Neonatal Clinical Trials
Neonatal Clinical Trials 1
239 - Does Continuous Transcutaneous CO2 Monitoring in ELBW Infants Affect Neonatal Neurological Morbidity? A Prospective, Multi-Center Study
Publication Number: 239.127
- LB
Liron Borenstein-Levin, MD (she/her/hers)
Neonatolgist
Rambam Medical center
Haifa, Hefa, Israel
Presenting Author(s)
Background:
Hypocarbia, hypercarbia, and extreme fluctuations of PaCO2 are associated with severe intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) and periventricular leukomalacia (PVL) among premature infants.
Objective:
To assess whether continuous non-invasive CO2 monitoring by transcutaneous CO2 monitor (TcCO2) among extremely low birth weight (ELBW) premature infants, during the first week of life, will decrease the rate of IVH or PVL.
Design/Methods:
Our study was designed as a prospective, observational, multicenter study in NICUs in Israel. For ethical reasons randomization was based on monitor availability. Each infant < 1000 g admitted to a participating NICU was monitored by TcCO2 monitor (Sentec, Therwil, Switzerland) from the first day of life for at least one week (study group). If TcCO2 monitor was not available upon NICU admission, the infant was recruited to the control group. However, as the study progressed, monitor availability increased in the participating NICUs and by the time study group recruitment was completed, the control group was too small to allow data analysis. Therefore, we added to the control group a retrospective group of matched ELBW infants, born before the start of the study, that were not monitored by TcCO2. Routine care was provided to all infants regardless of their allocation.
Results:
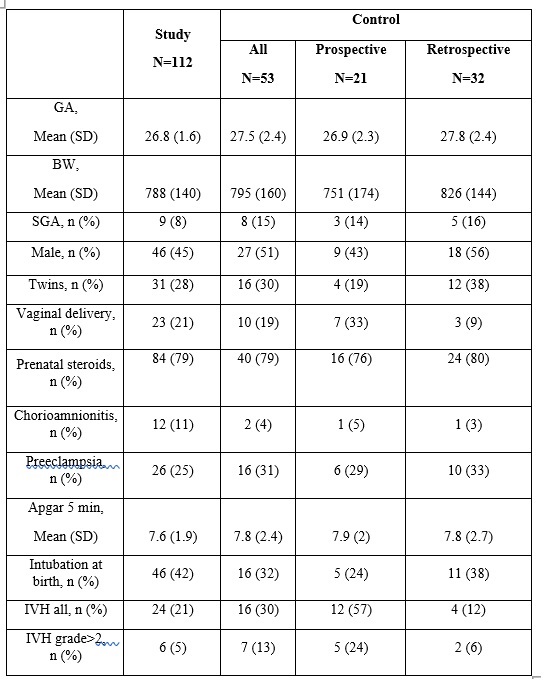
Overall 165 ELBW infants participated in the study. 112 infants in the study group, and 53 infants in the control group (21 infants prospective, and 32 infants retrospective recruitment). The groups had comparable gestational age, birth weight and baseline characteristics (Table 1). A trend toward a lower incidence of high grade IVH in the study group as compared to the control group was observed (5% vs. 13% respectively; p=0.07). No difference was found in the combined outcome of death, IVH or PVL (16% vs. 19% in study vs. control group, respectively; p=0.7).
Conclusion(s): Continuously monitoring CO2 during the first week of life among ELBW premature infants did not significantly reduce the short-term neurological complications, although there seems to be a trend toward a reduction in high grade IVH among the monitored group. During the study period, more NICUs is Israel adopted the policy of non-invasive continuous CO2 monitoring as a standard of care. This influenced our study, but highlights a change in care of ELBW premature infants. As non-invasive continuous CO2 monitoring is becoming more common in the NICU, for ethical reasons we believe it would be difficult to conduct a larger study that would answer our research question.