Neonatal Respiratory Assessment/Support/Ventilation
Neonatal Respiratory Assessment/Support/Ventilation 5: Surfactant and NIV 2
677 - PRESSURE TRANSMISSION AND ELECTRICAL DIAPHRAGM ACTIVITY IN PRETERM INFANTS DURING NASAL INTERMITTENT POSITIVE PRESSURE VENTILATION – A PROSPECTIVE PHYSIOLOGICAL STUDY
Publication Number: 677.443
- SN
Sunita Namdev, MD (she/her/hers)
Fellow
McMaster University Michael G. DeGroote School of Medicine
Hamilton, Ontario, Canada
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation (NIPPV) is a commonly used mode of non-invasive respiratory support in preterm infants, whereby a set drive pressure is intermittently super-imposed upon a continuous positive end-expiratory pressure. However, the transmission of the set drive pressures and their impact upon work of breathing is unknown.
Objective: To determine the degree of pressure transmission at the level of interface and impact on work of breathing for 3 different set NIPPV drive pressures.
Design/Methods: In this prospective study, 6 preterm neonates on continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) levels 5-7 cmH2O were placed on NIPPV with set drive pressures (i.e. peak pressure – end-expiratory pressure) set at 8, 12 and 16 cmH2O (above CPAP) in consecutive order for 15 min each. Pressure transmitted to the expiratory limb of the nasal interface (Fisher & Paykel) was measured using saline filled catheters connected to a commercially available pressure transducer. Electrical activity of the diaphragm (Edi) was measured using specialized catheters inserted into the stomach; minimum Edi (diaphragmatic activity as a surrogate of effort to maintain functional residual capacity) and maximum Edi (diaphragmatic activity as a surrogate of effort to generate tidal volumes) were measured for each NIPPV level, as well as during CPAP. Results were summarized as means (SD), ANOVA was used for comparative analysis and a P value < 0.05 was considered significant.
Results:
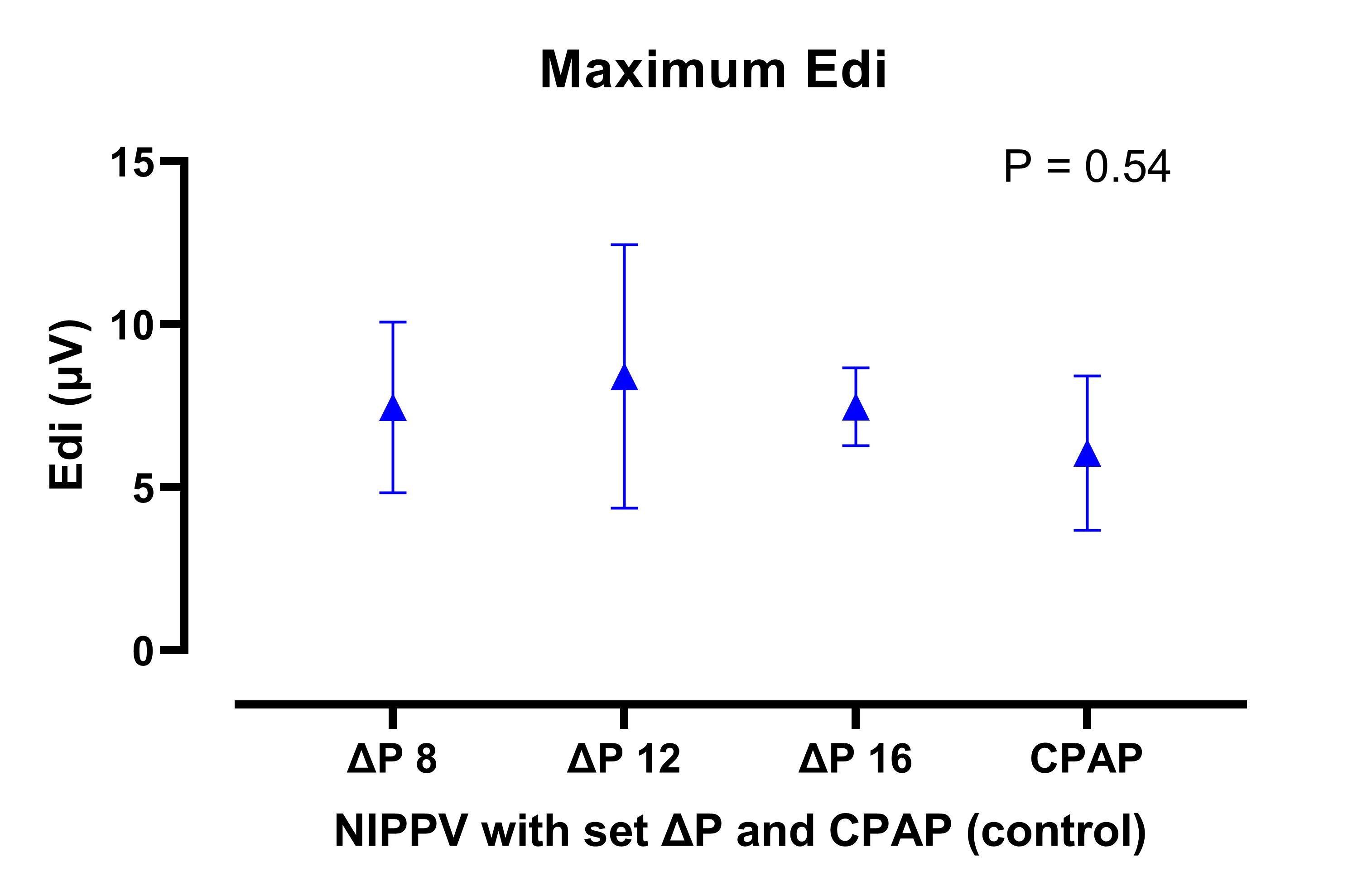
The mean (SD) birth GA was 28.1 (2.2) weeks and the mean (SD) chronological age at time of study was 20 (9) days. There was a significant drop in the pressures transmitted to the level of the interface with each of the 3 NIPPV levels (Figure 1), with mean (SD) drive pressures of 4.2 (0.5), 6.2 (1.6), and 7.9 (0.9) cmH2O at set drive pressures of 8, 12 and 16 cmH2O, respectively. There were no differences in either minimum (Figure 2) or maximum (Figure 3) Edi during the 3 NIPPV levels and CPAP, suggesting no improved work of breathing indices during NIPPV.
