Neonatal Quality Improvement
Neonatal Quality Improvement 7
217 - Improving Umbilical Catheter Malpositioning in the NICU
Publication Number: 217.441

Lakshmi Sridhar, MD (she/her/hers)
Neonatal-Perinatal Fellow Physician, PGY-6
University of Rochester, Golisano Children's Hospital
Rochester, New York, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Umbilical venous catheters (UVCs) need to be maintained at the appropriate positioning to prevent severe complications. Malpositioned UVCs in the portal venous system present a risk of hepatic necrosis, liver abscess, portal vein thrombosis, and cavernoma formation. Incorrect placement into the right atrium can lead to arrhythmias, pericardial effusion, and possible cardiac tamponade.
Objective:
To decrease the percent of malpositioned UVCs from a baseline of 62% to 40% by December 2022 in neonates born less than 30 weeks gestational age.
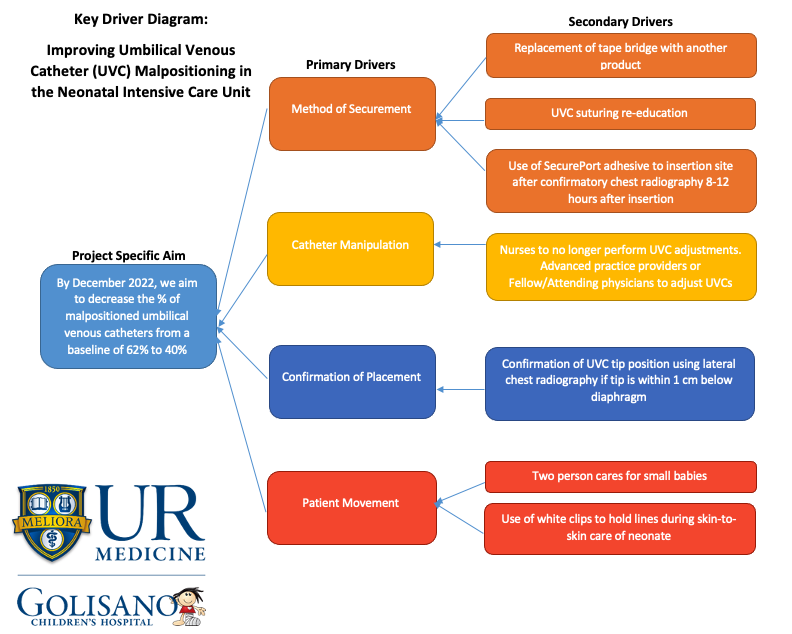
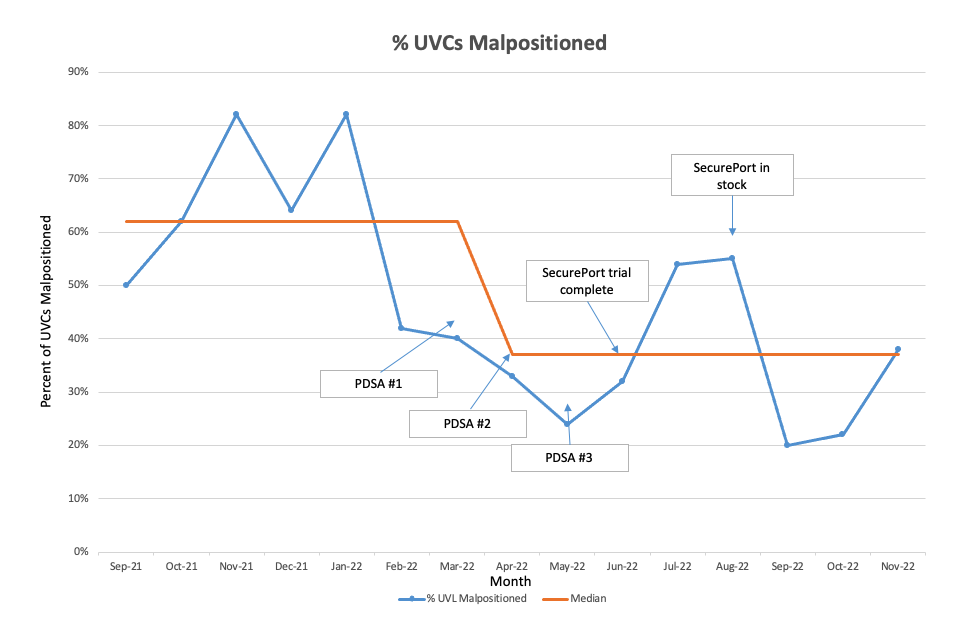
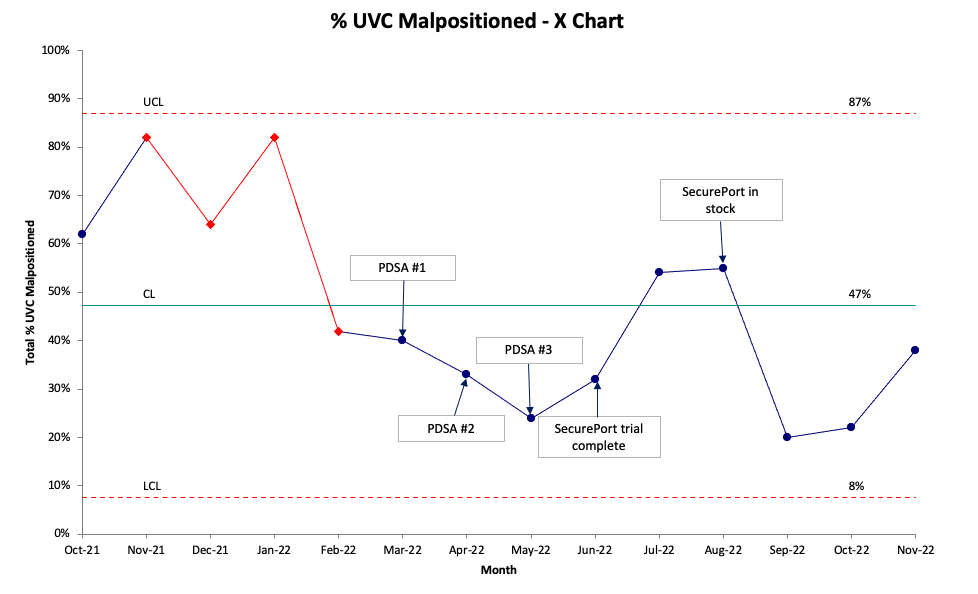
Design/Methods: This was a single-centered quality improvement study that took place in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) at Golisano Children’s Hospital in Rochester, NY over 13 months. A multidisciplinary team of physicians, advance practice providers, and nurses was created. Baseline data was obtained, and a SMART aim statement was created along with a key driver diagram (Figure 1). Various interventions were discussed, and a plan was created for