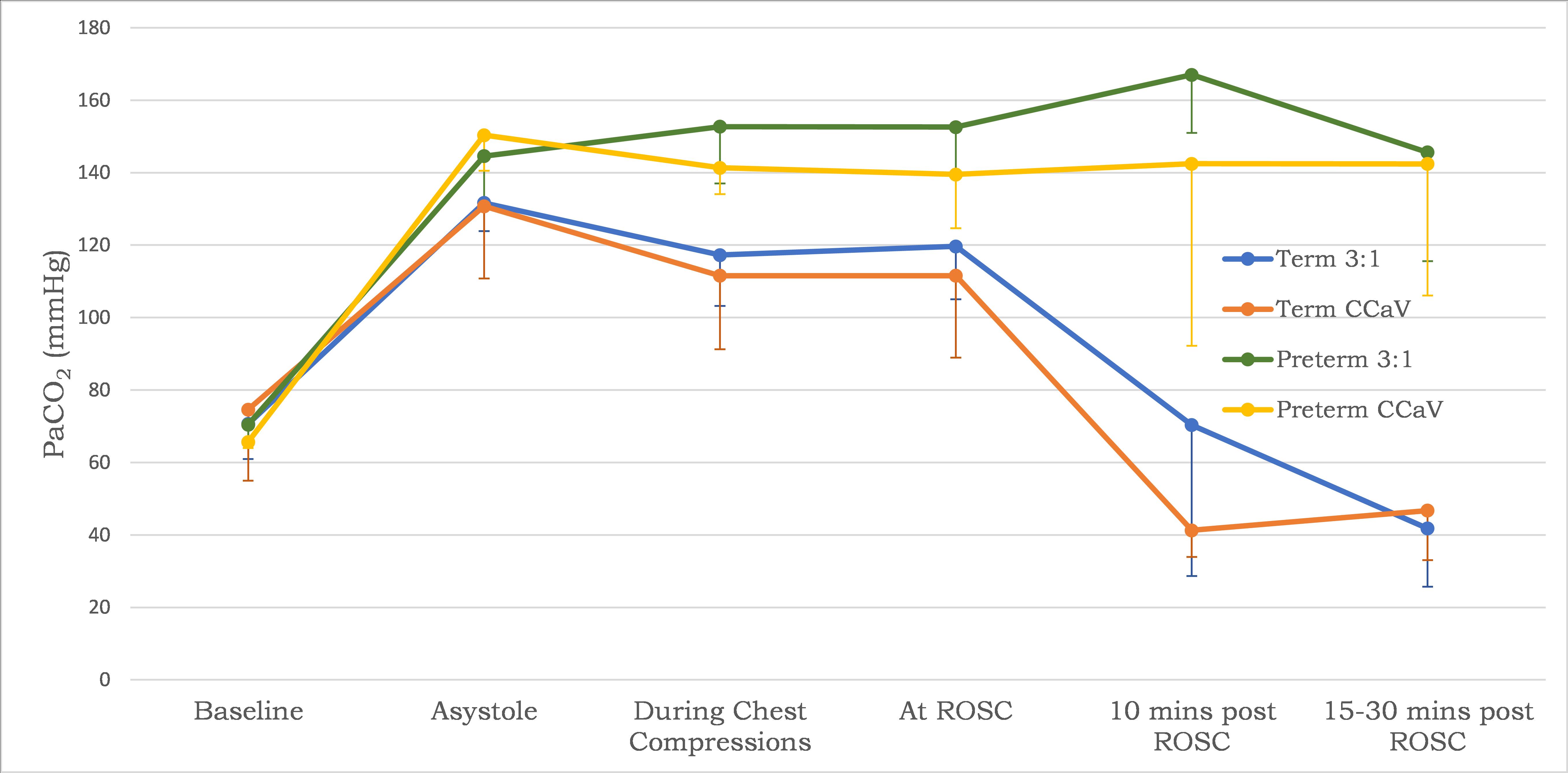
During chest compressions, PaO2 was higher with CCaV in both term and preterm lambs compared to traditional 3:1 C:V group (Table 2). However, both preterm groups had similar PaO2 at time of ROSC. PaCO2 began to decrease in the term but remained high after ROSC in the preterm groups (Figure 1) but these values were not statistical different between CCaV and 3:1 C:V groups.
Conclusion(s): Umbilical cord occlusion results in earlier cardiac arrest in term compared to preterm lambs. Resuscitation utilizing continuous chest compressions and asynchronous ventilation improves oxygenation during chest compressions in both the preterm and term lambs in cardiac arrest compared to traditional 3:1 C:V. The improved oxygenation at and after ROSC seen in the term lambs is not observed in the preterm lambs probably secondary to surfactant deficiency. Resuscitation studies in term animal models may not be applicable to preterm.