Conclusion(s): In this cohort of preterm neonates, a significant drop in drive pressures transmitted to the nasal interface was noted during NIPPV, with no difference in work of breathing indices compared to regular CPAP.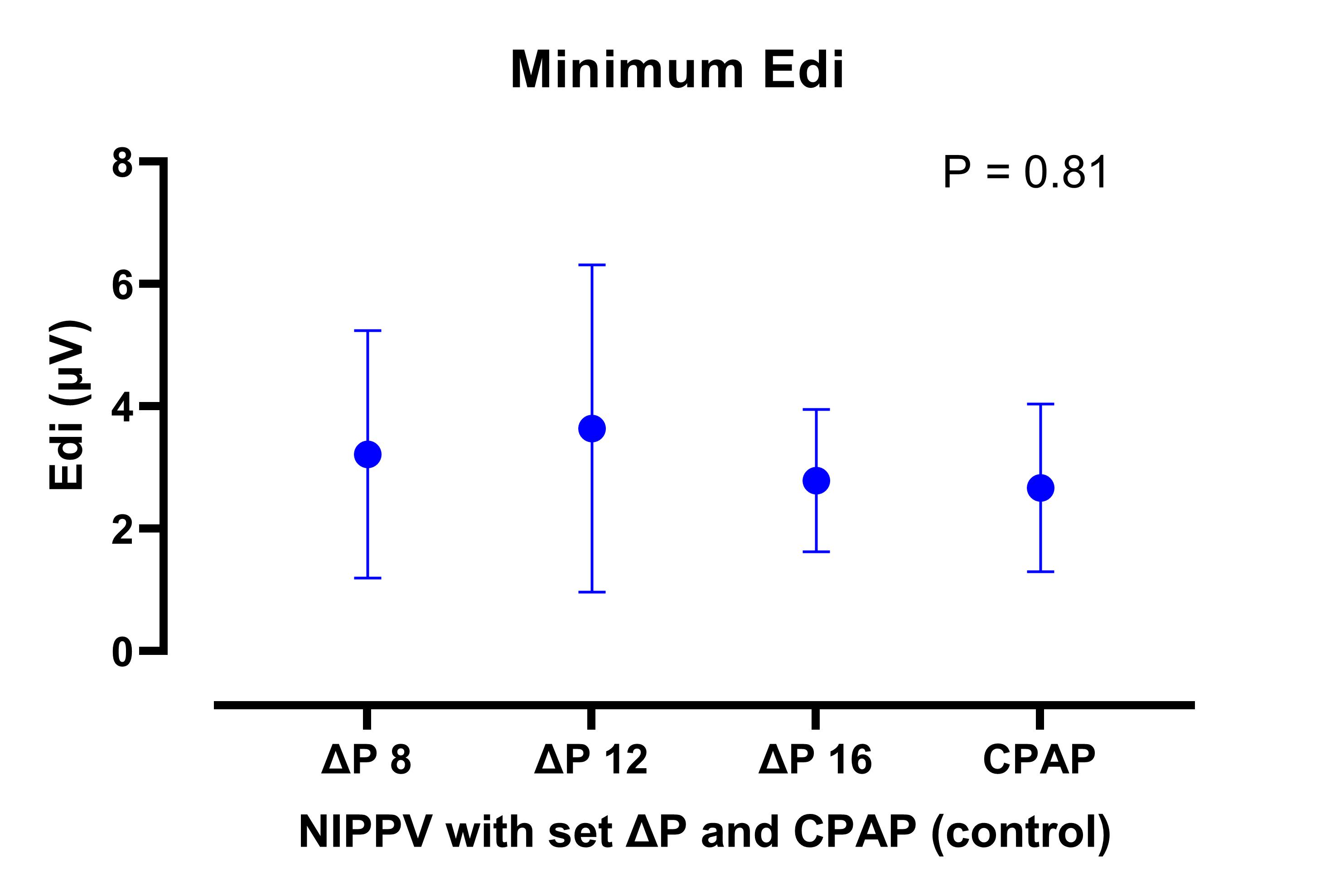
.jpg)