instituting these interventions using the iterative PDSA (Plan-Do-Study-Act) cycle model. The first intervention consisted of re-education of suturing technique to providers who placed UVCs. The second intervention was to have suspected malpositioned UVCs verified as malpositioned with a lateral chest radiograph and to have UVCs adjusted by advance practice providers or physicians instead of bedside nursing. The third intervention was utilizing a cyanoacrylate adhesive called SecurePort, which is applied at 8-12 hours after insertion, to hold the UVCs in place. A trial of SecurePort was performed for one month, data presented to the multidisciplinary team, and then instituted as a new standard of care in the NICU. Run charts and control charts (Figure 2 and 3) were created with outcome, process, and special cause variation in mind and reviewed with the multidisciplinary team at intervals for evaluation.
Results:
Malpositioned UVCs were reduced from a median baseline of 62% to a median of 37% after completion of three PDSA cycles (Figure 2 and 3).
Conclusion(s): Decreasing malpositioned UVCs can be achieved in multiple ways such as re-education of suturing, further evaluation by radiography to determine if a UVC is malpositioned, provider involvement in UVC adjustment, and utilizing SecurePort to prevent malpositioning. These interventions may be employed in other units that are experiencing difficulty with maintaining UVC positioning or facing complications of malpositioned UVCs.